Lecture 10
... by Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate • Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F26BP) is a switch molecule that increases glycolysis by activating phosphofructokinase 1 and inhibiting fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. • F26BP levels are controlled by an enzyme with 2 active sites. The un-phosphorylated enzyme has phosphofruct ...
... by Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate • Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F26BP) is a switch molecule that increases glycolysis by activating phosphofructokinase 1 and inhibiting fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. • F26BP levels are controlled by an enzyme with 2 active sites. The un-phosphorylated enzyme has phosphofruct ...
Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in nitric acid media by some Schiff
... is expected that the corrosion rate is maximum in the beginning and decreases when equilibrium is attained. However, contrary to the earlier studies25,26, the corrosion rates obtained from potentiostatic measurements are not significantly higher than those obtained by the mass loss methods. The vari ...
... is expected that the corrosion rate is maximum in the beginning and decreases when equilibrium is attained. However, contrary to the earlier studies25,26, the corrosion rates obtained from potentiostatic measurements are not significantly higher than those obtained by the mass loss methods. The vari ...
The demonstration of nickel in the urease of Helicobacter pylori by
... urease is greater than 500 kDa, then the suggested structure is hexameric. This would indicate that the probable number of nickel atoms is six. These results support the model of six copies of each of the two polypeptides in the native enzyme suggested by Hu and Mobley [11]. The detection of nickel ...
... urease is greater than 500 kDa, then the suggested structure is hexameric. This would indicate that the probable number of nickel atoms is six. These results support the model of six copies of each of the two polypeptides in the native enzyme suggested by Hu and Mobley [11]. The detection of nickel ...
Directed mutagenesis of the Trypanosoma cruzi trans
... only in retention of sialidase activity (Figure 4). The level of sialyltransferase activity of the P to Q mutant was approximately 25% that of wild-type TS (Figure 2). We had previously described the inability to express enzyme activity from constructs expressing only the catalytic domains (i.e., wi ...
... only in retention of sialidase activity (Figure 4). The level of sialyltransferase activity of the P to Q mutant was approximately 25% that of wild-type TS (Figure 2). We had previously described the inability to express enzyme activity from constructs expressing only the catalytic domains (i.e., wi ...
Threonine Metabolism via Two-carbon Compounds
... MgS04.7Hz0 and 4 g. carbon source made up to I 1. with glass-distilled water. Where carbon compounds contained no nitrogen, I g. (NH4)2S04was added. Growth on threonine was not enhanced by NH+4ions, and growth on glycine alone did not occur unless the inoculum had been grown initially on threonine m ...
... MgS04.7Hz0 and 4 g. carbon source made up to I 1. with glass-distilled water. Where carbon compounds contained no nitrogen, I g. (NH4)2S04was added. Growth on threonine was not enhanced by NH+4ions, and growth on glycine alone did not occur unless the inoculum had been grown initially on threonine m ...
A novel assay method for an amino acid racemase reaction based
... measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay method for the measurement of ALR activity is superior to the enz ...
... measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay method for the measurement of ALR activity is superior to the enz ...
Poster
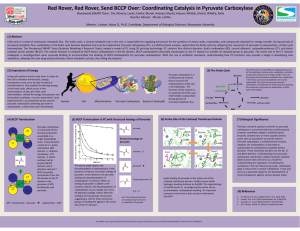
... (7) Biological Significance The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifun ...
... (7) Biological Significance The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifun ...
Anthranilate 4H-oxazol-5-ones
... clogP and cMR, polar surface area (PSA),16 and measured s values17 and atom counts for the whole molecule as well as the R1, R2 and R3 substituents, AcpS inhibition data (IC50) and MIC data (B. subtilis, E. faecalis ATCC, E. faecalis VRE and S. pneumo+) using SIMCA-P.18 Two PLS models were generated ...
... clogP and cMR, polar surface area (PSA),16 and measured s values17 and atom counts for the whole molecule as well as the R1, R2 and R3 substituents, AcpS inhibition data (IC50) and MIC data (B. subtilis, E. faecalis ATCC, E. faecalis VRE and S. pneumo+) using SIMCA-P.18 Two PLS models were generated ...
The biosynthesis of peptidoglycan lipid
... required before the lipid carrier becomes available for use in the various biosynthetic pathways. This reaction must also occur after each cycle of polymerization of cell wall components (e.g. of peptidoglycan) and the release of the linked saccharides, because the lipid carrier is in most cases lib ...
... required before the lipid carrier becomes available for use in the various biosynthetic pathways. This reaction must also occur after each cycle of polymerization of cell wall components (e.g. of peptidoglycan) and the release of the linked saccharides, because the lipid carrier is in most cases lib ...
Chemistry of Carbohydrates
... Reaction 3-produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 4- produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 5-produce 1 ATP molecule. Reaction 6-produce one FADH2+ molecule which enter the respi ...
... Reaction 3-produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 4- produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 5-produce 1 ATP molecule. Reaction 6-produce one FADH2+ molecule which enter the respi ...
The Citric acid cycle
... Similar effects are seen when people eat Fava beans. Fava beans stimulate peroxide formation and the demand for NADPH can not be met. Mature red blood cells lack a nucleus and the ability to make new proteins and membranes. Damage cannot be repaired so cells lyse. ...
... Similar effects are seen when people eat Fava beans. Fava beans stimulate peroxide formation and the demand for NADPH can not be met. Mature red blood cells lack a nucleus and the ability to make new proteins and membranes. Damage cannot be repaired so cells lyse. ...
Trypsinogen from bovine pancreas Product Number T1143 Storage
... reagent, 1-chloro-3-tosylamido-7-amino-2heptanone, the chloromethyl ketone derived from Nα-tosyl-L-lysine. Biochemistry, 4(10), 2219-2224 ...
... reagent, 1-chloro-3-tosylamido-7-amino-2heptanone, the chloromethyl ketone derived from Nα-tosyl-L-lysine. Biochemistry, 4(10), 2219-2224 ...
Lipid Biosynthesis Inhibitors - Plant and Soil Sciences eLibrary
... incorporationinto VLCFA in germinatingpea seedlings (53). In additionto being utilized in the synthesis of epicuticular wax and cutin, VLCFA are also used in the synthesis of suberin found on stem, root, and wound surfaces. If carbamothioatesact as general inhibitors of VLCFA synthesis, they should ...
... incorporationinto VLCFA in germinatingpea seedlings (53). In additionto being utilized in the synthesis of epicuticular wax and cutin, VLCFA are also used in the synthesis of suberin found on stem, root, and wound surfaces. If carbamothioatesact as general inhibitors of VLCFA synthesis, they should ...
Anchoring of Surface Proteins to the Cell Wall of Staphylococcus
... peptide/membrane anchor catalyzes the transpeptidation reaction of surface protein anchoring in vitro, using LPXTG peptides and NH2-Gly3 as a peptidoglycan substrate (9). Both the in vivo and in vitro reactions of sortase can be inhibited with the thiolate reagent methylmethane thiosulfonate (for ex ...
... peptide/membrane anchor catalyzes the transpeptidation reaction of surface protein anchoring in vitro, using LPXTG peptides and NH2-Gly3 as a peptidoglycan substrate (9). Both the in vivo and in vitro reactions of sortase can be inhibited with the thiolate reagent methylmethane thiosulfonate (for ex ...
Malate Dehydrogenase
... and 43 acidic residues (25 aspartates + 18 glutamates) in cMDH. In mMDH there are 25 lysines and 8 arginines for total of 33 basic residues, and 13 aspartates and 16 glutamates for a total of 29 acidic groups (Birktoft et al. 1989a). The sequence identity between cMDH and mMDH is relatively low, bei ...
... and 43 acidic residues (25 aspartates + 18 glutamates) in cMDH. In mMDH there are 25 lysines and 8 arginines for total of 33 basic residues, and 13 aspartates and 16 glutamates for a total of 29 acidic groups (Birktoft et al. 1989a). The sequence identity between cMDH and mMDH is relatively low, bei ...
1 - Free
... 27. list what you should measure to determine the specific activity of lactate dehydrogenase in a muscle homogenate. ...
... 27. list what you should measure to determine the specific activity of lactate dehydrogenase in a muscle homogenate. ...
Angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide fractions
... globulin peptide fraction (G2.2.2) purified by RP–HPLC. The initial reaction velocities were determined from the formation of product HA over time. The Km and V values for the reaction at different concentrations were determined according to Lineweaver-Burk plots. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Chemi ...
... globulin peptide fraction (G2.2.2) purified by RP–HPLC. The initial reaction velocities were determined from the formation of product HA over time. The Km and V values for the reaction at different concentrations were determined according to Lineweaver-Burk plots. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Chemi ...
Fatty acid synthesis
... Mitochondrial acetyl CoA is produced from • Oxidation of pyruvate •Degradation of fatty acids •Degradation of ketones bodies •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot ...
... Mitochondrial acetyl CoA is produced from • Oxidation of pyruvate •Degradation of fatty acids •Degradation of ketones bodies •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot ...
Mechanism of Thymidylate Synthase, Cont`d
... omit Pi from the mixture of the reaction, the results showed at time zero, a rapid increase in the absorbance was observed, that is, NADH was formed 3. However, the reaction stopped when all the enzyme-bound NAD+ has been ...
... omit Pi from the mixture of the reaction, the results showed at time zero, a rapid increase in the absorbance was observed, that is, NADH was formed 3. However, the reaction stopped when all the enzyme-bound NAD+ has been ...
“The only UNG useful in RT-PCR”
... This product is intended for research use only. Certain applications of ArcticZymes AS products may require licenses from others. It is the expressed duty of any receiver of ArcticZymes AS products to acquire such licenses, if necessary. In no event shall ArcticZymes AS be liable for claims for any ...
... This product is intended for research use only. Certain applications of ArcticZymes AS products may require licenses from others. It is the expressed duty of any receiver of ArcticZymes AS products to acquire such licenses, if necessary. In no event shall ArcticZymes AS be liable for claims for any ...
Identification of two amino acid residues which - Wiley-VCH
... a crystallized enzyme-substrate complex of the related enzyme chitobiase. The model contains a central hydrophilic region referred to as the “substrate cavity”. Figure 2 shows only this portion of the proposed structure. The three residues implicated in active site function cluster on the “left” sid ...
... a crystallized enzyme-substrate complex of the related enzyme chitobiase. The model contains a central hydrophilic region referred to as the “substrate cavity”. Figure 2 shows only this portion of the proposed structure. The three residues implicated in active site function cluster on the “left” sid ...
pentose phosphate pathway
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P • Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway • The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism • ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis • Or, if NADPH or ri ...
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P • Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway • The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism • ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis • Or, if NADPH or ri ...
Synthesis, Molecular Docking, and Biological Evaluation of Some
... gastrointestinal side-effects, it was discussed recently that COX-2 high selectivity could be the major cause of cardiac and renal problems (5,6), and hence, moderate selectivity could reduce the risk of both gastrointestinal and cardiac side-effects (7). Therefore, seeking for new molecules with an ...
... gastrointestinal side-effects, it was discussed recently that COX-2 high selectivity could be the major cause of cardiac and renal problems (5,6), and hence, moderate selectivity could reduce the risk of both gastrointestinal and cardiac side-effects (7). Therefore, seeking for new molecules with an ...
C H A P
... differences found could be explained by the different composition of the reaction mixture of each method with respect to the type and amount of substrate used and the ionic strength of the medium (see Chapter 3). In fact, a different type and amount of substrate used can affect the competition of th ...
... differences found could be explained by the different composition of the reaction mixture of each method with respect to the type and amount of substrate used and the ionic strength of the medium (see Chapter 3). In fact, a different type and amount of substrate used can affect the competition of th ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.