Enzyme - PharmaStreet
... • uncompetitive inhibitors are inhibitors that bind reversibly to an enzyme when the substrate is already bound to the active site. • In other words, the inhibitor binds to the enzyme–substrate complex. In this situation, increasing the substrate concentration will not overcome inhibition. Indeed, ...
... • uncompetitive inhibitors are inhibitors that bind reversibly to an enzyme when the substrate is already bound to the active site. • In other words, the inhibitor binds to the enzyme–substrate complex. In this situation, increasing the substrate concentration will not overcome inhibition. Indeed, ...
Exam 2
... G. ____________ Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because it contains a hemiacetal functional group that is in equilibrium with its open-chain form. H. ____________ It is possible to make an unfavorable reaction occur spontaneously by coupling it with a favorable reaction. I. _____________ The directi ...
... G. ____________ Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because it contains a hemiacetal functional group that is in equilibrium with its open-chain form. H. ____________ It is possible to make an unfavorable reaction occur spontaneously by coupling it with a favorable reaction. I. _____________ The directi ...
File
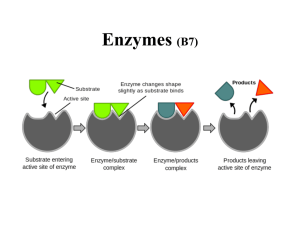
... active site fit very closely round the substrate molecule. The induced fit ensures that the active site comes into very close contact with the molecules of substrate and increases the chance of a reaction taking place ...
... active site fit very closely round the substrate molecule. The induced fit ensures that the active site comes into very close contact with the molecules of substrate and increases the chance of a reaction taking place ...
Enzymes
... converted by the normal mechanism by E, but then are trapped in a specific step during the mechanism in forms of intermediates which cannot further be processed by E (due to a specific covalent modification of E, generally). The covalently modified group on E is essential for catalysis. Example: mon ...
... converted by the normal mechanism by E, but then are trapped in a specific step during the mechanism in forms of intermediates which cannot further be processed by E (due to a specific covalent modification of E, generally). The covalently modified group on E is essential for catalysis. Example: mon ...
enzymes-inhibition-text
... with the catalysis (e.g. by reacting with side-chains important for the catalysis); ...
... with the catalysis (e.g. by reacting with side-chains important for the catalysis); ...
ENZYMES
... - each enzyme has an optimal pH at which its reaction rate is highest. - a change in the optimal pH alters the active site (tertiary structure) of the enzyme, thus disallowing effective collisions (denaturation). - eg. pepsin and trypsin both digest proteins in the digestive system, but do so under ...
... - each enzyme has an optimal pH at which its reaction rate is highest. - a change in the optimal pH alters the active site (tertiary structure) of the enzyme, thus disallowing effective collisions (denaturation). - eg. pepsin and trypsin both digest proteins in the digestive system, but do so under ...
protease inhibitors in development
... transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs or non-nukes) Fact sheet 460: attachment and fusion inhibitors Fact sheet 470: new classes of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs Fact sheet 480: immune therapies These drugs have not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use against HIV. ...
... transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs or non-nukes) Fact sheet 460: attachment and fusion inhibitors Fact sheet 470: new classes of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs Fact sheet 480: immune therapies These drugs have not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use against HIV. ...
Enzymes - terranovasciences
... the bonds in the substrate(s), reducing the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. ...
... the bonds in the substrate(s), reducing the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. ...
Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by
... The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. A protein may consist of a single ...
... The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. A protein may consist of a single ...
ch3a FA11 - Cal State LA
... • Mechanism: form an Enzyme-Substrate (ES) complex at active site – Enhance substrate reactivity • Enhance polarity of bonds via interaction with amino acid functional groups • Possibly form covalent bonded intermediates with amino acid side chains ...
... • Mechanism: form an Enzyme-Substrate (ES) complex at active site – Enhance substrate reactivity • Enhance polarity of bonds via interaction with amino acid functional groups • Possibly form covalent bonded intermediates with amino acid side chains ...
The Physiological Roles of Enzymes
... (a) Model of a monomeric enzyme. Binding of a positive allosteric effector, A (green), to the activator site, j, induces a new conformation to the enzyme, one that has a greater affinity for the substrate. Binding of a negative allosteric effector (purple) to the inhibitor site, i, results in an enz ...
... (a) Model of a monomeric enzyme. Binding of a positive allosteric effector, A (green), to the activator site, j, induces a new conformation to the enzyme, one that has a greater affinity for the substrate. Binding of a negative allosteric effector (purple) to the inhibitor site, i, results in an enz ...
Energy/Chemical Energy in the Cell Chapter 5
... • both speed up reactions by providing an alternative pathway of lower activation energy – neither changes the position of equilibrium or yield of the reaction • enzymes are highly specific for their substrate, whereas inorganic catalysts are often non-specific and can catalyze several reactions • e ...
... • both speed up reactions by providing an alternative pathway of lower activation energy – neither changes the position of equilibrium or yield of the reaction • enzymes are highly specific for their substrate, whereas inorganic catalysts are often non-specific and can catalyze several reactions • e ...
... In this Appendix there are 3 art@ies. These articles provide a basic understanding of the mechanism of how HCA works. The first article is by John Lowenstein of Brandeis University who was one of the key figures in the early research conductad on HCA. The article entitled “Experiments with Hydroxyci ...
AP151 ENZYMES
... • CATALYST: increase rates of chemical rxns without being altered or “used up” (100’s-1000’s rxns/second!!!) – lowering activation energy – few enzyme; lots of reaction ...
... • CATALYST: increase rates of chemical rxns without being altered or “used up” (100’s-1000’s rxns/second!!!) – lowering activation energy – few enzyme; lots of reaction ...
6.3 Enzymes and Nucleic Acids ~ powerpoint
... and convert them into energy. These enzymes are secreted along the digestive tract. • Enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids = trypsin and peptidases ...
... and convert them into energy. These enzymes are secreted along the digestive tract. • Enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids = trypsin and peptidases ...
Assay the Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) in Serum
... • An enzyme test is a blood test or urine test that measures levels of certain enzymes to assess how well the body’s systems are functioning and whether there has been any tissue damage. (why?) ...
... • An enzyme test is a blood test or urine test that measures levels of certain enzymes to assess how well the body’s systems are functioning and whether there has been any tissue damage. (why?) ...
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism - Biology E
... process even involves brief covalent bonding between the substrate and the side chain of an amino acid of the enzyme. Subsequent steps of the reaction restore the side chains to their original states, so that the active site is the same after the reaction as it was before. 21. Explain how pH, temper ...
... process even involves brief covalent bonding between the substrate and the side chain of an amino acid of the enzyme. Subsequent steps of the reaction restore the side chains to their original states, so that the active site is the same after the reaction as it was before. 21. Explain how pH, temper ...
Name - Mrs. Sommers` Class Site
... Match the following words with their descriptions: enzyme, substrate, product, active site. Some words will be used more than once! active site, product(s), enzyme, substrate(s) ...
... Match the following words with their descriptions: enzyme, substrate, product, active site. Some words will be used more than once! active site, product(s), enzyme, substrate(s) ...
Caught in the act – modelling how a biological catalyst works
... in the form of new drugs, genetic analysis and catalytic processes. Central to enzyme catalysis is the nebulous ‘transition state’ of a chemical reaction, in which bonds are partly formed and broken. Biologists have theorized for many years that enzymes are able to recognise and stabilize transition ...
... in the form of new drugs, genetic analysis and catalytic processes. Central to enzyme catalysis is the nebulous ‘transition state’ of a chemical reaction, in which bonds are partly formed and broken. Biologists have theorized for many years that enzymes are able to recognise and stabilize transition ...
Notes: Enzymes
... 1. Chemicals other than substrates and products may interact with an enzyme influencing the reaction rate. 2. Chemicals which bind to the active site but do not react will compete for formation of the ES complex and are known as competitive Inhibitors. Raising substrate concentrations will overcome ...
... 1. Chemicals other than substrates and products may interact with an enzyme influencing the reaction rate. 2. Chemicals which bind to the active site but do not react will compete for formation of the ES complex and are known as competitive Inhibitors. Raising substrate concentrations will overcome ...
LabEnzymes
... pH at which they work best, and if an enzyme is exposed to extremes of heat or pH it will not work at all. The interactions that hold the protein in its particular shape become disrupted under these conditions, and the 3dimensional structure unfolds. In this case, the enzyme is said to be denatured. ...
... pH at which they work best, and if an enzyme is exposed to extremes of heat or pH it will not work at all. The interactions that hold the protein in its particular shape become disrupted under these conditions, and the 3dimensional structure unfolds. In this case, the enzyme is said to be denatured. ...
Endergonic vs. exergonic reactions
... (____) released or required required for most biological reactions highly___________________ _________________ of different enzymes in cells control reactions of __________ o Enzymes vocabulary _________________________ reactant which binds to enzyme enzyme-substrate complex: temporary assoc ...
... (____) released or required required for most biological reactions highly___________________ _________________ of different enzymes in cells control reactions of __________ o Enzymes vocabulary _________________________ reactant which binds to enzyme enzyme-substrate complex: temporary assoc ...
Chapter 5 (part 4) Enzyme Regulation
... Regulation of Enzyme Activity (biochemical regulation) • 1st committed step of a biosynthetic pathway or enzymes at pathway branch points often regulated by feedback inhibition. ...
... Regulation of Enzyme Activity (biochemical regulation) • 1st committed step of a biosynthetic pathway or enzymes at pathway branch points often regulated by feedback inhibition. ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.