$doc.title
... is an operational amplifier, with both inputs uncommitted. This enables the first amplifier to be configured as an inverting amplifier, a noninverting amplifier, or even a difference amplifier. The second amplifier, A2, is internally configured as an inverting amplifier and biased about VDD/2. ...
... is an operational amplifier, with both inputs uncommitted. This enables the first amplifier to be configured as an inverting amplifier, a noninverting amplifier, or even a difference amplifier. The second amplifier, A2, is internally configured as an inverting amplifier and biased about VDD/2. ...
MAX6698 7-Channel Precision Remote-Diode, Thermistor, and Local Temperature Monitor General Description
... The MAX6698 is a precision multichannel temperature monitor that features one local, three remote thermal diode temperature-sensing channels, and three thermistor voltage-sensing channels. All channels have a programmable alert threshold for each temperature channel and a programmable overtemperatur ...
... The MAX6698 is a precision multichannel temperature monitor that features one local, three remote thermal diode temperature-sensing channels, and three thermistor voltage-sensing channels. All channels have a programmable alert threshold for each temperature channel and a programmable overtemperatur ...
Nyquist plot
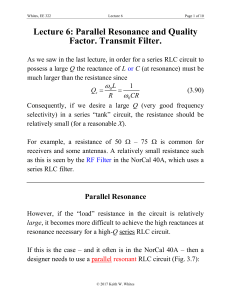
... Review of Circuit Elements •EIS data is commonly analyzed by fitting it to an equivalent electrical circuit model. Most of the circuit elements in the model are common electrical elements such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. To be useful, the elements in the model should have a basis in th ...
... Review of Circuit Elements •EIS data is commonly analyzed by fitting it to an equivalent electrical circuit model. Most of the circuit elements in the model are common electrical elements such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. To be useful, the elements in the model should have a basis in th ...
Using a Dallas/Maxim DS1811 in the Reset Section. There is also
... Put a jumper from the lower hole of R138 to the upper hole of R139 (note "lower" and "upper" being relative to the MPU board in its normally installed position in the game). Connect the reset pin of the DS1811 (bottom pin, as the flat side of the DS1811 is towards connector J4) to the collector hole ...
... Put a jumper from the lower hole of R138 to the upper hole of R139 (note "lower" and "upper" being relative to the MPU board in its normally installed position in the game). Connect the reset pin of the DS1811 (bottom pin, as the flat side of the DS1811 is towards connector J4) to the collector hole ...
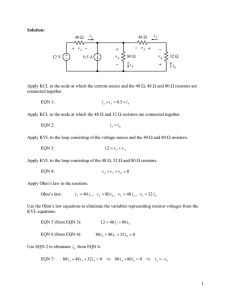
Chapter 2 Circuit Elements
... ammeter and the reference direction of the measured current. In (b) the current ia is directed to the right, while in (c) the current ib is directed to the left. The colored probe is shown here in blue. In the laboratory this probe will be red. We will refer to the colored probe as the “red probe”. ...
... ammeter and the reference direction of the measured current. In (b) the current ia is directed to the right, while in (c) the current ib is directed to the left. The colored probe is shown here in blue. In the laboratory this probe will be red. We will refer to the colored probe as the “red probe”. ...
Resistors - La Favre home page
... It is unlikely that your measured resistance for R1 is exactly the same as the resistance marked on it by the color code. There will probably be a small difference between the numbers. The fourth band on the R1 resistor should be gold colored, which indicates a tolerance value of 5%. That means that ...
... It is unlikely that your measured resistance for R1 is exactly the same as the resistance marked on it by the color code. There will probably be a small difference between the numbers. The fourth band on the R1 resistor should be gold colored, which indicates a tolerance value of 5%. That means that ...
Resistors - La Salle University
... It is convenient to define the potential energy per charge, known as the electric potential (or just potential). The potential difference (a.k.a. the voltage) is the difference in potential energy per charge between two charge arrangements Comes in volts (Joules per Coulomb, V=J/C). Measured ...
... It is convenient to define the potential energy per charge, known as the electric potential (or just potential). The potential difference (a.k.a. the voltage) is the difference in potential energy per charge between two charge arrangements Comes in volts (Joules per Coulomb, V=J/C). Measured ...
introduction to esd
... charged object due to contact, electrical short or dielectric breakdown. The reason of electrostatic charging is tribocharging (separation of electric charges that occurs when two materials are brought into contact and then seperated) or electrostatic induction (occurs when an electrically charged o ...
... charged object due to contact, electrical short or dielectric breakdown. The reason of electrostatic charging is tribocharging (separation of electric charges that occurs when two materials are brought into contact and then seperated) or electrostatic induction (occurs when an electrically charged o ...
Portable Audio – Customer Review
... • There are several ways TI provides a ruggedized plastic package for our 175C offerings • We have a different material set than the commercial/industrial devices to improve reliability at temperature • Special leadframe, mold compounds, and die attach to withstand the stresses from CTE mismatch • S ...
... • There are several ways TI provides a ruggedized plastic package for our 175C offerings • We have a different material set than the commercial/industrial devices to improve reliability at temperature • Special leadframe, mold compounds, and die attach to withstand the stresses from CTE mismatch • S ...
Lumped element model
The lumped element model (also called lumped parameter model, or lumped component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc.Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters.