ENGG2430A-Homework 5
... sample mean will be within 15 seconds of the true mean? Assume that it is known from previous studies that σ = 40 seconds. ...
... sample mean will be within 15 seconds of the true mean? Assume that it is known from previous studies that σ = 40 seconds. ...
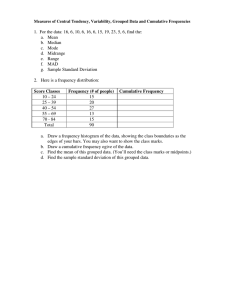
1. For the data: 16, 6, 10, 6, 16,... a. Mean b. Median
... Measures of Central Tendency, Variability, Grouped Data and Cumulative Frequencies ...
... Measures of Central Tendency, Variability, Grouped Data and Cumulative Frequencies ...
Descriptve.s02
... The median is the middle observation in data that have been arranged in ascending or descending numerical ...
... The median is the middle observation in data that have been arranged in ascending or descending numerical ...
8.1.4 The Central Limit Theorem - University of Northern Colorado
... monthly rates of return. A statistician thinks this is inefficient and proposes a new method called the R A P 20. This method starts with the current market value of stocks. Then randomly selects 20 stocks of publicly traded companies to determine their change in market value for the day and adjusts ...
... monthly rates of return. A statistician thinks this is inefficient and proposes a new method called the R A P 20. This method starts with the current market value of stocks. Then randomly selects 20 stocks of publicly traded companies to determine their change in market value for the day and adjusts ...
Descriptive Statistics –
... • For all distributions • Let k be greater than or equal to 1 • At least 1-(1/k2) of the observations are within k standard deviations of the mean • Examples • K=1 zero observations may be within one standard deviation of the mean • K=2 3/4th’s of observations must be within two standard deviations ...
... • For all distributions • Let k be greater than or equal to 1 • At least 1-(1/k2) of the observations are within k standard deviations of the mean • Examples • K=1 zero observations may be within one standard deviation of the mean • K=2 3/4th’s of observations must be within two standard deviations ...
continued - University of South Alabama
... population are called population parameters. For example population mean µ and population standard deviation σ are population parameters • Values of different numerical measures for sample are called sample statistics. For example sample mean and sample standard deviation s are sample statistics. • ...
... population are called population parameters. For example population mean µ and population standard deviation σ are population parameters • Values of different numerical measures for sample are called sample statistics. For example sample mean and sample standard deviation s are sample statistics. • ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... black balls; 3 white, 1 red and 2 black balls. A box is chosen at random and from it two balls are drawn at random. The two balls are 1 red and 1 white. What is the probability that they come from the second box? (ii)Students of a class were given an aptitude test. Their marks were found to be norma ...
... black balls; 3 white, 1 red and 2 black balls. A box is chosen at random and from it two balls are drawn at random. The two balls are 1 red and 1 white. What is the probability that they come from the second box? (ii)Students of a class were given an aptitude test. Their marks were found to be norma ...
Math 10 Name W C Exam 5: Chapter 13 1. State whether each
... Say you want to buy a house $113,500. The taxes on the house are $1200 per year, and homeowners' insurance is $320 per year. You want a conventional 10% interest rate loan requiring a 15% down payment and 3 points. Your gross income is $3990, but you have more than 10 monthly payments remaining on a ...
... Say you want to buy a house $113,500. The taxes on the house are $1200 per year, and homeowners' insurance is $320 per year. You want a conventional 10% interest rate loan requiring a 15% down payment and 3 points. Your gross income is $3990, but you have more than 10 monthly payments remaining on a ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.