day9
... These procedures share a fundamental concept • Sampling distribution – A theoretical distribution of the possible values of samples statistics if an infinite number of same-sized samples were taken from a population. ...
... These procedures share a fundamental concept • Sampling distribution – A theoretical distribution of the possible values of samples statistics if an infinite number of same-sized samples were taken from a population. ...
Bootstrap Resampling - Wharton Statistics
... Efron (1979), “Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife”, Annals of Statistics Diaconis & Efron (1983), “Computer intensive methods in statistics”, Scientific American ...
... Efron (1979), “Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife”, Annals of Statistics Diaconis & Efron (1983), “Computer intensive methods in statistics”, Scientific American ...
MATH408: PROBABILITY & STATISTICS
... Student’s t-distribution • What happens if the sample is small (n < 30)? • In this case we cannot use normal since the sample size is small and by using the sample standard deviation to estimate s, we bring in more variability into the picture and the appropriate distribution to use is the student' ...
... Student’s t-distribution • What happens if the sample is small (n < 30)? • In this case we cannot use normal since the sample size is small and by using the sample standard deviation to estimate s, we bring in more variability into the picture and the appropriate distribution to use is the student' ...
A Bootstrap Evaluation of the EM Algorithm for Censored Survival Data
... for t-statistics would perform very well, but is not currently acceptable to regulatory agencies. ...
... for t-statistics would perform very well, but is not currently acceptable to regulatory agencies. ...
251x9811 2/11/98
... is (rounded to the nearest per cent) 19% and the median is 24%, is the distribution skewed? To the right or the left? Where would you expect the mode to be relative to these two numbers? (2) Skewed to the left, above 24%. f) Ogive (1) A graph of the cumulative distribution g) Interval Data (1) Data ...
... is (rounded to the nearest per cent) 19% and the median is 24%, is the distribution skewed? To the right or the left? Where would you expect the mode to be relative to these two numbers? (2) Skewed to the left, above 24%. f) Ogive (1) A graph of the cumulative distribution g) Interval Data (1) Data ...
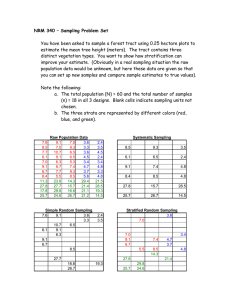
Notes on Sampling Variability
... Security Administration, 10% of passengers at this airport are chosen for random screening. ...
... Security Administration, 10% of passengers at this airport are chosen for random screening. ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.