Lecture28 - Purdue Physics
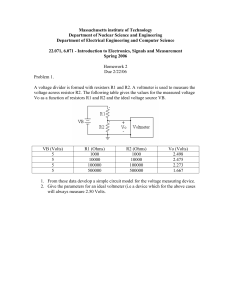
... C. The energy given up per electron is the same for all three. D. The current through one resistor is the same as the current through the battery. ...
... C. The energy given up per electron is the same for all three. D. The current through one resistor is the same as the current through the battery. ...
13.3 Section Review and Problems File
... 8. A digital camera uses one 6 V battery. The circuit that runs the flash and takes the pictures has a resistance of 3 ohms. What is the current in the circuit? Looking for: Solution: Given: Equation: 9. The motor in a toy car has a resistance of 3 ohms and needs 1.5 amperes of current to run proper ...
... 8. A digital camera uses one 6 V battery. The circuit that runs the flash and takes the pictures has a resistance of 3 ohms. What is the current in the circuit? Looking for: Solution: Given: Equation: 9. The motor in a toy car has a resistance of 3 ohms and needs 1.5 amperes of current to run proper ...
Ohm’s Law Lab (60 points)
... Procedure: Set up equipment as shown above. Use 100 and 250 resistances. Make sure you show your circuit to the teacher for approval before connecting the power supply. Increase carefully the voltage to read 2 V to 6 V. Use a switch in the circuit and close the switch only for as long as you need ...
... Procedure: Set up equipment as shown above. Use 100 and 250 resistances. Make sure you show your circuit to the teacher for approval before connecting the power supply. Increase carefully the voltage to read 2 V to 6 V. Use a switch in the circuit and close the switch only for as long as you need ...
water pressure - the second science-edu is born
... supply. If you want to measure the resistance of a particular component, you must take it out of the circuit altogether and test it separately. Ohmmeters work by passing a small current through the component and measuring the voltage produced. If you try this with the component connected into a circ ...
... supply. If you want to measure the resistance of a particular component, you must take it out of the circuit altogether and test it separately. Ohmmeters work by passing a small current through the component and measuring the voltage produced. If you try this with the component connected into a circ ...
Simple Electrical Circuits
... Simple circuit Figure how to make a bulb light up. How many wires do you need? What is essential to form a circuit – why might it be named “circuit”? Sketch your circuit below using the symbols on page 1. Is there a continuous path for the current to flow from one side of the battery to the other si ...
... Simple circuit Figure how to make a bulb light up. How many wires do you need? What is essential to form a circuit – why might it be named “circuit”? Sketch your circuit below using the symbols on page 1. Is there a continuous path for the current to flow from one side of the battery to the other si ...
Ohms - HCC Learning Web
... Connect the two resistors in PARALLEL with the voltage source. Start incrementing the voltage by 2 volts until you reach 12 volts. For each voltage, measure the current in the circuit with the ammeter. Graph the voltage versus current. From the slope, calculate the total resistance of the circuit. F ...
... Connect the two resistors in PARALLEL with the voltage source. Start incrementing the voltage by 2 volts until you reach 12 volts. For each voltage, measure the current in the circuit with the ammeter. Graph the voltage versus current. From the slope, calculate the total resistance of the circuit. F ...
Ohm*s Law
... To calculate resistance, R: put your finger over R, this leaves you with V over I, so the equation is R = V/I ...
... To calculate resistance, R: put your finger over R, this leaves you with V over I, so the equation is R = V/I ...
SC66 - Fieldpiece Instruments
... material. When disconnecting from a circuit, disconnect the “RED” lead first, then the common lead. Work with others. Use one hand for testing. Turn off power to the circuit under test before cutting, unsoldering, or breaking the circuit. Keep your fingers behind the finger guards on the probes. Do ...
... material. When disconnecting from a circuit, disconnect the “RED” lead first, then the common lead. Work with others. Use one hand for testing. Turn off power to the circuit under test before cutting, unsoldering, or breaking the circuit. Keep your fingers behind the finger guards on the probes. Do ...
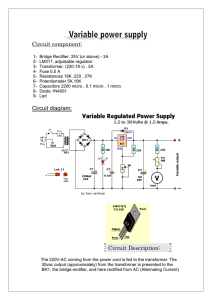
Circuit component
... R2. (This resistor is usually around 240 ohms, but 220 ohms will work fine without any problems). Because of this the voltage at the output can never decrease below 1.2 volts, but as the potentiometer (P1) increases in resistance the voltage across it, due to current from the regulator plus current ...
... R2. (This resistor is usually around 240 ohms, but 220 ohms will work fine without any problems). Because of this the voltage at the output can never decrease below 1.2 volts, but as the potentiometer (P1) increases in resistance the voltage across it, due to current from the regulator plus current ...
180.0 ° 50.01 Hz 49.99 Hz 230.2 V 228.1 V
... Currents up to 25 A and voltages up to 500 V can be applied directly to the instrument. The current input range can be extended by using external current transformers. ...
... Currents up to 25 A and voltages up to 500 V can be applied directly to the instrument. The current input range can be extended by using external current transformers. ...
A powerpoint for testing and fault finding a 555
... A logic probe is a hand-held pen-like probe used for analyzing and troubleshooting the logical states (Boolean 0 or 1) of a digital circuit. There are usually three different coloured LEDs on the probe's chassis; • A RED and GREEN LED indicate high and low states respectively • An AMBER LED indicate ...
... A logic probe is a hand-held pen-like probe used for analyzing and troubleshooting the logical states (Boolean 0 or 1) of a digital circuit. There are usually three different coloured LEDs on the probe's chassis; • A RED and GREEN LED indicate high and low states respectively • An AMBER LED indicate ...
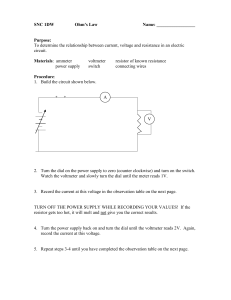
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... To determine the relationship between current, voltage and resistance in an electric circuit. Materials: ammeter power supply ...
... To determine the relationship between current, voltage and resistance in an electric circuit. Materials: ammeter power supply ...
Ammeter
... one handheld unit. Basic multimeter models can measure voltage, current and resistance. Advanced models can also measure temperature, inductance, capacitance, duty cycle and frequency. They can also test diodes and transistors. Some even work as an oscilloscope. The two main types of multimeter ...
... one handheld unit. Basic multimeter models can measure voltage, current and resistance. Advanced models can also measure temperature, inductance, capacitance, duty cycle and frequency. They can also test diodes and transistors. Some even work as an oscilloscope. The two main types of multimeter ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.