Ohm`s Law
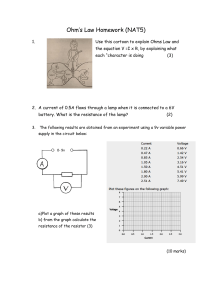
... Ohm’s Law The most important fundamental law in electronics is Ohm’s law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance. Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance and formulated the equation that bears his name. ...
... Ohm’s Law The most important fundamental law in electronics is Ohm’s law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance. Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance and formulated the equation that bears his name. ...
Building a Simple Circuit
... proportional to each other. • V=I x R. • Voltage = current x resistance. ...
... proportional to each other. • V=I x R. • Voltage = current x resistance. ...
Series Cicuit Lab
... Objectives: The purpose of this lab exercise will be to reinforce concepts learned in the classroom segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include: series connected resistance is additive, voltage drop is additive, and current measurements through-out the circuit is the same. . Students ...
... Objectives: The purpose of this lab exercise will be to reinforce concepts learned in the classroom segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include: series connected resistance is additive, voltage drop is additive, and current measurements through-out the circuit is the same. . Students ...
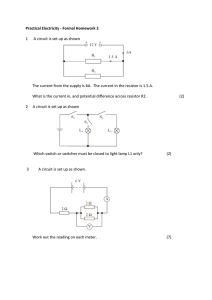
Name: Date: Class: Ohm`s Law Practice Problems How much
... 1. How much current is in a circuit that includes a 9-volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 3 ohms? 2. How much current is in a circuit that includes a 9-volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 12 ohms? 3. A circuit contains a 1.5 volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 3 ohms. Calc ...
... 1. How much current is in a circuit that includes a 9-volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 3 ohms? 2. How much current is in a circuit that includes a 9-volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 12 ohms? 3. A circuit contains a 1.5 volt battery and a bulb with a resistance of 3 ohms. Calc ...
Circuit Analysis Vocabulary Teachers Guide
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
BMLR2 Unit 5
... Draw out a series circuit and a parallel circuit as described in figure 18-1 & 18-7. ...
... Draw out a series circuit and a parallel circuit as described in figure 18-1 & 18-7. ...
Tutorial 4
... Tutorial 4 1) A series connected electrical circuit has a resistance of 25 ohms & an inductance of 0.15H. It is connected to a 200v, 30 Hz supply. Determine: Inductive Reactance The impedance in Polar Form Current and circuit phase angle Voltage drop across resistor Voltage drop across ind ...
... Tutorial 4 1) A series connected electrical circuit has a resistance of 25 ohms & an inductance of 0.15H. It is connected to a 200v, 30 Hz supply. Determine: Inductive Reactance The impedance in Polar Form Current and circuit phase angle Voltage drop across resistor Voltage drop across ind ...
LAB 2 Circuit Tools
... reading will be positive. If the meter were hooked up in the reverse manner, a negative reading would result. The voltmeter is therefore an excellent instrument not only for measuring the voltage level but also for determining the polarity. Since the meter is always placed in parallel with the eleme ...
... reading will be positive. If the meter were hooked up in the reverse manner, a negative reading would result. The voltmeter is therefore an excellent instrument not only for measuring the voltage level but also for determining the polarity. Since the meter is always placed in parallel with the eleme ...
Ch 16 Electricity test reivew
... 23. What happens to the current in a device if the resistance of the device increases and the voltage difference stays the same? 24. You install two batteries in a flashlight so that their positive ends are connected together. Will the flashlight work? Why or why not? ...
... 23. What happens to the current in a device if the resistance of the device increases and the voltage difference stays the same? 24. You install two batteries in a flashlight so that their positive ends are connected together. Will the flashlight work? Why or why not? ...
DC Voltmeters and Ammeters Ammeters Voltmeters Homework
... The coil works just like in the ________________ Given the ________________ and the ________________ of the coil → ________________ To give more range, a ________________ resistor is connected in ________________ with the coil Problems with Voltmeters o The voltmeter takes some the ________________ ...
... The coil works just like in the ________________ Given the ________________ and the ________________ of the coil → ________________ To give more range, a ________________ resistor is connected in ________________ with the coil Problems with Voltmeters o The voltmeter takes some the ________________ ...
Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit at the terminals U, V.
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
Lab 1: Current, Voltage, Resistance
... Connect the resistor in 1.1, the DC power supply (used as a constant voltage source) and the multimeter using the protoboard as shown below. Use red and black banana leads to connect the power supply to the binding posts and red and black wire from the binding posts to the contact points. Assemble a ...
... Connect the resistor in 1.1, the DC power supply (used as a constant voltage source) and the multimeter using the protoboard as shown below. Use red and black banana leads to connect the power supply to the binding posts and red and black wire from the binding posts to the contact points. Assemble a ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.