APUSH - READING GUIDE (CIVIL WAR) CHAPTER 19: Drifting
... 9. Analyze the meaning of the following statement- “a rich man’s war, but a poor man’s fight”. What does this statement tell us about the Southern draft movement and preferential treatment? IV. The North’s Economic Boom 10. According to your textbook, how many women posed as male soldiers during the ...
... 9. Analyze the meaning of the following statement- “a rich man’s war, but a poor man’s fight”. What does this statement tell us about the Southern draft movement and preferential treatment? IV. The North’s Economic Boom 10. According to your textbook, how many women posed as male soldiers during the ...
Chapter 16 Study Guide
... Ft. Sumter: the 1st shots of the Civil War fired here; Union surrendered the fort to Confederates. Emancipation Proclamation: Lincoln’s announcement that all slaves were free immediately. 13th Amendment: officially outlawed slavery in the U.S. 14th Amendment: granted slaves U.S. citizenship and righ ...
... Ft. Sumter: the 1st shots of the Civil War fired here; Union surrendered the fort to Confederates. Emancipation Proclamation: Lincoln’s announcement that all slaves were free immediately. 13th Amendment: officially outlawed slavery in the U.S. 14th Amendment: granted slaves U.S. citizenship and righ ...
NOTE: Read text pages 447-452. As you read, answer the following
... 1. What were three actions Lincoln took at the beginning of the war that may have been unconstitutional? 2. Why did he take each of the above actions? 3. What is conscription? 4. If a man did not want to fight on either side? How could they get out of their commitment? 5. What were the “draft riots” ...
... 1. What were three actions Lincoln took at the beginning of the war that may have been unconstitutional? 2. Why did he take each of the above actions? 3. What is conscription? 4. If a man did not want to fight on either side? How could they get out of their commitment? 5. What were the “draft riots” ...
Reconstruction and The New South 1865-1900
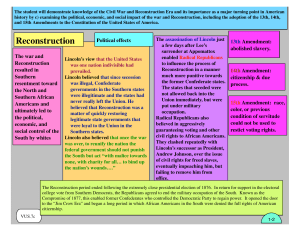
... Review for Reconstruction Test 1. What was the Emancipation Proclamation? 4 Million Former Slaves are Freed by Abe Lincoln decree. 2. What was the Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction? The goals of Lincoln’s reconstruction plan. 3. What was the main focus of Lincoln’s reconstruction plan? “For ...
... Review for Reconstruction Test 1. What was the Emancipation Proclamation? 4 Million Former Slaves are Freed by Abe Lincoln decree. 2. What was the Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction? The goals of Lincoln’s reconstruction plan. 3. What was the main focus of Lincoln’s reconstruction plan? “For ...
The Civil War
... an agricultural way of life, and the Northern States, dedicated to a more modern way of life and to ending the expansion-and, later, the existence-of slavery. The terrible bloodshed left a heritage of grief and bitterness that declined only slowly and, even today, has not fully disappeared. ...
... an agricultural way of life, and the Northern States, dedicated to a more modern way of life and to ending the expansion-and, later, the existence-of slavery. The terrible bloodshed left a heritage of grief and bitterness that declined only slowly and, even today, has not fully disappeared. ...
The Civil War
... – Lee escaped, but cornered at Appomattox Court House – Surrendered April 9, 1865 ...
... – Lee escaped, but cornered at Appomattox Court House – Surrendered April 9, 1865 ...
File - Braly US History
... Douglas (“Mr. Popular Sovereignty”) replied with his “Freeport Doctrine.” …”since ...
... Douglas (“Mr. Popular Sovereignty”) replied with his “Freeport Doctrine.” …”since ...
Civil War PP
... • b. Describe President Lincoln’s efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural address and the Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to suspend habeas corpus. • c. Describe the roles of Ulysses Grant, Robert E. Lee, “Stonewall” Jackson, William T ...
... • b. Describe President Lincoln’s efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural address and the Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to suspend habeas corpus. • c. Describe the roles of Ulysses Grant, Robert E. Lee, “Stonewall” Jackson, William T ...
The Civil War Period 1845-1880
... The War Between the North and South • The 23 Northern states, primarily anti-slavery, were known as The Union States and included states such as Connecticut, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Maine, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont • The 11 Southern states, primarily ...
... The War Between the North and South • The 23 Northern states, primarily anti-slavery, were known as The Union States and included states such as Connecticut, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Maine, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont • The 11 Southern states, primarily ...
Southern secession
... • After Lincoln elected, Southern leaders believe they no longer have a voice in government- many felt that to preserve their economy and their way of life, they needed to leave the union. • South Carolina is the first state to leave the union (December 20, 1860) • 6 more states soon follow ...
... • After Lincoln elected, Southern leaders believe they no longer have a voice in government- many felt that to preserve their economy and their way of life, they needed to leave the union. • South Carolina is the first state to leave the union (December 20, 1860) • 6 more states soon follow ...
Civil War Begins
... forever free… And upon this act, sincerely believed to be an act of justice, warranted by the Constitution upon military necessity, I invoke the considerate judgment of mankind, and the gracious favor of almighty God. ...
... forever free… And upon this act, sincerely believed to be an act of justice, warranted by the Constitution upon military necessity, I invoke the considerate judgment of mankind, and the gracious favor of almighty God. ...
The Tide of War Turns
... B: The Battle of Gettysburg - The fighting here raged for 3 days - 90,000 Union troops clashed with 75,000 Confederate troops - The turning point of the Battle was when General George Pickett was ordered to mount a direct attack on the middle of the Union lines; a deadly mistake - This was known as ...
... B: The Battle of Gettysburg - The fighting here raged for 3 days - 90,000 Union troops clashed with 75,000 Confederate troops - The turning point of the Battle was when General George Pickett was ordered to mount a direct attack on the middle of the Union lines; a deadly mistake - This was known as ...
U.S. History Chapter 11 Civil War Events
... After what battle does Lincoln issue this proclamation? Antietam B. Overtime Lincoln saw that he could not save the Union without ending slavery. How did Lincoln authorize the freeing of slaves? Seizing enemy “property” C. The Proclamation did not free any slaves immediately b/c it applied only to s ...
... After what battle does Lincoln issue this proclamation? Antietam B. Overtime Lincoln saw that he could not save the Union without ending slavery. How did Lincoln authorize the freeing of slaves? Seizing enemy “property” C. The Proclamation did not free any slaves immediately b/c it applied only to s ...
Chapter 20-21 Identifications
... A) Both the Union and the Confederacy mobilized their economies and societies to wage the war even while facing considerable home front opposition. B) Lincoln and most Union supporters began the Civil War to preserve the Union, but Lincoln’s decision to issue the Emancipation Proclamation reframed t ...
... A) Both the Union and the Confederacy mobilized their economies and societies to wage the war even while facing considerable home front opposition. B) Lincoln and most Union supporters began the Civil War to preserve the Union, but Lincoln’s decision to issue the Emancipation Proclamation reframed t ...
Name Period_______ APUSH Homework, Chap 21 The Furnace of
... 1. ______ The political effects of the Emancipation Proclamation were to a. bolster public support for the war and the Republican party. b. increase conflict between Lincoln and the radical wing of the Republican party. c. turn the Democratic party from support of the war toward favoring recognition ...
... 1. ______ The political effects of the Emancipation Proclamation were to a. bolster public support for the war and the Republican party. b. increase conflict between Lincoln and the radical wing of the Republican party. c. turn the Democratic party from support of the war toward favoring recognition ...
Military History of the Civil War
... if he freed the slaves, these states would decide to secede from the Union and join the Confederacy. If this happened, the Confederacy would receive a major boost in economic support and manpower. Lincoln also questioned whether he had the constitutional right to the free the slaves. No clause in th ...
... if he freed the slaves, these states would decide to secede from the Union and join the Confederacy. If this happened, the Confederacy would receive a major boost in economic support and manpower. Lincoln also questioned whether he had the constitutional right to the free the slaves. No clause in th ...
The Civil War
... The issue of slavery still on the minds of loyal slave states: Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri, Virginia (secedes April 1861), Tennessee (secedes May 1861), and North Carolina (secedes May ...
... The issue of slavery still on the minds of loyal slave states: Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri, Virginia (secedes April 1861), Tennessee (secedes May 1861), and North Carolina (secedes May ...
Battle of Antietam
... Lincoln wanted a _____________ victory before issuing the Emancipation Proclamation but ___________ was such a loss to the Confederate Army Lincoln felt confident enough to issue the Emancipation Proclamation. ...
... Lincoln wanted a _____________ victory before issuing the Emancipation Proclamation but ___________ was such a loss to the Confederate Army Lincoln felt confident enough to issue the Emancipation Proclamation. ...
CIVIL WAR UNIT STUDY GUIDE
... c. Identify major battles and campaigns: Fort Sumter, Gettysburg, the Atlanta Campaign, Sherman’s March to the Sea, and Appomattox Court House. d. Describe the roles of Abraham Lincoln, Robert E. Lee, Ulysses S. Grant, Jefferson Davis, and Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson. e. Describe the effects of war o ...
... c. Identify major battles and campaigns: Fort Sumter, Gettysburg, the Atlanta Campaign, Sherman’s March to the Sea, and Appomattox Court House. d. Describe the roles of Abraham Lincoln, Robert E. Lee, Ulysses S. Grant, Jefferson Davis, and Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson. e. Describe the effects of war o ...
THE CIVIL WAR by Ken Burns – Video Guide Questions
... 14. Who was Mary Todd?________ 15. In what year did Congress pass an act that allowed Kansas & Nebraska to decide for themselves whether or not to permit slavery?______________ 16. Who said, “A house divided against itself cannot stand”?_______________________________ THE METEOR 17. Who led the raid ...
... 14. Who was Mary Todd?________ 15. In what year did Congress pass an act that allowed Kansas & Nebraska to decide for themselves whether or not to permit slavery?______________ 16. Who said, “A house divided against itself cannot stand”?_______________________________ THE METEOR 17. Who led the raid ...
17-4 The Legacy of War The Civil War brought great changes and
... what it all meant, that this was the day for which she had been so long praying, but fearing that she would never live to see. ---Booker T. Washington, quoted in his autobiography, • The Emancipation Proclamation applied primarily to slaves in the Confederacy, however. Many African Americans in the ...
... what it all meant, that this was the day for which she had been so long praying, but fearing that she would never live to see. ---Booker T. Washington, quoted in his autobiography, • The Emancipation Proclamation applied primarily to slaves in the Confederacy, however. Many African Americans in the ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.