Pharm 22, 23- Drugs for Affective Disorders Depression
... Locus ceruleus (LC) activates norepinephrine (NE) release stimulates the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system NE increases glutamate release Drugs with anxiolytic or antipanic effects inhibit LC firing and decrease noradrenergic activity GABA receptor The GABAA chloride ion chann ...
... Locus ceruleus (LC) activates norepinephrine (NE) release stimulates the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system NE increases glutamate release Drugs with anxiolytic or antipanic effects inhibit LC firing and decrease noradrenergic activity GABA receptor The GABAA chloride ion chann ...
Module 2: Drug and Alcohol Awareness
... information and advice about effects of substances on mental and physical health and vice versa. Dual Diagnosis Capability 8 level 2 ...
... information and advice about effects of substances on mental and physical health and vice versa. Dual Diagnosis Capability 8 level 2 ...
Recent developments in treatment of PD
... Implants of fetal cells 1st double-blind placebo-controlled surgical trial reported in 2001 (Freed, NEJM). 40 patients, 20 received implants and 20 had placebo procedure PET images showed implants grew Little evidence for improvement after 1 year 15% had dyskinesia that could not be controlled by d ...
... Implants of fetal cells 1st double-blind placebo-controlled surgical trial reported in 2001 (Freed, NEJM). 40 patients, 20 received implants and 20 had placebo procedure PET images showed implants grew Little evidence for improvement after 1 year 15% had dyskinesia that could not be controlled by d ...
Antianxiety, Mood Disorder and Antipsychotic Medications
... Glutamatergic dysfunction may be genetically linked as well as causative in the cognitive impairments and negative s/s of this disorder. ...
... Glutamatergic dysfunction may be genetically linked as well as causative in the cognitive impairments and negative s/s of this disorder. ...
2.exilam details
... Etizolam is a benzodiazepine type compound. Effects of Etizolam could be moderate to mild, depending on the strength. One of the most common effects is sleepiness during daytime at very high dose. Other effects include thirst, jaundice, rash, nausea and weakness. DRUG FORM & METHOD OF USE: Having mu ...
... Etizolam is a benzodiazepine type compound. Effects of Etizolam could be moderate to mild, depending on the strength. One of the most common effects is sleepiness during daytime at very high dose. Other effects include thirst, jaundice, rash, nausea and weakness. DRUG FORM & METHOD OF USE: Having mu ...
APPNov. 08 and 09
... By the end of this unit, you will be able to: 1. Describe various states of consciousness and their impact on behavior. 2. Discuss aspects of sleep and dreaming: a. stages and characteristics of the sleep cycle; b. theories of sleep and dreaming; c. symptoms and treatments of sleep disorders. 3. Des ...
... By the end of this unit, you will be able to: 1. Describe various states of consciousness and their impact on behavior. 2. Discuss aspects of sleep and dreaming: a. stages and characteristics of the sleep cycle; b. theories of sleep and dreaming; c. symptoms and treatments of sleep disorders. 3. Des ...
Lecture 4
... are not suitable for long-term pain management as they cause complete numbness and can have serious side-effects over time. • Opioid painkillers such as morphine are highly effective at reducing pain, but longterm use can lead to dependence and tolerance. As the body becomes used to the drug it beco ...
... are not suitable for long-term pain management as they cause complete numbness and can have serious side-effects over time. • Opioid painkillers such as morphine are highly effective at reducing pain, but longterm use can lead to dependence and tolerance. As the body becomes used to the drug it beco ...
Lecture 14
... Negative symptoms: withdrawal from society, flattened emotional responses, defect in selective attention (can’t distinguish between important and insignificant) Affects up to 1% of population, high suicide rate (10%) Amphetamines promote dopamine release => mimic schizophrenia ...
... Negative symptoms: withdrawal from society, flattened emotional responses, defect in selective attention (can’t distinguish between important and insignificant) Affects up to 1% of population, high suicide rate (10%) Amphetamines promote dopamine release => mimic schizophrenia ...
History of psychopharmacology
... United States of America. However, the development and utilisation of pharmacologic interventions saw this figure dramatically decrease to approximately 200,000 in-patients within 10 years (Sherr, 2000). The term psychopharmacology was first ...
... United States of America. However, the development and utilisation of pharmacologic interventions saw this figure dramatically decrease to approximately 200,000 in-patients within 10 years (Sherr, 2000). The term psychopharmacology was first ...
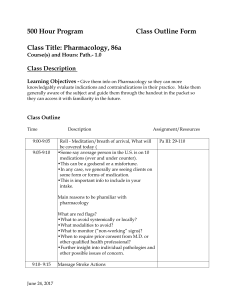
86a-CO-Pharmacology
... Roll - Meditation/breath of arrival, What will be covered today ( •Some say average person in the U.S. is on 10 medications (over and under counter). •This can be a godsend or a misfortune. •In any case, we generally are seeing clients on some form or forms of medication. •This is important info to ...
... Roll - Meditation/breath of arrival, What will be covered today ( •Some say average person in the U.S. is on 10 medications (over and under counter). •This can be a godsend or a misfortune. •In any case, we generally are seeing clients on some form or forms of medication. •This is important info to ...
Katherine Douglas Hallucinogens Reaction Paper Hallucinogens
... Hallucinogens are a class of drugs that change a person’s thought processes, mood and perceptions. A person’s “trip” while on a hallucinogen can vary greatly based on their previous experiences and expectations as well as the dose of the drug. There are a few common effects of hallucinogens which in ...
... Hallucinogens are a class of drugs that change a person’s thought processes, mood and perceptions. A person’s “trip” while on a hallucinogen can vary greatly based on their previous experiences and expectations as well as the dose of the drug. There are a few common effects of hallucinogens which in ...
PSYC 342: Psychopharmacology
... • Not schizoaffective disorder or a mood disorder with psychotic features • Not due to substance abuse or a general medical disorder ...
... • Not schizoaffective disorder or a mood disorder with psychotic features • Not due to substance abuse or a general medical disorder ...
drug_action_notes
... caused by inactive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) is treated by the drug neostigmine, which inhibits acetylcholinesterase, so increasing the amount of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. Nerve gas and organophosphate insecticides (DDT) inhibit acetylcholinesterase, so nicotinic acetylch ...
... caused by inactive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) is treated by the drug neostigmine, which inhibits acetylcholinesterase, so increasing the amount of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. Nerve gas and organophosphate insecticides (DDT) inhibit acetylcholinesterase, so nicotinic acetylch ...
A PHARMACOLOGISTS VIEW OF THE BRAIN
... a. the excitatory amino acid transmitters increase sodium permeability 1. this drives the neuron towards the threshold potential (about -40 mv), at which point an action potential is generated b. the inhibitory amino acid transmitters increase chloride permeability 1. this either hyperpolarizes the ...
... a. the excitatory amino acid transmitters increase sodium permeability 1. this drives the neuron towards the threshold potential (about -40 mv), at which point an action potential is generated b. the inhibitory amino acid transmitters increase chloride permeability 1. this either hyperpolarizes the ...
Lesson 1 - UCLA Brain Research Institute
... Doctors would sell and overprescribe drugs In 2010, enactment of the Prescription Drug ...
... Doctors would sell and overprescribe drugs In 2010, enactment of the Prescription Drug ...
module 10 Drugs and Consciousness Module Preview Psychoactive
... 10-3. Identify the major stimulants, and explain how they affect neural activity and behavior. Stimulants, such as caffeine, nicotine, and the amphetamines and the even more powerful cocaine, Ecstasy, and methamphetamines, excite neural activity and arouse body functions. As with nearly all psychoac ...
... 10-3. Identify the major stimulants, and explain how they affect neural activity and behavior. Stimulants, such as caffeine, nicotine, and the amphetamines and the even more powerful cocaine, Ecstasy, and methamphetamines, excite neural activity and arouse body functions. As with nearly all psychoac ...
Antidepressants and Anxiolytics
... • May increase sexual desire • May cause excitation • Dopamine associated with addictive behaviors – Bupoprion marketed for smoking cessation (Zyban) – Also may help concentration ADD ...
... • May increase sexual desire • May cause excitation • Dopamine associated with addictive behaviors – Bupoprion marketed for smoking cessation (Zyban) – Also may help concentration ADD ...
document
... Stimulants such as Adderall increase attention but also raise blood pressure and heart rate. These side effects can be made worse when prescription drugs are not taken as prescribed or are abused in combination with other substances—including alcohol, other prescription drugs, and even over-the-coun ...
... Stimulants such as Adderall increase attention but also raise blood pressure and heart rate. These side effects can be made worse when prescription drugs are not taken as prescribed or are abused in combination with other substances—including alcohol, other prescription drugs, and even over-the-coun ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.