CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY OF DRUGS AFFECTING THE
... butyrophenones, piperazine compounds, and piperidine compounds. Trade names include drugs such as Thorazine, Haldol, Clozaril and Risperdal. These drugs are referred to as Neuroleptics and are most commonly prescribed as anti-psychotics. This type of tranquilizer is not widely abused. • Minor Tranqu ...
... butyrophenones, piperazine compounds, and piperidine compounds. Trade names include drugs such as Thorazine, Haldol, Clozaril and Risperdal. These drugs are referred to as Neuroleptics and are most commonly prescribed as anti-psychotics. This type of tranquilizer is not widely abused. • Minor Tranqu ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. ______________ - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. _______ - (__________-___________________ acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because wh ...
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. ______________ - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. _______ - (__________-___________________ acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because wh ...
T5_a: High resolution copy of the slides of the talk
... Drug addiction and drug abuse Chronic or habitual use of any chemical substance to alter states of body or mind for other than medically warranted purposes. Psychological dependence is the subjective feeling that the user needs the drug to maintain a feeling of well‐being; physical dependence i ...
... Drug addiction and drug abuse Chronic or habitual use of any chemical substance to alter states of body or mind for other than medically warranted purposes. Psychological dependence is the subjective feeling that the user needs the drug to maintain a feeling of well‐being; physical dependence i ...
userfiles/140/my files/powerpoint presentations/social_drugs_nmhs
... chemicals, like THC, can mimic or block actions of neurotransmitters & interfere with normal functions Cannabinoid receptors are activated by a neurotransmitter called anandamide Anandamide is a cannabinoid your body makes. ...
... chemicals, like THC, can mimic or block actions of neurotransmitters & interfere with normal functions Cannabinoid receptors are activated by a neurotransmitter called anandamide Anandamide is a cannabinoid your body makes. ...
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lec 7: Schizophrenia and Parkinson`s
... Decrease in DA neurotransmission is therapeutic ...
... Decrease in DA neurotransmission is therapeutic ...
Antidepressant drugs - Dr Lynch
... Little scientific evidence regarding predictors of relapse or recurrence ...
... Little scientific evidence regarding predictors of relapse or recurrence ...
Depression and Suicide
... Little scientific evidence regarding predictors of relapse or recurrence ...
... Little scientific evidence regarding predictors of relapse or recurrence ...
Brain_Basics - UCSD Cognitive Science
... and saturate the brain’s reward systems individual can become conditioned/habituated/adapted to the intense level of drug-induced pleasure (develops tolerance ...
... and saturate the brain’s reward systems individual can become conditioned/habituated/adapted to the intense level of drug-induced pleasure (develops tolerance ...
Answers
... secretion from parietal cells. Lansoprazole is a proton pump (K+/H+ ATPase) inhibitor which blocks secretion of acid from parietal cells. Lansoprazole is more effective since it blocks stomach acid secretion directly. Ranitidine only blocks histamine-induced upregulation of stomach acid production, ...
... secretion from parietal cells. Lansoprazole is a proton pump (K+/H+ ATPase) inhibitor which blocks secretion of acid from parietal cells. Lansoprazole is more effective since it blocks stomach acid secretion directly. Ranitidine only blocks histamine-induced upregulation of stomach acid production, ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. ______________ - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. _______ - (__________-___________________ acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because wh ...
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. ______________ - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. _______ - (__________-___________________ acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because wh ...
8th Grade Illegal Drugs
... A group of drugs that slow down the CNS, cause drowsiness, and can be used as painkillers. ...
... A group of drugs that slow down the CNS, cause drowsiness, and can be used as painkillers. ...
Depression and Suicide - the Peninsula MRCPsych Course
... This is defined by ratio of NA to 5HT reuptake inhibition e.g. around 40 times greater for clomipramine for 5HT Reuptake inhibition is not their only possible mode of action i.e. antagonism effects and effects on autoreceptors. Some have questioned whether anticholinergic effects may be related to e ...
... This is defined by ratio of NA to 5HT reuptake inhibition e.g. around 40 times greater for clomipramine for 5HT Reuptake inhibition is not their only possible mode of action i.e. antagonism effects and effects on autoreceptors. Some have questioned whether anticholinergic effects may be related to e ...
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
... compared to other anticonvulsants (further studies needed) Risk of dermatologic AE (including life threatening Stevens-Johnson syndrome Slow titration to avoid side effects) ...
... compared to other anticonvulsants (further studies needed) Risk of dermatologic AE (including life threatening Stevens-Johnson syndrome Slow titration to avoid side effects) ...
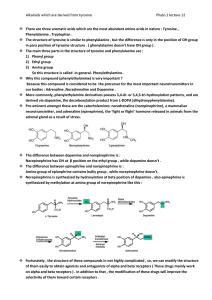
Norepinephrine
... At therapeutic doses, amphetamine causes emotional and cognitive effects such as euphoria, change in desire for sex, increased wakefulness, and improved cognitive control . Larger doses of amphetamine may impair cognitive function and induce rapid muscle breakdown. Drug addiction is a serious ri ...
... At therapeutic doses, amphetamine causes emotional and cognitive effects such as euphoria, change in desire for sex, increased wakefulness, and improved cognitive control . Larger doses of amphetamine may impair cognitive function and induce rapid muscle breakdown. Drug addiction is a serious ri ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... MAO in gut (will break down monoamines and inactivate certain NT) Depot binding o Blood albumin: if the molecule is bound to a depot (like albumin) they cannot reach their sites of action o Fat cells: another example, most slowly, and less likely to interfere with the initial effects of the drug ...
... MAO in gut (will break down monoamines and inactivate certain NT) Depot binding o Blood albumin: if the molecule is bound to a depot (like albumin) they cannot reach their sites of action o Fat cells: another example, most slowly, and less likely to interfere with the initial effects of the drug ...
CNS pharmacology
... Depression - Causes Most focus on neurochemical processes - abnormal amounts of NTs - decreased post-synaptic sensitivity NB serotonin, nor-adrenaline and dopamine - all effected by anti-depressants Anti-depressants therapeutic effect: increasing NT levels or decreasing re-uptake ...
... Depression - Causes Most focus on neurochemical processes - abnormal amounts of NTs - decreased post-synaptic sensitivity NB serotonin, nor-adrenaline and dopamine - all effected by anti-depressants Anti-depressants therapeutic effect: increasing NT levels or decreasing re-uptake ...
Addiction - ISpatula
... Effects of Heavy Marijuana Use on Attention, Learning, & Memory in Undergraduates Researchers compared 65 "heavy users," (smoked a median of 29 of the past 30 days), and 64 "light users," (smoked a median of 1 of the past 30 days). After 19-24 hours of abstinence from marijuana and other illicit dr ...
... Effects of Heavy Marijuana Use on Attention, Learning, & Memory in Undergraduates Researchers compared 65 "heavy users," (smoked a median of 29 of the past 30 days), and 64 "light users," (smoked a median of 1 of the past 30 days). After 19-24 hours of abstinence from marijuana and other illicit dr ...
SEDATIVES / HYPNOTICS Barbiturates • Second choice as sedative
... used mainly in children and the elder, and the patients when failed to other drug. Chloral hydrate is a non-selective CNS depressant Withdrawl from drug causes disrupted sleep and intense nightmares Combination of chloral hydrate and alcohol can produce increased intoxication, stupor, and am ...
... used mainly in children and the elder, and the patients when failed to other drug. Chloral hydrate is a non-selective CNS depressant Withdrawl from drug causes disrupted sleep and intense nightmares Combination of chloral hydrate and alcohol can produce increased intoxication, stupor, and am ...
Final + Answers
... NSAIDS act via their ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) and therefore prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins sensitize pain receptors; therefore, NSAIDs have an indirect analgesic effect by ‘desensitizing’ pain receptors. Opiods are opiate receptor agonists. Opioid analgesia is mediated throug ...
... NSAIDS act via their ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) and therefore prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins sensitize pain receptors; therefore, NSAIDs have an indirect analgesic effect by ‘desensitizing’ pain receptors. Opiods are opiate receptor agonists. Opioid analgesia is mediated throug ...
Dr Richard Stevenson
... ***duration 24 – 48 hours*** Treatments Benzodiazepines +/- haloperidol ...
... ***duration 24 – 48 hours*** Treatments Benzodiazepines +/- haloperidol ...
What is mental life
... Typical Antipsychotics (1st generation antipsychotics aka Neuroleptics) o The original antipsychotics o Even though these are older medications, they are sometimes the 1st line drugs (e.g. Haloperidol where IV delivery is needed) o DOPAMINE ANTAGONISTS Atypical Antipsychotics (2nd generation antipsy ...
... Typical Antipsychotics (1st generation antipsychotics aka Neuroleptics) o The original antipsychotics o Even though these are older medications, they are sometimes the 1st line drugs (e.g. Haloperidol where IV delivery is needed) o DOPAMINE ANTAGONISTS Atypical Antipsychotics (2nd generation antipsy ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.