Drugs and Toxicology
... • Detoxification—about 90 percent in the liver • About 5 percent is excreted unchanged in breath, perspiration, and urine ...
... • Detoxification—about 90 percent in the liver • About 5 percent is excreted unchanged in breath, perspiration, and urine ...
Hallucinogens
... Note: Oral sedative dose 1-5 mg; subanesthetic dose 7.5 mg. Based on Petersen & Stillman, ...
... Note: Oral sedative dose 1-5 mg; subanesthetic dose 7.5 mg. Based on Petersen & Stillman, ...
Lecture 7 - Antidepressants new 11-12
... Too long (3-11 days): Fluoxetine (Prozac) Moderate length (~24hr): Sertraline, Paroxetine, Citalopram. Metabolism: P450 then conjugation They are enzyme inhibitors Weak inhibitors < Sertraline, Citalopram interaction Strong inhibitors > Fluoxetine, Paroxetine metabolism of TCA, neurolep ...
... Too long (3-11 days): Fluoxetine (Prozac) Moderate length (~24hr): Sertraline, Paroxetine, Citalopram. Metabolism: P450 then conjugation They are enzyme inhibitors Weak inhibitors < Sertraline, Citalopram interaction Strong inhibitors > Fluoxetine, Paroxetine metabolism of TCA, neurolep ...
Amphetamines
... Amphetamine stimulates the central nervous system by increasing the amount of certain chemicals in the body. Main Action of Amphetamine; Increase the synaptic activity of the dopamine and norepinephrine. ...
... Amphetamine stimulates the central nervous system by increasing the amount of certain chemicals in the body. Main Action of Amphetamine; Increase the synaptic activity of the dopamine and norepinephrine. ...
Antipsychotic drugs
... performed less efficiently, there is a compensatory increased activity in the mesolimbic pathway, and this produces the positive symptoms of hallucinations and delusions. • As the limbic system is also involved in pleasurable sensations, this pathway may also be involved in ...
... performed less efficiently, there is a compensatory increased activity in the mesolimbic pathway, and this produces the positive symptoms of hallucinations and delusions. • As the limbic system is also involved in pleasurable sensations, this pathway may also be involved in ...
Treatment Strategies for DWI Offenders
... Number of those 15 to 24 dying of heroin overdose rose ...
... Number of those 15 to 24 dying of heroin overdose rose ...
All elements for protein synthesis are present in dendrites
... Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavrioal Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Gonda (Goldschmied) Center for Neuroscience and ...
... Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavrioal Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Gonda (Goldschmied) Center for Neuroscience and ...
... Abstract Drugs of abuse, such as amphetamine, share the ability to activate the mesolimbic dopamine (DA) system. The behavioral effects of amphetamine are mediated in large part by increasing DA neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens. However, there is evidence that serotonin (5-HT) systems may ...
Chapter 4
... The study of the effects of dugs on the nervous system and on behavior Q: What is a drug? A: “An exogenous chemical not necessary for normal cellular functioning that significantly alters the functions of certain cells of the body when taken in relatively low doses” Drug effect – the changes ...
... The study of the effects of dugs on the nervous system and on behavior Q: What is a drug? A: “An exogenous chemical not necessary for normal cellular functioning that significantly alters the functions of certain cells of the body when taken in relatively low doses” Drug effect – the changes ...
Overview - science of addiction
... psychoactive drugs have been characterized • They produce psychoactive effects by acting in the CNS • To do this they must be able to cross the blood brain barrier • They then act to disrupt neuronal communication at the level of the synapse. ...
... psychoactive drugs have been characterized • They produce psychoactive effects by acting in the CNS • To do this they must be able to cross the blood brain barrier • They then act to disrupt neuronal communication at the level of the synapse. ...
Sedatives
... Has been referred to as "milk of amnesia" because of the milk-like appearance of its iv preparation. Not scheduled, easy to obtain, and wears off quickly, so is abused. Most likely by medical staff because access & skill. ...
... Has been referred to as "milk of amnesia" because of the milk-like appearance of its iv preparation. Not scheduled, easy to obtain, and wears off quickly, so is abused. Most likely by medical staff because access & skill. ...
Drugs as Evidence
... Crack cocaine: freebase "cooked" in the ratio is 50/50 to 40/60% cocaine/ sodium bicarbonate. ...
... Crack cocaine: freebase "cooked" in the ratio is 50/50 to 40/60% cocaine/ sodium bicarbonate. ...
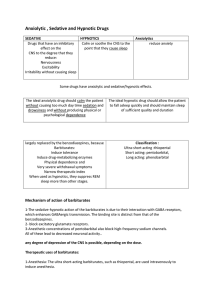
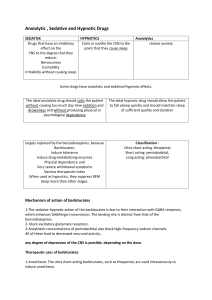
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs
... 5-Physical dependence: Abrupt withdrawal from barbiturates may cause tremors, anxiety, weakness, nausea and vomiting 6-. Poisoning: death resulting from drug overdoses because of severe depression of respiration and cardiovascular depression ...
... 5-Physical dependence: Abrupt withdrawal from barbiturates may cause tremors, anxiety, weakness, nausea and vomiting 6-. Poisoning: death resulting from drug overdoses because of severe depression of respiration and cardiovascular depression ...
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
... 5-Physical dependence: Abrupt withdrawal from barbiturates may cause tremors, anxiety, weakness, nausea and vomiting 6-. Poisoning: death resulting from drug overdoses because of severe depression of respiration and cardiovascular depression ...
... 5-Physical dependence: Abrupt withdrawal from barbiturates may cause tremors, anxiety, weakness, nausea and vomiting 6-. Poisoning: death resulting from drug overdoses because of severe depression of respiration and cardiovascular depression ...
SECZYL TABLET
... Has a longer terminal elimination half-life (approximately 17 to 29 hours) than commonly used drugs in this class. Secnidazole have a much longer half-life than Metronidazole, allowing single-dose or once daily administration. DOSAGE One day treatment: Secnidazole is given 2 gm as a single dose af ...
... Has a longer terminal elimination half-life (approximately 17 to 29 hours) than commonly used drugs in this class. Secnidazole have a much longer half-life than Metronidazole, allowing single-dose or once daily administration. DOSAGE One day treatment: Secnidazole is given 2 gm as a single dose af ...
New Psychoactive Substances NPS
... of drug intoxications at emergency departments and intensive care units 50 substances identified: - synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists ("Spice") - piperazines - substituted phenethylamines - synthetic cathinones - hallucinogenic tryptamines - piperidines ...
... of drug intoxications at emergency departments and intensive care units 50 substances identified: - synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists ("Spice") - piperazines - substituted phenethylamines - synthetic cathinones - hallucinogenic tryptamines - piperidines ...
Opiates
... Powder than can be dissolved, can be in pills, can be in rocks to be smoked (ice) Made from repulsive ingredients (can be home-made) prolonged sense of euphoria, as well as increased energy, focus, confidence, sexual prowess and feelings of desirability. Binge/Crash pattern, continual use HUGE rush, ...
... Powder than can be dissolved, can be in pills, can be in rocks to be smoked (ice) Made from repulsive ingredients (can be home-made) prolonged sense of euphoria, as well as increased energy, focus, confidence, sexual prowess and feelings of desirability. Binge/Crash pattern, continual use HUGE rush, ...
Psychoactive Drugs
... Effects occur between 3.5 & 4 hours after ingestion. Vivid hallucinations most salient. --trip is long (10 hours) ...
... Effects occur between 3.5 & 4 hours after ingestion. Vivid hallucinations most salient. --trip is long (10 hours) ...
Psychotropic Meds - nursing-
... Inhibits MAO, thus interfering with breakdown of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin ...
... Inhibits MAO, thus interfering with breakdown of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin ...
Dr Darton Presentation
... [ataraxy – detachment; indifference – distinct from sedation] • Block dopamine – and other neurotransmitters ...
... [ataraxy – detachment; indifference – distinct from sedation] • Block dopamine – and other neurotransmitters ...
Lorem Ipsum - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... decarboxylase inhibitor that is combined with levadopa which enables levadopa to get to and cross over the blood-brain barrier This medication combination is called Sinemet ...
... decarboxylase inhibitor that is combined with levadopa which enables levadopa to get to and cross over the blood-brain barrier This medication combination is called Sinemet ...
Neurotransmitter release in the brain
... connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. The transmitter molecules (typically 10,000-100,000 molecules pe ...
... connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. The transmitter molecules (typically 10,000-100,000 molecules pe ...
Medications and Alzheimer`s Disease
... effects and some anti-anxiety properties. Adverse Effects: Dry mouth, constipation, rapid heartbeat, blurred vision, urinary retention, and dizziness on change of position. These effects may be very prominent. In some persons with heart conditions, some of these drugs may aggravate the condition. Th ...
... effects and some anti-anxiety properties. Adverse Effects: Dry mouth, constipation, rapid heartbeat, blurred vision, urinary retention, and dizziness on change of position. These effects may be very prominent. In some persons with heart conditions, some of these drugs may aggravate the condition. Th ...
Antidepressant agents - به سامانه مديريت
... Also used for treatment of other disorders including: -Anxiety disorders, dysthymia, chronic pain and behavioral problems ...
... Also used for treatment of other disorders including: -Anxiety disorders, dysthymia, chronic pain and behavioral problems ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.