Pharmacology of stimulant substances
... preservative-free solutions for injection by the various spinal routes (epidural, intrathecal, caudal, and others) powders for compounding liquids both with and without alcohol for oral and sub-lingual administration, available in regular and bottles, dropper bottles, bottles with a pump similar to ...
... preservative-free solutions for injection by the various spinal routes (epidural, intrathecal, caudal, and others) powders for compounding liquids both with and without alcohol for oral and sub-lingual administration, available in regular and bottles, dropper bottles, bottles with a pump similar to ...
幻灯片 1
... pump of vesicular membranes in central and peripheral adrenergic neurons for prolonged periods of time. • The storage vesicles are destroyed as a result of their interaction with reserpine and nerve endings lose their ability to concentrate and store norepinephrine and dopamine. ...
... pump of vesicular membranes in central and peripheral adrenergic neurons for prolonged periods of time. • The storage vesicles are destroyed as a result of their interaction with reserpine and nerve endings lose their ability to concentrate and store norepinephrine and dopamine. ...
Adrenergic Agonists SAR
... Agonists can select for a1, a2, B1, B2, or non selectively bind to both B receptors. Or, drugs can act indirectly: drug enters storage granule and displaces Norepi and some dopamine. Most activity is seen at the B receptors. Mixed agonists select for a1 receptors but demonstrate some results typical ...
... Agonists can select for a1, a2, B1, B2, or non selectively bind to both B receptors. Or, drugs can act indirectly: drug enters storage granule and displaces Norepi and some dopamine. Most activity is seen at the B receptors. Mixed agonists select for a1 receptors but demonstrate some results typical ...
Emergency Drugs
... shock due to non-anaphylactoid causes, during general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons, during labor (may delay the second stage), cardiac dilatation or coronary insufficiency; cases where vasopressor drugs are contraindicated (e.g., thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, hypertension, toxemia of pregnan ...
... shock due to non-anaphylactoid causes, during general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons, during labor (may delay the second stage), cardiac dilatation or coronary insufficiency; cases where vasopressor drugs are contraindicated (e.g., thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, hypertension, toxemia of pregnan ...
Consciousness - Cengage Learning
... C. The meditator uses a mental focusing method (e.g., repeating a mantra, a soothing phrase) to organize attention. D. Meditation is often accompanied by lowered heart rate, muscle tension, blood pressure, and oxygen consumption. Also, dopamine is increased. E. Meditation may reduce stress-related p ...
... C. The meditator uses a mental focusing method (e.g., repeating a mantra, a soothing phrase) to organize attention. D. Meditation is often accompanied by lowered heart rate, muscle tension, blood pressure, and oxygen consumption. Also, dopamine is increased. E. Meditation may reduce stress-related p ...
Peripheral nerve pathophysiology
... Origin of peripheral nervous system disease These diseases can be broadly classified into four major categories: Spinal dystrophies (motor neuron body) Peripheral neuropathies (nerve: body+axon) Diseases of the myoneural junction Myopathies Groups one through three are primarily diseases of ...
... Origin of peripheral nervous system disease These diseases can be broadly classified into four major categories: Spinal dystrophies (motor neuron body) Peripheral neuropathies (nerve: body+axon) Diseases of the myoneural junction Myopathies Groups one through three are primarily diseases of ...
Cholinergics and Anticholinergics
... nerve gases (sarin, tabun, soman) These agents cause excessive cholinergic stimulation (muscarinic) and neuromuscular blockade ...
... nerve gases (sarin, tabun, soman) These agents cause excessive cholinergic stimulation (muscarinic) and neuromuscular blockade ...
Poison Control Centers Synthetic Drugs of Abuse
... Scores of different agents have been identified in “K2” ...
... Scores of different agents have been identified in “K2” ...
File
... • Highly lipid soluble drugs such as Thiopentone sodium , on I.V administration immediately gets distributed to areas of high blood flow such as Brain and causes general anesthesia . • Immediately with in a few minutes ,it recrosses the BBB and gets distributed into the blood and then to the less pe ...
... • Highly lipid soluble drugs such as Thiopentone sodium , on I.V administration immediately gets distributed to areas of high blood flow such as Brain and causes general anesthesia . • Immediately with in a few minutes ,it recrosses the BBB and gets distributed into the blood and then to the less pe ...
Table 1: Some important drug interactions with Antidepressants
... fluoxetine. Occasional reports of problem but monitor for any adverse effects when the serotonin syndrome combination is started ...
... fluoxetine. Occasional reports of problem but monitor for any adverse effects when the serotonin syndrome combination is started ...
Understanding Theories of Addictive Disorders
... B. Sedative hypnotics C. Narcotic analgesics D. Stimulants E. Hallucinogenics F. Inhalants G.Steroids H. Other ...
... B. Sedative hypnotics C. Narcotic analgesics D. Stimulants E. Hallucinogenics F. Inhalants G.Steroids H. Other ...
Potentially inappropriate drug use and hip
... • To examine aspects of prescribing quality among older people acutely admitted to hospital (study I, paper I) • To explore associations between exposure to psychotropic drugs and the risk of hip fracture (study II, papers II and III) ...
... • To examine aspects of prescribing quality among older people acutely admitted to hospital (study I, paper I) • To explore associations between exposure to psychotropic drugs and the risk of hip fracture (study II, papers II and III) ...
*****************#***********#******|6******7#**8#**9
... • Miosis (缩瞳): contraction of sphincter muscle of iris • Lowing intraocular pressure: enlarging angle of anterior chamber, increasing drainage of aqueous humor • Spasm of accommodation (调节痉挛): contraction of ciliary muscle, contraction for near vision ...
... • Miosis (缩瞳): contraction of sphincter muscle of iris • Lowing intraocular pressure: enlarging angle of anterior chamber, increasing drainage of aqueous humor • Spasm of accommodation (调节痉挛): contraction of ciliary muscle, contraction for near vision ...
Lesson 39 "Avoiding Illegal Drug Use"
... • Each group will have the responsibility of researching and presenting information on the drug or group of drugs assigned to them. You will have that majority of the period today to complete this project, and will present the information at the end of class today or on Friday. The worksheet I gave ...
... • Each group will have the responsibility of researching and presenting information on the drug or group of drugs assigned to them. You will have that majority of the period today to complete this project, and will present the information at the end of class today or on Friday. The worksheet I gave ...
N receptors
... the nervous system that permits integration of information and transmits this info to other cells 1) The dendrites receive info from other neurons (or sensory endings) ...
... the nervous system that permits integration of information and transmits this info to other cells 1) The dendrites receive info from other neurons (or sensory endings) ...
Gastrointestinal Drugs
... Objective 23: discuss the pathophysiology of nausea and vomiting ◦ Nausea: sensation of abdominal discomfort that is intermittently accompanied by the desire to vomit ◦ Vomiting: the forceful expulsion of gastric contents up the esophagus and out of the mouth ...
... Objective 23: discuss the pathophysiology of nausea and vomiting ◦ Nausea: sensation of abdominal discomfort that is intermittently accompanied by the desire to vomit ◦ Vomiting: the forceful expulsion of gastric contents up the esophagus and out of the mouth ...
7-Skeletal_Muscle_Relaxants modified
... Mechanism of Action All bind nicotinic Ach receptors and competitively block Acetylcholine, thereby preventing muscle contraction i.e. They are competitive antagonists ...
... Mechanism of Action All bind nicotinic Ach receptors and competitively block Acetylcholine, thereby preventing muscle contraction i.e. They are competitive antagonists ...
Pharmacodynamics
... - Found in target cells or tissues - Determine the dose or concentration of drug required to form a significant no. of drugreceptor complexes - No. of receptors may limit maximal effect a drug may produce - Mediate effects of agonists and antagonists ...
... - Found in target cells or tissues - Determine the dose or concentration of drug required to form a significant no. of drugreceptor complexes - No. of receptors may limit maximal effect a drug may produce - Mediate effects of agonists and antagonists ...
Treatments and Therapy for Psychological Disorders
... PSYCHOTHERAPY is based on the interaction between a trained therapist using psychological techniques, and a client, who is experiencing emotional, behavioral, or interpersonal problems. ...
... PSYCHOTHERAPY is based on the interaction between a trained therapist using psychological techniques, and a client, who is experiencing emotional, behavioral, or interpersonal problems. ...
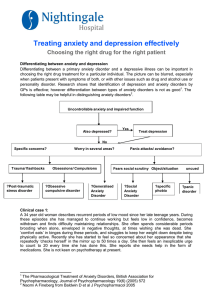
Treating anxiety and depression effectively
... were marginally more efficacious than SSRIs. In one large study escitalopram demonstrated superior efficacy over citalopram in treating depression based on improvement in MADRS scale scores4. What anxiolytic drugs are available? There are a range of potential treatments that can be effective for anx ...
... were marginally more efficacious than SSRIs. In one large study escitalopram demonstrated superior efficacy over citalopram in treating depression based on improvement in MADRS scale scores4. What anxiolytic drugs are available? There are a range of potential treatments that can be effective for anx ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.