fff-Antipsychotics (Neuroleptics)
... Isosteric replacement of N atom of phenothiazine with sp2 carbon (methylidene) led to thioxanthenes. Thioxanthenes are also nonpolar in which substituent at 2position led to formation of either cis (Z) or trans (E) isomers. Z isomer is more active than trans isomer or its saturated analog because it ...
... Isosteric replacement of N atom of phenothiazine with sp2 carbon (methylidene) led to thioxanthenes. Thioxanthenes are also nonpolar in which substituent at 2position led to formation of either cis (Z) or trans (E) isomers. Z isomer is more active than trans isomer or its saturated analog because it ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... activate the receptor in some fashion, which directly or indirectly brings about the effect. Some receptors incorporate effector machinery in the same molecule, so that drug binding brings about the effect directly, e.g., opening of an ion channel or activation of enzyme activity. Other receptors ar ...
... activate the receptor in some fashion, which directly or indirectly brings about the effect. Some receptors incorporate effector machinery in the same molecule, so that drug binding brings about the effect directly, e.g., opening of an ion channel or activation of enzyme activity. Other receptors ar ...
2 receptor
... - takes place within the same cells where the amines are synthesized, and in liver - Extraneuronal O-methylation of norepinephrine and epinephrine to metanephrines represent minor pathways of metabolism. MHPG(3-甲氧4-羟苯乙二醇): ...
... - takes place within the same cells where the amines are synthesized, and in liver - Extraneuronal O-methylation of norepinephrine and epinephrine to metanephrines represent minor pathways of metabolism. MHPG(3-甲氧4-羟苯乙二醇): ...
Week 6 lecture slides
... as a selective alcohol antagonist that selectively blocks the nausea. However, ondansetron doesn’t just block alcoholinduced nausea. Low doses of ethanol cause locomotor stimulation in rats (they run around more), and this response shows sensitization. This means that after repeated ethanol doses, t ...
... as a selective alcohol antagonist that selectively blocks the nausea. However, ondansetron doesn’t just block alcoholinduced nausea. Low doses of ethanol cause locomotor stimulation in rats (they run around more), and this response shows sensitization. This means that after repeated ethanol doses, t ...
Adrenoceptor Blocking Agents
... Non-selective blockers: Block both alpha-one and alpha-two adrenergic receptors. Alpha blockers are antagonists (they have no intrinsic activity but do produce pharmacological changes). ’ cause they block the effects of endogenous agonists (epinephrine; norepinephrine) ...
... Non-selective blockers: Block both alpha-one and alpha-two adrenergic receptors. Alpha blockers are antagonists (they have no intrinsic activity but do produce pharmacological changes). ’ cause they block the effects of endogenous agonists (epinephrine; norepinephrine) ...
Lamb Mechanisms Drug Action
... Cellular Sites of Drug Action Antibiotics inhibit bacterial but not host functions. ...
... Cellular Sites of Drug Action Antibiotics inhibit bacterial but not host functions. ...
The receptors have a long extracellular domain
... The GABA a and c receptor are members of the ligand-gated channel superfamily. By analogy to the well studied nicotinic acytocholine receptors, GABAc receptors are thought to exhibit the structure shown schematically in Fig. 2. These receptors are pentomers, i.e. five subunits constitute the funct ...
... The GABA a and c receptor are members of the ligand-gated channel superfamily. By analogy to the well studied nicotinic acytocholine receptors, GABAc receptors are thought to exhibit the structure shown schematically in Fig. 2. These receptors are pentomers, i.e. five subunits constitute the funct ...
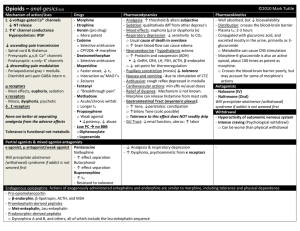
Opioids – anal-gesics (lol) ©2010 Mark Tuttle Mechanism of action
... - Sedation: qualitatively diff from other depress’s - Distribution: crosses the blood-brain barrier - Heroin (pro drug) - Mood effects: euphoria (μ) or dysphoria (κ) - Plasma t½: 2-3 hours o More potent - Respiratory depression: ↓ sensitivity to CO2 - Conjugated with glucuronic acid, and - Codeine o ...
... - Sedation: qualitatively diff from other depress’s - Distribution: crosses the blood-brain barrier - Heroin (pro drug) - Mood effects: euphoria (μ) or dysphoria (κ) - Plasma t½: 2-3 hours o More potent - Respiratory depression: ↓ sensitivity to CO2 - Conjugated with glucuronic acid, and - Codeine o ...
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 87 of
... 8. Which of the following histamine receptors (HR) triggers histamine-mediated eosinophil and mast cell chemotaxis? A. HR1 B. HR2 C. HR3 D. HR4 E. All of the above 9. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of anti-histamines? A. Irreversible antagonist B. Inverse agonist C. In ...
... 8. Which of the following histamine receptors (HR) triggers histamine-mediated eosinophil and mast cell chemotaxis? A. HR1 B. HR2 C. HR3 D. HR4 E. All of the above 9. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of anti-histamines? A. Irreversible antagonist B. Inverse agonist C. In ...
Document
... constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agoni ...
... constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agoni ...
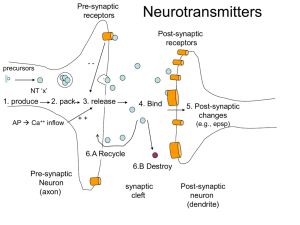
L2a.a transmitter201..
... underlies much of what we call 'brain function', and understanding how it happens has been a holy grail for neurobiologists for decades. Needless to say, no single mechanism is responsible for the many phenomena that fall within the term; however, the discovery of long-term potentation (LTP), and th ...
... underlies much of what we call 'brain function', and understanding how it happens has been a holy grail for neurobiologists for decades. Needless to say, no single mechanism is responsible for the many phenomena that fall within the term; however, the discovery of long-term potentation (LTP), and th ...
5-HT2a – receptor agonist
... • „Non-classical hallucinogens“ – no effect on 5HT2A receptors in CNS • Mechanisms of action: non-competitive NMDAreceptor antagonist (antagonizes glutamic acid – main excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS), D2receptor partial agonist • Problems of abuse: great neurotoxicity (much more than of „classic ...
... • „Non-classical hallucinogens“ – no effect on 5HT2A receptors in CNS • Mechanisms of action: non-competitive NMDAreceptor antagonist (antagonizes glutamic acid – main excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS), D2receptor partial agonist • Problems of abuse: great neurotoxicity (much more than of „classic ...
Assist professor Hayder M. Alkuraishy PROKINETIC and
... Additionally, stimulation of submucosal intrinsic afferent neurons activates secretomotor reflexes resulting in epithelial secretion. 5-HT receptors also are found on other neurons in the ENS, where they can be either stimulatory (5-HT3 and 5-HT4) or inhibitory (5-HT1a). In addition, serotonin also ...
... Additionally, stimulation of submucosal intrinsic afferent neurons activates secretomotor reflexes resulting in epithelial secretion. 5-HT receptors also are found on other neurons in the ENS, where they can be either stimulatory (5-HT3 and 5-HT4) or inhibitory (5-HT1a). In addition, serotonin also ...
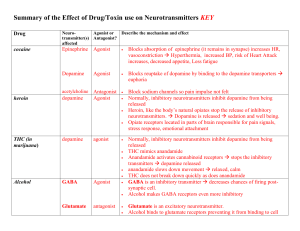
Mouse party Summary-the Effect of Drug use on Neurotransmitters
... Pass into terminal bulbs of neurons. Enter dopamine, serotonin and adrenalin vesicles causing massive release and prevents their breakdown. (transporters work in reverse) Overstimulation Euphoria, alertness, anti-fatigue. Chronic use dopamine neurons degenerate less ability to feel ...
... Pass into terminal bulbs of neurons. Enter dopamine, serotonin and adrenalin vesicles causing massive release and prevents their breakdown. (transporters work in reverse) Overstimulation Euphoria, alertness, anti-fatigue. Chronic use dopamine neurons degenerate less ability to feel ...
Brief Receptor Theory
... – A protein that binds a small molecule – A protein that binds another protein – A nucleic acid that binds a protein ...
... – A protein that binds a small molecule – A protein that binds another protein – A nucleic acid that binds a protein ...
07 Adrenoceptor-antagonist
... Pharmacokinetic Properties of the BetaReceptor Antagonists • Distribution: the β–adrenergic antagonists are rapidly distributed and have large volumes of distribution. Propranolol and penbutolol are quite lipophilic and readily BBB • Clearance: most β–adrenergic antagonists have elemination half-li ...
... Pharmacokinetic Properties of the BetaReceptor Antagonists • Distribution: the β–adrenergic antagonists are rapidly distributed and have large volumes of distribution. Propranolol and penbutolol are quite lipophilic and readily BBB • Clearance: most β–adrenergic antagonists have elemination half-li ...
Kristen Ray - USD Biology
... Influence biological and neurological processes such as aggression, anxiety, appetite, cognition, learning, and memory ...
... Influence biological and neurological processes such as aggression, anxiety, appetite, cognition, learning, and memory ...
Psychoactive drugs • Drugs which affect mental processes • May be
... striatum of: Right, control (normal) monkeys and; Left, monkeys after long-term (18-22 months) use of cocaine. Green coloring represents receptor density about half that represented by yellow. Effectively, the brains of cocaine-using monkeys have become less responsive to dopamine (after Moore et al ...
... striatum of: Right, control (normal) monkeys and; Left, monkeys after long-term (18-22 months) use of cocaine. Green coloring represents receptor density about half that represented by yellow. Effectively, the brains of cocaine-using monkeys have become less responsive to dopamine (after Moore et al ...
Pharmacology 101 (Part 3) The Grand Finale
... All functions within the body are mediated by control systems which depend on enzymes, receptors on cell walls, carrier molecules, and specific macromolecules such as DNA. Most drugs act by influencing one of these systems at a cellular level. In general, drugs act by binding to proteins. These prot ...
... All functions within the body are mediated by control systems which depend on enzymes, receptors on cell walls, carrier molecules, and specific macromolecules such as DNA. Most drugs act by influencing one of these systems at a cellular level. In general, drugs act by binding to proteins. These prot ...
CHEMICAL SIGNALLING IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... underlies much of what we call 'brain function', and understanding how it happens has been a holy grail for neurobiologists for decades. Needless to say, no single mechanism is responsible for the many phenomena that fall within the term; however, the discovery of long-term potentation (LTP), and th ...
... underlies much of what we call 'brain function', and understanding how it happens has been a holy grail for neurobiologists for decades. Needless to say, no single mechanism is responsible for the many phenomena that fall within the term; however, the discovery of long-term potentation (LTP), and th ...
Specific NT systems
... – Health: HIV, hepatitis C, overdose – Financial: loss of employment, cost of drugs – Few direct problems from chronic use (surprisingly) • (constipation, bladder cancer, pregnancy) ...
... – Health: HIV, hepatitis C, overdose – Financial: loss of employment, cost of drugs – Few direct problems from chronic use (surprisingly) • (constipation, bladder cancer, pregnancy) ...
Topics to be Covered
... • Putting a key (neurotransmitter) into a key slot (binding site on the receptor) causes a near by elevator to turn on and open it’s doors (G-protein or second messenger opens near by ion channel) and sends a message that the elevator is operating to a control center elsewhere in the building (G-pro ...
... • Putting a key (neurotransmitter) into a key slot (binding site on the receptor) causes a near by elevator to turn on and open it’s doors (G-protein or second messenger opens near by ion channel) and sends a message that the elevator is operating to a control center elsewhere in the building (G-pro ...
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist

The discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first cannabinoid receptor antagonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and it has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of cannabinoid antagonists. Cannabidiol, a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB1/2 antagonist.