Drug Action - people.vcu.edu
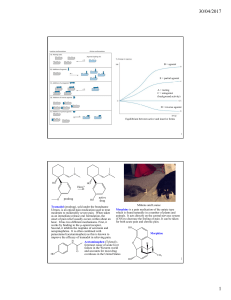
... ‘the hydrophobic effect?’ …. Lipophilicity was thought to be important ‘the medium effect?’ … generally changed conditions ‘the receptor effect?’ … Langley and Ehrlich’s hypothesis (1905) ...
... ‘the hydrophobic effect?’ …. Lipophilicity was thought to be important ‘the medium effect?’ … generally changed conditions ‘the receptor effect?’ … Langley and Ehrlich’s hypothesis (1905) ...
Alcohol antagonists - MIT OpenCourseWare
... receptors. Ethanol also binds to and activates 5-HT3 receptors. Specifically, ethanol has been shown to bind to 5-HT3A receptors, and ethanol stabilizes the open configuration of the 5-HT3 ion channel. The 5-HT3 ion channel conducts sodium ions, so it is excitatory. Ethanol and serotonin both cause ...
... receptors. Ethanol also binds to and activates 5-HT3 receptors. Specifically, ethanol has been shown to bind to 5-HT3A receptors, and ethanol stabilizes the open configuration of the 5-HT3 ion channel. The 5-HT3 ion channel conducts sodium ions, so it is excitatory. Ethanol and serotonin both cause ...
Review notes
... GAPS, GEFS, RGSs important in this regulation Main Targets: Phospholipase C, Adenylate cyclase G-Proteins: Guanine nucleotide binding proteins 2 groups: Small GTP binding Heterotrimeric G proteins ...
... GAPS, GEFS, RGSs important in this regulation Main Targets: Phospholipase C, Adenylate cyclase G-Proteins: Guanine nucleotide binding proteins 2 groups: Small GTP binding Heterotrimeric G proteins ...
ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS AS THERAPEUTIC TARGETS
... The pharmacodynamic principles that aid in the understanding of adrenergic receptors and the actions of drugs on these receptors. ...
... The pharmacodynamic principles that aid in the understanding of adrenergic receptors and the actions of drugs on these receptors. ...
Adrenergic System Adrenoceptor Blocking Drugs
... If Beta-blockers or diuretics fail to control hypertension, Prazosin or other SELECTIVE alpha1-blockers may be added. B) Secondary Hypertension: The alpha Adrenoceptor antagonists are most useful when increased blood pressure reflects excess circulating concentration of catecholamines which may resu ...
... If Beta-blockers or diuretics fail to control hypertension, Prazosin or other SELECTIVE alpha1-blockers may be added. B) Secondary Hypertension: The alpha Adrenoceptor antagonists are most useful when increased blood pressure reflects excess circulating concentration of catecholamines which may resu ...
Document
... • Synthetic: Isoproterenol, dobutamine • Structure: catechol moiety, ethylamine side chain • Inactivation: COMT, MAO; found in the gut, liver and other tissues • Low oral bioavailability, short plasma half-lives • Must be administered parenterally for systemic actions; Anaphylactic shock ...
... • Synthetic: Isoproterenol, dobutamine • Structure: catechol moiety, ethylamine side chain • Inactivation: COMT, MAO; found in the gut, liver and other tissues • Low oral bioavailability, short plasma half-lives • Must be administered parenterally for systemic actions; Anaphylactic shock ...
How? Morphine is a pain medication of the opiate type which is
... balance, electrolyte balance, and arterial blood pressure regulation. In the gut, nociceptin has been found to have varying effects on the stomach and the intestines. It also stimulates increased consumption of food. And finally, studies have © Oxford University Press, 2013 shown that nociceptin may ...
... balance, electrolyte balance, and arterial blood pressure regulation. In the gut, nociceptin has been found to have varying effects on the stomach and the intestines. It also stimulates increased consumption of food. And finally, studies have © Oxford University Press, 2013 shown that nociceptin may ...
Chemical transmission and drug action in the central nervous
... 1. Neuroleptic drugs (D receptors) antipsychotic drugs, antischizophrenic drugs Increase of dopaminergic activity in the brain is the cause of schizoprenia, 2. Antidepressive drugs – antidepressans (NA, 5HT) Depression and bipolar disorders are ...
... 1. Neuroleptic drugs (D receptors) antipsychotic drugs, antischizophrenic drugs Increase of dopaminergic activity in the brain is the cause of schizoprenia, 2. Antidepressive drugs – antidepressans (NA, 5HT) Depression and bipolar disorders are ...
to file - Planet Ross 2K2
... 1. Tyramine, methyldopa – used for hypertension (m); false neurotransmitters which are taken up by adrenergic neurons then transformed into octopamine which displaces norepinephrine form adrenergic vesicles; causes sympathetic effects if administered with MAO inhibitor (prolonging effect of norepine ...
... 1. Tyramine, methyldopa – used for hypertension (m); false neurotransmitters which are taken up by adrenergic neurons then transformed into octopamine which displaces norepinephrine form adrenergic vesicles; causes sympathetic effects if administered with MAO inhibitor (prolonging effect of norepine ...
Drug presentation 1 - EMS PROGRAMS ENTRY PAGE
... You can’t effectively push CO off of hemoglobin once its got the site ...
... You can’t effectively push CO off of hemoglobin once its got the site ...
Pharmacodynamics
... Two drugs act on different receptors or by different mechanisms, but have opposite effects on same physiological function ...
... Two drugs act on different receptors or by different mechanisms, but have opposite effects on same physiological function ...
Detection of multiple nuclear receptor–coregulator interactions in a single
... Figure 2: The modulation of 15 different nuclear receptors are shows as function of their synthetic of natural ligands across 155 coregulator proteins on the PamChip array. The modulation is the difference in binding of the ligand binding domain (LBD) of the nuclear receptor and the LBDligand comple ...
... Figure 2: The modulation of 15 different nuclear receptors are shows as function of their synthetic of natural ligands across 155 coregulator proteins on the PamChip array. The modulation is the difference in binding of the ligand binding domain (LBD) of the nuclear receptor and the LBDligand comple ...
Psych 260
... (With the exception of the last question, each question is worth 1 pt. Write your answers for the last questions directly on the quiz, and hand it in along with your scantron. Be sure to put your name on both the scantron and your quiz!) 1. ___________ refers to the process by which drugs are absorb ...
... (With the exception of the last question, each question is worth 1 pt. Write your answers for the last questions directly on the quiz, and hand it in along with your scantron. Be sure to put your name on both the scantron and your quiz!) 1. ___________ refers to the process by which drugs are absorb ...
Chapter 2 - VU Research Portal
... thymus, small intestine, colon, heart, lung, and also in the CNS. related publications has steadily increased over time. ...
... thymus, small intestine, colon, heart, lung, and also in the CNS. related publications has steadily increased over time. ...
Materials and Methods
... range of concentrations starting from clinically relevant doses to supra-clinical doses. Thus are the first 2 concentrations of iloprost and treprostinil, the first 3 concentrations of epoprostenol and the first concentration of MRE-269 comparable to what is used in the clinic. This is based on prev ...
... range of concentrations starting from clinically relevant doses to supra-clinical doses. Thus are the first 2 concentrations of iloprost and treprostinil, the first 3 concentrations of epoprostenol and the first concentration of MRE-269 comparable to what is used in the clinic. This is based on prev ...
ANTIPSYCHOTICS Objectives: After this lecture has been presented
... 1. clozapine (“Clozaril” – approved by the FDA in 1989, it seems to help those with negative antipsychotic symptoms. This drug poses a risk for agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening blood disorder. In addition, a recent retrospective study revealed cardiovascular complications such as myoc ...
... 1. clozapine (“Clozaril” – approved by the FDA in 1989, it seems to help those with negative antipsychotic symptoms. This drug poses a risk for agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening blood disorder. In addition, a recent retrospective study revealed cardiovascular complications such as myoc ...
Pharmacology 6 – SNS Antagonists
... 1. Name common examples of non-selective and selective SNS antagonists and what are they clinically used for. 2. How do SNS antagonists produce their anti-hypertensive effects and what are their side effects. 3. Compare the effects produced by selective and non-selective antagonists, name examples o ...
... 1. Name common examples of non-selective and selective SNS antagonists and what are they clinically used for. 2. How do SNS antagonists produce their anti-hypertensive effects and what are their side effects. 3. Compare the effects produced by selective and non-selective antagonists, name examples o ...
Pharmacodynamics
... Enzyme-linked receptors - Binding of the ligand to the extra cellular domain activates or inhibits the related cytosolic enzyme - The most common are the receptors that have a tyrosine kinase activity as part of their structure, in which the binding results in phosphorylation of tyrosine residues o ...
... Enzyme-linked receptors - Binding of the ligand to the extra cellular domain activates or inhibits the related cytosolic enzyme - The most common are the receptors that have a tyrosine kinase activity as part of their structure, in which the binding results in phosphorylation of tyrosine residues o ...
Sites of drug metabolism
... Drug metabolism is the term used to describe the biotransformation of pharmaceutical substances in the body so that they can be eliminated more easily. Drug metabolism often converts lipophilic chemical compound into more readily excreted polar products. ...
... Drug metabolism is the term used to describe the biotransformation of pharmaceutical substances in the body so that they can be eliminated more easily. Drug metabolism often converts lipophilic chemical compound into more readily excreted polar products. ...
Spare Receptors
... How can an agonist be “partial”? The precise mechanism is not known. We can imagine that a receptor can take two shapes: the inactive form, and an active form, in the absence, as well as the presence of bound ligand; A full agonist binds to the active form more tightly than to inactive form; while ...
... How can an agonist be “partial”? The precise mechanism is not known. We can imagine that a receptor can take two shapes: the inactive form, and an active form, in the absence, as well as the presence of bound ligand; A full agonist binds to the active form more tightly than to inactive form; while ...
ِِAntipsychotic Drugs
... • The first effective drug to be used for the treatment of schizophrenia was chlorpromazine then a wide range of drug with differing potency and side effect profile has been introduced it is better to become familiar with small range of these drugs that will cover differing situations. ...
... • The first effective drug to be used for the treatment of schizophrenia was chlorpromazine then a wide range of drug with differing potency and side effect profile has been introduced it is better to become familiar with small range of these drugs that will cover differing situations. ...
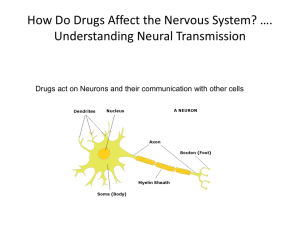
Neural Transmission - People Server at UNCW
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. • Implicated in relaxation/anti-anxiety ...
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. • Implicated in relaxation/anti-anxiety ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
... provided us with knowledge about many aspects of neural communication at the synaptic level. • Drugs either facilitate or inhibit activity at the synapse. – Antagonistic drugs block the effects of neurotransmitters (e.g., novacaine, caffeine). – Agonist drugs mimic or increase the effects of neurotr ...
... provided us with knowledge about many aspects of neural communication at the synaptic level. • Drugs either facilitate or inhibit activity at the synapse. – Antagonistic drugs block the effects of neurotransmitters (e.g., novacaine, caffeine). – Agonist drugs mimic or increase the effects of neurotr ...
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist

The discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first cannabinoid receptor antagonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and it has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of cannabinoid antagonists. Cannabidiol, a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB1/2 antagonist.