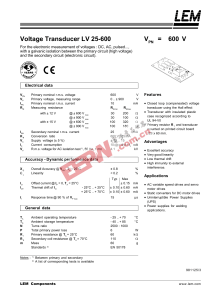
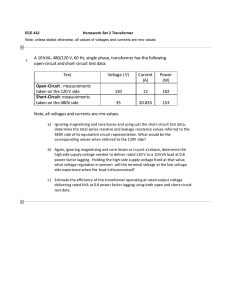
103_appendix
... duration. Resistive heating causes burns, usually on the skin at the entry points, because the skin resistance is high. Voltages greater than 240V can puncture the skin. The brain and other nervous tissue lose all functional excitability when high currents are passed through them. Also, excessive cu ...
... duration. Resistive heating causes burns, usually on the skin at the entry points, because the skin resistance is high. Voltages greater than 240V can puncture the skin. The brain and other nervous tissue lose all functional excitability when high currents are passed through them. Also, excessive cu ...
Electrical Class Handout (Primary)
... (by a larger diameter wire or by a metal bar inside the panel) and the ground wire bus (a metal bar) is further connected to a grounding conductor that connects those components to the building ground system: one or more grounding electrodes and possibly a connection to an incoming metal water pipe ...
... (by a larger diameter wire or by a metal bar inside the panel) and the ground wire bus (a metal bar) is further connected to a grounding conductor that connects those components to the building ground system: one or more grounding electrodes and possibly a connection to an incoming metal water pipe ...
Basic Circuits Notes
... Voltmeter – meter used to measure the voltage (the change in electric potential from one side of a resistor to the other or from one place in a circuit to another place in the circuit). Because you are measuring the difference in electric potential between two locations (even if it is just from ...
... Voltmeter – meter used to measure the voltage (the change in electric potential from one side of a resistor to the other or from one place in a circuit to another place in the circuit). Because you are measuring the difference in electric potential between two locations (even if it is just from ...
Introduction
... • An electric circuit is a “continues” chain of conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
... • An electric circuit is a “continues” chain of conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
Signal Buffer Board HOWTO Rev 1
... used to change the impedance of input potentiometers, as higher impedance (above 5K) can cause channel-to-channel bleedover at an A-to-D converter. The circuit can also be used to amplify pot sweep, if it is too small. Note that amplification also amplifies noise, which is undesirable in the system, ...
... used to change the impedance of input potentiometers, as higher impedance (above 5K) can cause channel-to-channel bleedover at an A-to-D converter. The circuit can also be used to amplify pot sweep, if it is too small. Note that amplification also amplifies noise, which is undesirable in the system, ...
Current Electricity
... circuit; measured in Amperes (A) Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move around the circuit; measured in Ohms (Ω) ...
... circuit; measured in Amperes (A) Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move around the circuit; measured in Ohms (Ω) ...
This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017
... FACULTY OF POWER AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Please note! This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017. Changes may occur! ...
... FACULTY OF POWER AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Please note! This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017. Changes may occur! ...
Grounding and Bonding - Peck Ormsby Construction
... Provide bonding jumpers and wire, grounding bushings, clamps and appurtenances required for complete grounding system to bond equipment and raceways to equipment grounding conductors. ...
... Provide bonding jumpers and wire, grounding bushings, clamps and appurtenances required for complete grounding system to bond equipment and raceways to equipment grounding conductors. ...
ELI `THE GREAT`
... balloon on your head and then touch someone and electrocute them. And make there hair stick up. • The forces of attraction between charged particles caused by static electricity are used in air pollution control, xerography and automobile painting. ...
... balloon on your head and then touch someone and electrocute them. And make there hair stick up. • The forces of attraction between charged particles caused by static electricity are used in air pollution control, xerography and automobile painting. ...
Resistors in Series and Parallel
... One last note… There are two types of current. DC (direct current) means it flows in one direction such as the current from a battery. AC (alternating current) means that it alternates the direction of flow. In the case of home electric circuits, they alternate at 60 Hz. As fun as it sounds AC is a ...
... One last note… There are two types of current. DC (direct current) means it flows in one direction such as the current from a battery. AC (alternating current) means that it alternates the direction of flow. In the case of home electric circuits, they alternate at 60 Hz. As fun as it sounds AC is a ...
UFC Low ProFileTM SERIES 400 Hz AND 28 VDC
... Since its beginning in 1960, Unitron has specialized in the design and development of reliable solid-state power systems. Through an innovative design, advanced self-diagnostic systems (BITE) and modular construction, Unitron products assure maximum power availability and minimal repair time. The Lo ...
... Since its beginning in 1960, Unitron has specialized in the design and development of reliable solid-state power systems. Through an innovative design, advanced self-diagnostic systems (BITE) and modular construction, Unitron products assure maximum power availability and minimal repair time. The Lo ...
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments
... circuit at all. An amplifier, for example, might equally well be assembled from several centimeter-sized components connected by pieces of solid copper wire, or from a micron-scale pattern of thin metal and semiconductor films on the surface of a silicon wafer. Details of the geometry only become im ...
... circuit at all. An amplifier, for example, might equally well be assembled from several centimeter-sized components connected by pieces of solid copper wire, or from a micron-scale pattern of thin metal and semiconductor films on the surface of a silicon wafer. Details of the geometry only become im ...
Electrical Technician Ashland_docx
... Knowledge of practices, methods, techniques, tools and equipment used in the design, manufacture, installation, testing, calibration, and repair of electrical equipment and devices common to the mining industry Must have thorough knowledge and understanding of high voltage electrical testing and saf ...
... Knowledge of practices, methods, techniques, tools and equipment used in the design, manufacture, installation, testing, calibration, and repair of electrical equipment and devices common to the mining industry Must have thorough knowledge and understanding of high voltage electrical testing and saf ...
Dettagli
... • For monitoring of 1 and 3 phase power supply network 230 V AC. • Besides voltage and current you can get value of actual active and reactive power in all phases and this information can be used for automation of connected object. For example for monitoring 1/4 hour maximum. • For permanent moni ...
... • For monitoring of 1 and 3 phase power supply network 230 V AC. • Besides voltage and current you can get value of actual active and reactive power in all phases and this information can be used for automation of connected object. For example for monitoring 1/4 hour maximum. • For permanent moni ...
Electrical Safety Talking Points
... Importance of Ground Fault Circuit Protection. How does it work? Ground Fault Circuit Protection is designed to prevent against electrical shock. The protective device most commonly used is known as a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). GFCIs are found on power tools and on GFCI electrical outl ...
... Importance of Ground Fault Circuit Protection. How does it work? Ground Fault Circuit Protection is designed to prevent against electrical shock. The protective device most commonly used is known as a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). GFCIs are found on power tools and on GFCI electrical outl ...
Schematic Diagrams - Oregon State EECS
... A schematic diagram is a concise, symbolic description of an electrical circuit. It specifies the elements that make up an electrical circuit and how they are connected. Schematic diagrams form one of the basic languages of electrical engineering. On a schematic, there may be many parts which are id ...
... A schematic diagram is a concise, symbolic description of an electrical circuit. It specifies the elements that make up an electrical circuit and how they are connected. Schematic diagrams form one of the basic languages of electrical engineering. On a schematic, there may be many parts which are id ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.