Power Point Presentation - Levine Lectronics and Lectric
... being made between two phases of the system or between one phase and an adjacent grounded metal surface. Because they are low resistance, high current events, this type of fault may actually be less destructive because the energy is spread over a large area and the protective devices are activated v ...
... being made between two phases of the system or between one phase and an adjacent grounded metal surface. Because they are low resistance, high current events, this type of fault may actually be less destructive because the energy is spread over a large area and the protective devices are activated v ...
DET 2 / 2 Auto Earth Tester
... Power for the instrument is supplied from a rechargeable lead acid battery which gives 5 hours of life per charge, equivalent to six hundred individual tests lasting 30 seconds each. The DET2/2 is built into a robust plastic case and has its four terminals, equipped for spade or 4 mm connectors, mou ...
... Power for the instrument is supplied from a rechargeable lead acid battery which gives 5 hours of life per charge, equivalent to six hundred individual tests lasting 30 seconds each. The DET2/2 is built into a robust plastic case and has its four terminals, equipped for spade or 4 mm connectors, mou ...
Electricity Quiz (English) - Electricity Safety And Conservation
... How many milliamps does it take (before you can’t let go)? _____________ ...
... How many milliamps does it take (before you can’t let go)? _____________ ...
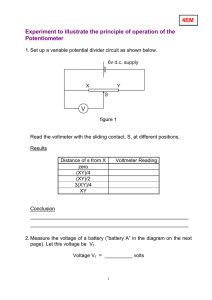
V Experiment to illustrate the principle of operation of the Potentiometer 4EM
... b) Move S to X. The bulb lights. Which supply is lighting the bulb, battery A or the 6v supply ? ____________________ c) Move S to Y. The bulb lights. Which supply is now lighting the bulb ? ____________________ ...
... b) Move S to X. The bulb lights. Which supply is lighting the bulb, battery A or the 6v supply ? ____________________ c) Move S to Y. The bulb lights. Which supply is now lighting the bulb ? ____________________ ...
BASIC ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
... resistance. Almost all thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) which means their resistance decreases as their temperature increases. It is possible to make thermistors with a positive temperature coefficient (resistance increases as temperature increases) but these are rarely used ...
... resistance. Almost all thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) which means their resistance decreases as their temperature increases. It is possible to make thermistors with a positive temperature coefficient (resistance increases as temperature increases) but these are rarely used ...
geiger counter schematic
... circuit uses a 1:1 telephone isolation transformer typically used in modems. The voltage is determined by the string of devices including the neon bulbs. Select a combination of neon lamps, varistors or zeners to achieve the desired voltage. Zeners are available at high voltages but neon lamps are p ...
... circuit uses a 1:1 telephone isolation transformer typically used in modems. The voltage is determined by the string of devices including the neon bulbs. Select a combination of neon lamps, varistors or zeners to achieve the desired voltage. Zeners are available at high voltages but neon lamps are p ...
A Solid State Replacement for the 62 set dynamotor
... There was a young man called Wyatt, Whose voice was remarkably quiet, Then, one day it faded away…………… ...
... There was a young man called Wyatt, Whose voice was remarkably quiet, Then, one day it faded away…………… ...
10. Full 2911k
... 3. Electrical equipment fastened in place must be grounded if it is within 8 feet vertical distance or 5 feet horizontal distance of a grounded surface. Noncurrent carrying metal parts in contact with electrical equipment, likely to become energized, or when subject to contact by persons must be gro ...
... 3. Electrical equipment fastened in place must be grounded if it is within 8 feet vertical distance or 5 feet horizontal distance of a grounded surface. Noncurrent carrying metal parts in contact with electrical equipment, likely to become energized, or when subject to contact by persons must be gro ...
RA6LSA INST - ConTech Lighting
... • Read all the instructions before installation. Save instructions for later use. • Turn off power at fuse or circuit breaker box before installation or before doing any maintenance work. • Product must be grounded to avoid potential electric shock and any other potential hazards. • Product must be ...
... • Read all the instructions before installation. Save instructions for later use. • Turn off power at fuse or circuit breaker box before installation or before doing any maintenance work. • Product must be grounded to avoid potential electric shock and any other potential hazards. • Product must be ...
GLOSSARY ON POWER
... A wire or combination of wires not insulated from one another, suitable for carrying electric current. ...
... A wire or combination of wires not insulated from one another, suitable for carrying electric current. ...
Document
... False triggering of phase controllers and power factor correction logic Can cause compensation capacitors to overheat ...
... False triggering of phase controllers and power factor correction logic Can cause compensation capacitors to overheat ...
Guidance On Electrical Installation Practices To Reduce EMF From
... installation. The connection of the main earthing conductor to the mass of earth is by means of an earth electrode, usually in conjunction with a metallic water pipe and other parts of the building structure. The neutral return current from the installation is primarily intended to flow back to the ...
... installation. The connection of the main earthing conductor to the mass of earth is by means of an earth electrode, usually in conjunction with a metallic water pipe and other parts of the building structure. The neutral return current from the installation is primarily intended to flow back to the ...
04.AnalyzingSeriesCircuitsWNotes
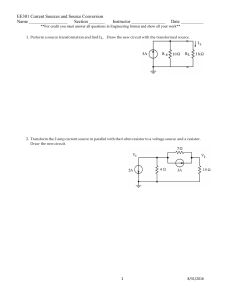
... supply. Draw a schematic diagram for the circuit and complete the chart calculations. ...
... supply. Draw a schematic diagram for the circuit and complete the chart calculations. ...
ELECTRICITY Section 1 - Introduction
... separate radiators for cooling the large quantities of oil. When the warm oil has risen to the top of the tank, it flows down the radiator and the cool oil is then returned to the bottom of the tank. Pumps are sometimes used to assist oil circulation and forced ventilation through the radiators may ...
... separate radiators for cooling the large quantities of oil. When the warm oil has risen to the top of the tank, it flows down the radiator and the cool oil is then returned to the bottom of the tank. Pumps are sometimes used to assist oil circulation and forced ventilation through the radiators may ...
SS320-A - Kenick
... The SS320A meter base surge protector is your first line of defense against incoming transient surges attempting to enter a home. It has a low profile design and can be installed on up to Class 320 (320 amp) residential and commercial single phase meter enclosures. ...
... The SS320A meter base surge protector is your first line of defense against incoming transient surges attempting to enter a home. It has a low profile design and can be installed on up to Class 320 (320 amp) residential and commercial single phase meter enclosures. ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.