B37EA - EPS School Projects - Heriot
... Energy, power, charge, voltage, current and resistance. Calculation of voltage multipliers and current shunts to extend meter operating range. Conductors moving in a magnetic field, force exerted and e.m.f. induced. Introduction to feedback control systems. Illustration of the various roles of engin ...
... Energy, power, charge, voltage, current and resistance. Calculation of voltage multipliers and current shunts to extend meter operating range. Conductors moving in a magnetic field, force exerted and e.m.f. induced. Introduction to feedback control systems. Illustration of the various roles of engin ...
IA = Ica - Engineering.com
... •For simplicity, assume initial currents are in phase with voltage (primarily resistive) •For simplicity, assume currents associated with high-side non-faulted leg are unchanged by the fault •Assume curent associated with high side faulted leg increase in magnitude and rotate toward the lagging dire ...
... •For simplicity, assume initial currents are in phase with voltage (primarily resistive) •For simplicity, assume currents associated with high-side non-faulted leg are unchanged by the fault •Assume curent associated with high side faulted leg increase in magnitude and rotate toward the lagging dire ...
NEPTUNE Power Low Voltage Circuit - APL-UW Website
... • Controller would have maximum current setting from Observatory Control System • Over-current trip point can vary – lights or pump may turn on in response to an event • Controller monitors current and opens switch if overcurrent trip point exceeded ...
... • Controller would have maximum current setting from Observatory Control System • Over-current trip point can vary – lights or pump may turn on in response to an event • Controller monitors current and opens switch if overcurrent trip point exceeded ...
16.3 Ohm`s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
... Typical sources of potential difference are batteries (which are just two or more cells connected together), and power supplies (electron pumps). In drawing a cell or battery on a circuit schematic, remember that the longer side of the symbol is the positive terminal. ...
... Typical sources of potential difference are batteries (which are just two or more cells connected together), and power supplies (electron pumps). In drawing a cell or battery on a circuit schematic, remember that the longer side of the symbol is the positive terminal. ...
AmpStrike-project-description - Electronics-Lab
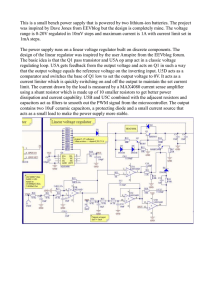
... The power supply runs on a linear voltage regulator built on discrete components. The design of the linear regulator was inspired by the user Amspire from the EEVblog forum. The basic idea is that the Q1 pass transistor and U5A op amp act in a classic voltage regulating loop. U5A gets feedback from ...
... The power supply runs on a linear voltage regulator built on discrete components. The design of the linear regulator was inspired by the user Amspire from the EEVblog forum. The basic idea is that the Q1 pass transistor and U5A op amp act in a classic voltage regulating loop. U5A gets feedback from ...
LSC-7D - Alltec
... The LSC-7D requires a 0.5 μH inductance shunt (approximately 8.0 ft conductor length) to count nature’s smallest lightning strike (3 kA). This inductance can be in the form of a wire length, tower, or pipe segment. To calculate, use the following approximations: • 0.3 μH per foot per wire • 0.067 ...
... The LSC-7D requires a 0.5 μH inductance shunt (approximately 8.0 ft conductor length) to count nature’s smallest lightning strike (3 kA). This inductance can be in the form of a wire length, tower, or pipe segment. To calculate, use the following approximations: • 0.3 μH per foot per wire • 0.067 ...
Student Handout: Project #2 Basic Electricity
... the volts, amps, power, etc. (List or Table) LIST OF ELECTRICAL REFITTINGS NEEDED: tell what needs to be done to be able to use the above items. (Table) can be done in Excel with auto calculations COSTS: In this section you explain what the cost of each expense is and how the overall amount fits wit ...
... the volts, amps, power, etc. (List or Table) LIST OF ELECTRICAL REFITTINGS NEEDED: tell what needs to be done to be able to use the above items. (Table) can be done in Excel with auto calculations COSTS: In this section you explain what the cost of each expense is and how the overall amount fits wit ...
Electrical engineering
... No. 3 Basic Electronics Laboratory a. Identification of different types of resistors, capacitors and tolls used in electronic workshop, study of colour code. b. Identification of different types of transformers, chockes, coils, switches, fues, connectors, PCB, etc. c. Identification of circuit eleme ...
... No. 3 Basic Electronics Laboratory a. Identification of different types of resistors, capacitors and tolls used in electronic workshop, study of colour code. b. Identification of different types of transformers, chockes, coils, switches, fues, connectors, PCB, etc. c. Identification of circuit eleme ...
Electrical Check Machine (ECM) of the defrosting circuit
... 5. Wire continuity After the over voltage is performed, the continuity of up to four wire circuits can be measured. A high sensitivity no contact magnetic probe is used to perform the test while the circuit is powered. The system is able to perform the test from 1 to 4 different equipotential circui ...
... 5. Wire continuity After the over voltage is performed, the continuity of up to four wire circuits can be measured. A high sensitivity no contact magnetic probe is used to perform the test while the circuit is powered. The system is able to perform the test from 1 to 4 different equipotential circui ...
Nissan Pulsar, Sentra, and 310`s with E15, E16 and E16I engines
... 1. Start engine and let engine idle. Turn all accessories off. 2. Place a voltmeter across the battery terminals. 3. While watching voltmeter disconnect fuse in the fuse box one at a time. When the voltage increases to 14v , you've found the circuit with the excessive current demand. 4. If voltage i ...
... 1. Start engine and let engine idle. Turn all accessories off. 2. Place a voltmeter across the battery terminals. 3. While watching voltmeter disconnect fuse in the fuse box one at a time. When the voltage increases to 14v , you've found the circuit with the excessive current demand. 4. If voltage i ...
Single Line Diagram Symbols
... Rarely used to directly control significant power (more than a watt), since the power dissipated in the potentiometer would be comparable to the power in the controlled load. o ...
... Rarely used to directly control significant power (more than a watt), since the power dissipated in the potentiometer would be comparable to the power in the controlled load. o ...
Two low power LED flashers
... experiments and gadgets. For examples see the experiments below: shake-a-gen rectifier and storage device sea water battery Although they are cheap and available there seem to be so many different types how do you know which one to use? The purpose of this little article is to compare a number of co ...
... experiments and gadgets. For examples see the experiments below: shake-a-gen rectifier and storage device sea water battery Although they are cheap and available there seem to be so many different types how do you know which one to use? The purpose of this little article is to compare a number of co ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... NOTE: Since voltage is measured from one point to another, we usually assign the negative terminal of a battery to be zero volts (0 V). ...
... NOTE: Since voltage is measured from one point to another, we usually assign the negative terminal of a battery to be zero volts (0 V). ...
ICL7106/7107
... The ICL7106 and ICL7107 are high performance,low power 3 1 / 2 digit A/D converters. Included are seven segment decoders, display drivers, a reference, and a clock. The ICL7106 is designed to interface with a liquid crystal display (LCD) and includes a multiplexed backplane drive, the ICL7107 will d ...
... The ICL7106 and ICL7107 are high performance,low power 3 1 / 2 digit A/D converters. Included are seven segment decoders, display drivers, a reference, and a clock. The ICL7106 is designed to interface with a liquid crystal display (LCD) and includes a multiplexed backplane drive, the ICL7107 will d ...
Microshock. - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... In areas where this happens (ICU’s CCU’s Cardiac Angio Labs etc) Extra bonding cables are used reduce the risk of Microshock. These are long green cables attached to the normal mains leads and they are plugged into special connectors. ...
... In areas where this happens (ICU’s CCU’s Cardiac Angio Labs etc) Extra bonding cables are used reduce the risk of Microshock. These are long green cables attached to the normal mains leads and they are plugged into special connectors. ...
M.Tech in Electrical 2nd semester
... Lines: Nominal-T Method, Nominal Method, Phasor Diagrams for Tnd Circuits , Dr. Steinmetz’ Split Capacitor, Method for Medium Transmission Lines, Long Transmission Lines, PhaseModifier for Voltage Control of Transmission System, Equivalent Circuits for Long Lines, Charts for Transmission Lines, G ...
... Lines: Nominal-T Method, Nominal Method, Phasor Diagrams for Tnd Circuits , Dr. Steinmetz’ Split Capacitor, Method for Medium Transmission Lines, Long Transmission Lines, PhaseModifier for Voltage Control of Transmission System, Equivalent Circuits for Long Lines, Charts for Transmission Lines, G ...
What is a Kelvin connection and when should it be
... current (R = E/I). Thus, we should be able to determine the resistance of the subject component if we measure the current going through it and the voltage dropped across it: ...
... current (R = E/I). Thus, we should be able to determine the resistance of the subject component if we measure the current going through it and the voltage dropped across it: ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.