Installation Requirements for Conformance to Standards
... Locally applicable grounding safety regulations and machinery directives shall be followed for providing a protective ground to earth. In addition, the following safety guidelines should be followed: 1. Ground conductors shall be as short and as large in size as possible. The conductors must always ...
... Locally applicable grounding safety regulations and machinery directives shall be followed for providing a protective ground to earth. In addition, the following safety guidelines should be followed: 1. Ground conductors shall be as short and as large in size as possible. The conductors must always ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws: Voltage and Current in Circuits
... Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in simple circuits. Many circuits are more complex and cannot be solved with Ohm’s Law. These circuits have many power sources and branches which would make the use of Ohm’s Law impractical or impossible. In 1857 the Germa ...
... Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in simple circuits. Many circuits are more complex and cannot be solved with Ohm’s Law. These circuits have many power sources and branches which would make the use of Ohm’s Law impractical or impossible. In 1857 the Germa ...
AC Current transducer AP
... The electric measuring transducer may only be installed and put into operation by qualified personnel that have received an appropriate training. The corresponding national regulations shall be observed during installation and operation of the transducer and any electrical conductor. The transducer ...
... The electric measuring transducer may only be installed and put into operation by qualified personnel that have received an appropriate training. The corresponding national regulations shall be observed during installation and operation of the transducer and any electrical conductor. The transducer ...
Electricity Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated
... Alternating current thus pulses back and forth within a conductor without the charge moving any net distance over time. The time-averaged value of an alternating current is zero, but it delivers energy in first one direction, and then the reverse. Alternating current is affected by electrical proper ...
... Alternating current thus pulses back and forth within a conductor without the charge moving any net distance over time. The time-averaged value of an alternating current is zero, but it delivers energy in first one direction, and then the reverse. Alternating current is affected by electrical proper ...
IMT4
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
Series_Parallel_Connection_on_GS_1
... In case of parallel connection of voltage source, one source is overload for the other one. (supposed to internal impedance of voltage source ≒0 Ω) The output current I1 and I2 are balanced each other, or either of them reach to the current limiter value and the other compensates for balancing. Ther ...
... In case of parallel connection of voltage source, one source is overload for the other one. (supposed to internal impedance of voltage source ≒0 Ω) The output current I1 and I2 are balanced each other, or either of them reach to the current limiter value and the other compensates for balancing. Ther ...
BASIC DEFINITIONS SERIES CIRCUIT PARALLEL CIRCUIT
... NOTE You cannot isolate a bulb in this type of circuit i.e. If one bulb blows, all the lights will go out (think Christmas lights....). This circuit is only useful for connecting a very small number of bulbs. ...
... NOTE You cannot isolate a bulb in this type of circuit i.e. If one bulb blows, all the lights will go out (think Christmas lights....). This circuit is only useful for connecting a very small number of bulbs. ...
Lab 4 Common Base Characteristics of a BJT Transistor
... still be in forward active region until the forward bias exceeds 200-300 mV as indicated in Fig. 4-3. Later current should fall to zero. f) Repeat the procedure e) for different values of IE (vary IE from 2-10mA in steps of 2mA). g) Finally Plot the V-I characteristics with IC on Y-axis and VCB on X ...
... still be in forward active region until the forward bias exceeds 200-300 mV as indicated in Fig. 4-3. Later current should fall to zero. f) Repeat the procedure e) for different values of IE (vary IE from 2-10mA in steps of 2mA). g) Finally Plot the V-I characteristics with IC on Y-axis and VCB on X ...
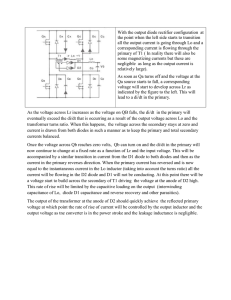
With the output diode rectifier configuration at the point when the left
... Once the voltage across Qb reaches zero volts, Qb can turn on and the di/dt in the primary will now continue to change at a fixed rate as a function of Lr and the input voltage. This will be accompanied by a similar transition in current from the D1 diode to both diodes and then as the current in th ...
... Once the voltage across Qb reaches zero volts, Qb can turn on and the di/dt in the primary will now continue to change at a fixed rate as a function of Lr and the input voltage. This will be accompanied by a similar transition in current from the D1 diode to both diodes and then as the current in th ...
The Exact Equivalent Circuit of a Transformer
... complex, nonlinear function of the voltage applied to the transformer. 4. Leakage flux. The fluxes which escape the core and pass through only one of the transformer windings are leakage fluxes. These escaped fluxes produce a self-inductance in the primary and secondary coils, and the effects of thi ...
... complex, nonlinear function of the voltage applied to the transformer. 4. Leakage flux. The fluxes which escape the core and pass through only one of the transformer windings are leakage fluxes. These escaped fluxes produce a self-inductance in the primary and secondary coils, and the effects of thi ...
Specialists in distribution grids with photovoltaic systems
... solutions to achieve more flexible and higher performing grids. The Magnetic Stepless Self-regulating Distribution Transformer (MDT) replace the existing sub-station transformers to counter the problems of voltage rise on LV networks which include power from Photo Voltaic or other distributed genera ...
... solutions to achieve more flexible and higher performing grids. The Magnetic Stepless Self-regulating Distribution Transformer (MDT) replace the existing sub-station transformers to counter the problems of voltage rise on LV networks which include power from Photo Voltaic or other distributed genera ...
3M™ TufQUIN TFT 2-2-2 Triplex Electrical Insulation Paper
... 3M™TufQUIN TFT Triplex Electrical Insulation Paper is TufQUIN Hybrid Insulating Paper bonded to both sides of polyester (PET) film. TufQUIN TFT Paper is qualified for use as major ground insulation in electrical insulation systems rated through Class 200(N) per UL 1446 and IEC Std. 61857. It is suit ...
... 3M™TufQUIN TFT Triplex Electrical Insulation Paper is TufQUIN Hybrid Insulating Paper bonded to both sides of polyester (PET) film. TufQUIN TFT Paper is qualified for use as major ground insulation in electrical insulation systems rated through Class 200(N) per UL 1446 and IEC Std. 61857. It is suit ...
Introduction
... 14.5 Premises GroundFault Current Path Single Point Neutral Bond. Metal parts of premises wiring must be bonded to a low-impedance path designed so that the circuit protection device will quickly open and clear a ground fault. Fig 14–5 ...
... 14.5 Premises GroundFault Current Path Single Point Neutral Bond. Metal parts of premises wiring must be bonded to a low-impedance path designed so that the circuit protection device will quickly open and clear a ground fault. Fig 14–5 ...
Investigating Electrical Energy
... last longer because less energy is needed from each battery! ...
... last longer because less energy is needed from each battery! ...
mmic amplifier biasing procedure
... this would typically be –1Volt. Note that “increasing the gate voltage” in this case causes a more negative voltage on the gate of the amplifier due to the way the gate power supply is connected to the amplifier. There is no “drain current” since the drain power supply is currently set to zero volts ...
... this would typically be –1Volt. Note that “increasing the gate voltage” in this case causes a more negative voltage on the gate of the amplifier due to the way the gate power supply is connected to the amplifier. There is no “drain current” since the drain power supply is currently set to zero volts ...
Circuits
... • Charges will not flow without this potential difference, which provides the “electric pressure” to move the electric field ...
... • Charges will not flow without this potential difference, which provides the “electric pressure” to move the electric field ...
Principles of Electrical Grounding
... steel column. In Figure 11 we again have the motor failure. This time we have Safe Sally. The short circuit current is conducted away through the low impedance path. In this figure we illustrate another problem that of a high impedance connection between the building steel and the power ground. Sall ...
... steel column. In Figure 11 we again have the motor failure. This time we have Safe Sally. The short circuit current is conducted away through the low impedance path. In this figure we illustrate another problem that of a high impedance connection between the building steel and the power ground. Sall ...
Xilinx Design Hints and Issues
... #20, pages 42-43). Low-impedance ceramic decoupling capacitors are required to supply dynamically changing Icc inside the chip, and to provide a return path for external current changes. In CMOS systems, all power is dynamic. The instantaneous current peaks are much higher than the average dc curren ...
... #20, pages 42-43). Low-impedance ceramic decoupling capacitors are required to supply dynamically changing Icc inside the chip, and to provide a return path for external current changes. In CMOS systems, all power is dynamic. The instantaneous current peaks are much higher than the average dc curren ...
Low voltage high resistance grounding systems
... secondary leads shall first be connected to front accessible shortcircuiting terminal blocks before connecting to any other device. Shorting screws with provisions for storage shall be provided. All groups of control wires shall be provided with terminal blocks with suitably numbered strips. Provide ...
... secondary leads shall first be connected to front accessible shortcircuiting terminal blocks before connecting to any other device. Shorting screws with provisions for storage shall be provided. All groups of control wires shall be provided with terminal blocks with suitably numbered strips. Provide ...
CONDUCTOR MATERIAL
... conductive, but due to cost it is not practical except as a thin plating to mitigate skin effect losses at high frequencies. Because of its ease of connection by soldering or clamping, copper is still the most common choice for most light-gauge wires. Compared to copper, aluminium has worse conducti ...
... conductive, but due to cost it is not practical except as a thin plating to mitigate skin effect losses at high frequencies. Because of its ease of connection by soldering or clamping, copper is still the most common choice for most light-gauge wires. Compared to copper, aluminium has worse conducti ...
Oscilloscope Tutorial
... • Proper grounding is an important step when setting up to take measurements. • Properly grounding the oscilloscope protects you from a hazardous shock and protects your circuits from damage. • Grounding the oscilloscope is necessary for safety. If a high voltage contacts the case of an ungrounded o ...
... • Proper grounding is an important step when setting up to take measurements. • Properly grounding the oscilloscope protects you from a hazardous shock and protects your circuits from damage. • Grounding the oscilloscope is necessary for safety. If a high voltage contacts the case of an ungrounded o ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.