An algebraic approach to Arabic sentence structure (2003).
... non-European (and non-Indo-European) language. As it turned out, for the fragment of Arabic we investigated, only a small part of the algebraic machinery of pregroups was needed, which we will briefly summarize. The main idea is to attach to each word, sometimes also to morphemes, one or more types. ...
... non-European (and non-Indo-European) language. As it turned out, for the fragment of Arabic we investigated, only a small part of the algebraic machinery of pregroups was needed, which we will briefly summarize. The main idea is to attach to each word, sometimes also to morphemes, one or more types. ...
Conjugating –ar verbs
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
Conjugating –ar verbs
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
File
... drama, science fiction and mystery. This was first said by Shakespeare: “To thine own self be true.” ...
... drama, science fiction and mystery. This was first said by Shakespeare: “To thine own self be true.” ...
English for IT specialists
... Her computer is cheaper than his computer. His computer is more expensive than hers. Notes the difference between the two examples (his computer) and (hers). One should add (–er) to short words of one syllable. ...
... Her computer is cheaper than his computer. His computer is more expensive than hers. Notes the difference between the two examples (his computer) and (hers). One should add (–er) to short words of one syllable. ...
spag glossary - St Margaret`s Lee Primary School
... A clause is a group of words which does contain a verb; it is part of a sentence. There are two kinds of clauses: 1. A main clause (makes sense on its own) e.g.: Sue bought a ...
... A clause is a group of words which does contain a verb; it is part of a sentence. There are two kinds of clauses: 1. A main clause (makes sense on its own) e.g.: Sue bought a ...
File
... sentence, the form of the verb changes, depending on the subject used. This is called a conjugation . Ex: I walk. Je marche. ...
... sentence, the form of the verb changes, depending on the subject used. This is called a conjugation . Ex: I walk. Je marche. ...
Chapter 7 Reference Sheet
... Case-endings are the letters we put on the end of a noun or adjective in order to indicate what it is doing in the sentence, and how it relates to the other words in the sentence. We have only learned two of these so far: Nominative: if a noun or adjective is in the Nominative case, then we know tha ...
... Case-endings are the letters we put on the end of a noun or adjective in order to indicate what it is doing in the sentence, and how it relates to the other words in the sentence. We have only learned two of these so far: Nominative: if a noun or adjective is in the Nominative case, then we know tha ...
Parts of speech
... • To find the subject of a sentence, first find the complete verb of the sentence. • Then ask, “Who or what is doing _______ (whatever the main verb is)? • A sentence may contain more than one subject and more than one verb. ...
... • To find the subject of a sentence, first find the complete verb of the sentence. • Then ask, “Who or what is doing _______ (whatever the main verb is)? • A sentence may contain more than one subject and more than one verb. ...
File - American Studies Radboud University
... NP inside a prepositional object = when the preceding verb + particle is a prepositional verb or an ordinary intransitive verb. NP after a phrasal verb makes it a direct object. Passive verbs the woman is being eaten by the bear. * not passive: The bear eats the woman. Transitive verbs are needed ...
... NP inside a prepositional object = when the preceding verb + particle is a prepositional verb or an ordinary intransitive verb. NP after a phrasal verb makes it a direct object. Passive verbs the woman is being eaten by the bear. * not passive: The bear eats the woman. Transitive verbs are needed ...
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
Name: Period: Date:
... I throw the eraser to Ben. (Why is Ben no longer an IO?) addition of the word “to” 15. Predicate Noun (PN) - always follows LV; noun/pronoun which renames the subject EX. I am a teacher in the classroom. (Is the verb action/linking?) LV (Replacement/flip-flop) ...
... I throw the eraser to Ben. (Why is Ben no longer an IO?) addition of the word “to” 15. Predicate Noun (PN) - always follows LV; noun/pronoun which renames the subject EX. I am a teacher in the classroom. (Is the verb action/linking?) LV (Replacement/flip-flop) ...
Grammatical Feature: Definition: Example:
... A clause is a group of words which does contain a verb; it is part of a sentence. There are two kinds of clauses: 1. A main clause (makes sense on its own) e.g.: Sue bought a ...
... A clause is a group of words which does contain a verb; it is part of a sentence. There are two kinds of clauses: 1. A main clause (makes sense on its own) e.g.: Sue bought a ...
Guide to Quiz 2 1. Saber vs. conocer: Although "saber" and "conocer
... 1. Saber vs. conocer: Although "saber" and "conocer" mean the same in English, they are used in different situations in Spanish. What criteria do we use to make this distinction (1)? Do these verbs have any irregular forms? 2. Los verbos reflexivos: What is a reflexive verb? What are the reflexive p ...
... 1. Saber vs. conocer: Although "saber" and "conocer" mean the same in English, they are used in different situations in Spanish. What criteria do we use to make this distinction (1)? Do these verbs have any irregular forms? 2. Los verbos reflexivos: What is a reflexive verb? What are the reflexive p ...
Nouns Verbs
... • The main problem with definitions like these is that they are based on semantic criteria. The theft of our property caused us to question the honesty of our neighbors. A theft is not a person, place, or thing. It’s an action. By semantic criteria, this word should be a verb. But it’s not – ‘theft’ ...
... • The main problem with definitions like these is that they are based on semantic criteria. The theft of our property caused us to question the honesty of our neighbors. A theft is not a person, place, or thing. It’s an action. By semantic criteria, this word should be a verb. But it’s not – ‘theft’ ...
Useful First-Conjugation Verbs Ending in
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
Grade 8 English Language Arts Exam Review
... 3. Pronouns can show ownership or possession. Look at these possessive pronouns: his CD, her calculator, their clothes, its engine. Rewrite these phrases using possessive pronouns. Jake's carton: ...
... 3. Pronouns can show ownership or possession. Look at these possessive pronouns: his CD, her calculator, their clothes, its engine. Rewrite these phrases using possessive pronouns. Jake's carton: ...
Chapter 10: Subject-Verb Agreement
... List of prepositions are linked to wordpress Less easily recognized prepositions are: except, but, like, and between ...
... List of prepositions are linked to wordpress Less easily recognized prepositions are: except, but, like, and between ...
Nouns, Articles, Adjectives and Definitions
... Nouns are normally accompanied by a corresponding article (el/la/los/las). These articles can be used as a guideline to determine whether a noun is masculine or feminine, especially in the case of some words that are derived from languages other than Latin and their gender may be unclear. Not all no ...
... Nouns are normally accompanied by a corresponding article (el/la/los/las). These articles can be used as a guideline to determine whether a noun is masculine or feminine, especially in the case of some words that are derived from languages other than Latin and their gender may be unclear. Not all no ...
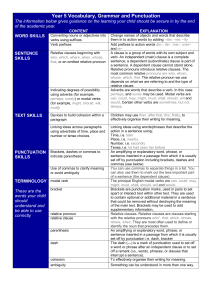
READING Read text – UP to 420 WRITING Plan, Draft, Revise, Edit
... Follow rules for discussions Responding to the comments of other Ask and answer questions with purpose. Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. Read silently and orally accurately and fluently with expression to comprehend ...
... Follow rules for discussions Responding to the comments of other Ask and answer questions with purpose. Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. Read silently and orally accurately and fluently with expression to comprehend ...
Nominative Case is also used for
... Nominative and Accusative Case Accusative Case is used for: Direct Object – the person/thing that receives the verb’s action directly. In other words, the “receiver,” or the person/thing acted upon by the subject. NOTE: When a preposition (e.g. “to, for”) separates the verb from the word receiving ...
... Nominative and Accusative Case Accusative Case is used for: Direct Object – the person/thing that receives the verb’s action directly. In other words, the “receiver,” or the person/thing acted upon by the subject. NOTE: When a preposition (e.g. “to, for”) separates the verb from the word receiving ...
document
... difficult to explain. To say that case refers to a system of endings for nouns that reveal a noun’s function in a sentence is a bit bland, but the way to do it. In modern English, we are left only with one case for nouns and three cases for pronouns. The one surviving case is genitive, which shows p ...
... difficult to explain. To say that case refers to a system of endings for nouns that reveal a noun’s function in a sentence is a bit bland, but the way to do it. In modern English, we are left only with one case for nouns and three cases for pronouns. The one surviving case is genitive, which shows p ...