parts_of_speech-part1_grade_9 - Al
... Instead of nouns the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How things are done the adverbs tell, As slowly, quickly, ill, or well. ...
... Instead of nouns the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How things are done the adverbs tell, As slowly, quickly, ill, or well. ...
World Englishes_Strand4
... was not the language spoken by most of the population. It is used for a range of functions among those who speak or write it in the region where it is used. It has become ‘localised’ or ‘nativised’ by adopting some language features of its own (e.g., sounds, intonation patterns, ...
... was not the language spoken by most of the population. It is used for a range of functions among those who speak or write it in the region where it is used. It has become ‘localised’ or ‘nativised’ by adopting some language features of its own (e.g., sounds, intonation patterns, ...
Grammar Hammer - SchoolNotes.com
... To test which form of the pronoun is correct, use it without the noun or pronoun it is paired with: Bad swing: The senator’s use of the double negative surprised my students and I. Test: The senator…surprised I. The senator…surprised me. Direct Hit: The senator’s use of the double negative surprised ...
... To test which form of the pronoun is correct, use it without the noun or pronoun it is paired with: Bad swing: The senator’s use of the double negative surprised my students and I. Test: The senator…surprised I. The senator…surprised me. Direct Hit: The senator’s use of the double negative surprised ...
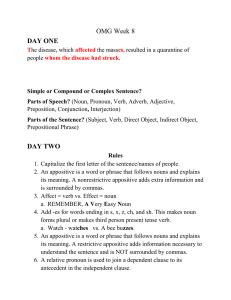
Sixth Grade OMG Week 8
... a. REMEMBER, A Very Easy Noun Add -es for words ending in s, x, z, ch, and sh. This makes noun forms plural or makes third person present tense verb. a. Watch - watches vs. A bee buzzes. An appositive is a word or phrase that follows nouns and explains its meaning. A restrictive appositive adds info ...
... a. REMEMBER, A Very Easy Noun Add -es for words ending in s, x, z, ch, and sh. This makes noun forms plural or makes third person present tense verb. a. Watch - watches vs. A bee buzzes. An appositive is a word or phrase that follows nouns and explains its meaning. A restrictive appositive adds info ...
7-PDF39-40_the history of english
... Thus, the endings -ás and -án in Spanish verb forms, such as tu comprarás 'you will buy' and ellos comprarán 'they will buy', have actually developed from ancestral Latin habe¯re 'to have' (a full verb). We will revisit this process of grammaticalization in more detail in Section 1.6 but let us now ...
... Thus, the endings -ás and -án in Spanish verb forms, such as tu comprarás 'you will buy' and ellos comprarán 'they will buy', have actually developed from ancestral Latin habe¯re 'to have' (a full verb). We will revisit this process of grammaticalization in more detail in Section 1.6 but let us now ...
Gender, Number, and Case
... In Latin, nouns have certain characteristics that help us understand their meaning in a sentence and how they relate to other words. These characteristics are gender, number, and case. There are five patterns for how these characteristics manifest themselves. Think of it like a body part. Eyes are e ...
... In Latin, nouns have certain characteristics that help us understand their meaning in a sentence and how they relate to other words. These characteristics are gender, number, and case. There are five patterns for how these characteristics manifest themselves. Think of it like a body part. Eyes are e ...
Slide 1
... Judy runs on the beach every morning. Polamalu runs like a girl. There could also be more than one subject!! Example: Judy and her dog run on the beach every morning. In German the subject takes the Nominative Case!!! ...
... Judy runs on the beach every morning. Polamalu runs like a girl. There could also be more than one subject!! Example: Judy and her dog run on the beach every morning. In German the subject takes the Nominative Case!!! ...
Verbs Nouns and Basic Sentences
... nouns or pronouns, but they can also be adjectives (and sometimes other word classes). Subject Complements give us more information about the Subject, so they refer to the same person or thing as the Subject. For example: ...
... nouns or pronouns, but they can also be adjectives (and sometimes other word classes). Subject Complements give us more information about the Subject, so they refer to the same person or thing as the Subject. For example: ...
parts_of_speech_g_8 - Al-Oruba International Schools
... Instead of nouns the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How things are done the adverbs tell, As slowly, quickly, ill, or well. ...
... Instead of nouns the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How things are done the adverbs tell, As slowly, quickly, ill, or well. ...
The Most Common Writing Errors
... Pronoun/Antecedent Agreement and Reference • Pronouns take the place of nouns (he, she, it, they, I, you) • The antecedent is the word to which the pronoun refers. For example: Mary went to the store and she bought candy. (Mary is the antecedent for the pronoun she.) ...
... Pronoun/Antecedent Agreement and Reference • Pronouns take the place of nouns (he, she, it, they, I, you) • The antecedent is the word to which the pronoun refers. For example: Mary went to the store and she bought candy. (Mary is the antecedent for the pronoun she.) ...
Finite State Automata (most slides repeated from Lecture #2) Words
... same type. • Also, woodchuck and woodchucks are two grammatical forms of the same lexeme (woodchuck). ...
... same type. • Also, woodchuck and woodchucks are two grammatical forms of the same lexeme (woodchuck). ...
Words and the Lexicon
... same type. • Also, woodchuck and woodchucks are two grammatical forms of the same lexeme (woodchuck). ...
... same type. • Also, woodchuck and woodchucks are two grammatical forms of the same lexeme (woodchuck). ...
GRAMMAR (note the spelling!)
... "fused sentence") has at least two parts, either one of which can stand by itself (in other words, two independent clauses), but the two parts have been put together instead of being properly connected. ...
... "fused sentence") has at least two parts, either one of which can stand by itself (in other words, two independent clauses), but the two parts have been put together instead of being properly connected. ...
Parts of Speech: Verbs
... • am, are, is, was, were, do, did, have, has, had can, may , will (shall) be, will (shall) have, has (had) been, can (may) be, can (may) have, could (would, should) be, could (would, should) have, will (shall) have been, might have, might have been, must, must have, must have been • The parts of a v ...
... • am, are, is, was, were, do, did, have, has, had can, may , will (shall) be, will (shall) have, has (had) been, can (may) be, can (may) have, could (would, should) be, could (would, should) have, will (shall) have been, might have, might have been, must, must have, must have been • The parts of a v ...
The verbs “lay” and “lie” are both known as irregular verbs. An
... You'll lay an egg if you don't lie down. ...
... You'll lay an egg if you don't lie down. ...
Syllabus
... Syllabus You will be following the JACT Reading Greek (CUP second edition) and Latin course books (CUP first edition). You will be provided with a copy of the textbooks for the duration of the course, but if you would like to buy your own copy to keep, then these are available to buy through Amazon. ...
... Syllabus You will be following the JACT Reading Greek (CUP second edition) and Latin course books (CUP first edition). You will be provided with a copy of the textbooks for the duration of the course, but if you would like to buy your own copy to keep, then these are available to buy through Amazon. ...
LATIN GRAMMAR NOTES
... but manus (hand) and domus (home) are feminine. There are two quite common neuter nouns: genū (knee) and cornū (horn). These have subject and direct object singular form in –ū, subject and direct object plurals in –ua, but other endings are like exercitus. Fifth declension nouns are all feminine exc ...
... but manus (hand) and domus (home) are feminine. There are two quite common neuter nouns: genū (knee) and cornū (horn). These have subject and direct object singular form in –ū, subject and direct object plurals in –ua, but other endings are like exercitus. Fifth declension nouns are all feminine exc ...
Freshman Grammar Program
... A concrete noun names an object that can be seen, heard, smelled, touched, or tasted. An abstract noun names an ideas, quality, or state. ...
... A concrete noun names an object that can be seen, heard, smelled, touched, or tasted. An abstract noun names an ideas, quality, or state. ...
Comments on Word formation in Kazym Khanty - Ob
... There are several types of composition in Kazym-Khanty. First of all, there are so-called pair nouns which generalize the meaning of its components (cf. nouns example 1). In case of declination, both components are declined. Besides, there are metaphoric words as compounds which components are phone ...
... There are several types of composition in Kazym-Khanty. First of all, there are so-called pair nouns which generalize the meaning of its components (cf. nouns example 1). In case of declination, both components are declined. Besides, there are metaphoric words as compounds which components are phone ...
English Year 5 - Tewkesbury C of E Primary
... –cial is common after a vowel letter and –tial after a consonant letter, but there are some exceptions. Exceptions: initial, financial, commercial, provincial (the spelling of the last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word wi ...
... –cial is common after a vowel letter and –tial after a consonant letter, but there are some exceptions. Exceptions: initial, financial, commercial, provincial (the spelling of the last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word wi ...
English – Year 5 – Tracker - Statutory Age Expected Requirement
... –cial is common after a vowel letter and –tial after a consonant letter, but there are some exceptions. Exceptions: initial, financial, commercial, provincial (the spelling of the last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word wi ...
... –cial is common after a vowel letter and –tial after a consonant letter, but there are some exceptions. Exceptions: initial, financial, commercial, provincial (the spelling of the last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word wi ...