
Parts of Speech - Dayton Independent Schools
... action, the verb can show state of being. Action verbs include words such as satisfied, write, or exhibit. The state of being verbs are words such as am, is, are, was, were, being, and been. Adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They answer the questions: when, where, why ...
... action, the verb can show state of being. Action verbs include words such as satisfied, write, or exhibit. The state of being verbs are words such as am, is, are, was, were, being, and been. Adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They answer the questions: when, where, why ...
English Grammar Glossary of Terms
... Intransitive verbs have no receiver of the action. They are classified as intransitive complete or intransitive linking. Example: He's been singing all day Introductory there To be an introductory there, it must meet these rules: 1) It must be the first word of a sentence (Sometimes a prepositional ...
... Intransitive verbs have no receiver of the action. They are classified as intransitive complete or intransitive linking. Example: He's been singing all day Introductory there To be an introductory there, it must meet these rules: 1) It must be the first word of a sentence (Sometimes a prepositional ...
making the sentence accessible
... However, this definition does not provide most students with a reliable way to find the verb of a sentence. First, students often don’t understand what “state of being” means, and second, “action” does not always indicate a verb: Example: Running is good exercise. Students will often pick out runnin ...
... However, this definition does not provide most students with a reliable way to find the verb of a sentence. First, students often don’t understand what “state of being” means, and second, “action” does not always indicate a verb: Example: Running is good exercise. Students will often pick out runnin ...
Exam Review - WordPress.com
... only have a spelling change in the __________________________________ for the past. Watch out for dormir! Also, focus on these irregular verbs in the past: -CAR verb in the yo form= ...
... only have a spelling change in the __________________________________ for the past. Watch out for dormir! Also, focus on these irregular verbs in the past: -CAR verb in the yo form= ...
Grammar * Unit 1 Lessons 1-17
... • If the word ends in y, look at the letter before the y –vowel Add an s ...
... • If the word ends in y, look at the letter before the y –vowel Add an s ...
English Language Introduction
... (1) The first word of every sentence begins with a capital letter. For example: The moon was full that night. (2) The first letter of every proper noun, the particular name of a person, title, begins with a capital letter. The alphabet are divided into two groups of letters: vowels and consonants. ...
... (1) The first word of every sentence begins with a capital letter. For example: The moon was full that night. (2) The first letter of every proper noun, the particular name of a person, title, begins with a capital letter. The alphabet are divided into two groups of letters: vowels and consonants. ...
AR verbs and AR verb endings - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... To talk about what you like and don’t like to do, use (no) me gusta + [infinitive(s)]. Note that the singular gusta is always used, even with more than one infinitive. ...
... To talk about what you like and don’t like to do, use (no) me gusta + [infinitive(s)]. Note that the singular gusta is always used, even with more than one infinitive. ...
A sentence base may consist of only the subject and the verb
... subject = behavior verb = was discussed ...
... subject = behavior verb = was discussed ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR SPANISH 1: UNIDAD 1:L1
... To go through customs Baggage claim Other words and phrases: Train station Tourist office Bus stop To take a taxi Can you please tell me where…is? ...
... To go through customs Baggage claim Other words and phrases: Train station Tourist office Bus stop To take a taxi Can you please tell me where…is? ...
Angleški glagol 1
... These three classes of non-finite forms serve to distinguish three classes of non-finite verbal phrases: infinitival, gerundial, and participial. The non-finite forms do not express the grammatical categories of person, number and mood, hence there is no person or number agreement between the subjec ...
... These three classes of non-finite forms serve to distinguish three classes of non-finite verbal phrases: infinitival, gerundial, and participial. The non-finite forms do not express the grammatical categories of person, number and mood, hence there is no person or number agreement between the subjec ...
Spanish Stem-Changing Verbs
... • Note: the verb “querer” is pronounced: • Quer- (“care” in English) • -er (“air” in English • Querer. Care-air. (rhymes with “Care Bear”) ...
... • Note: the verb “querer” is pronounced: • Quer- (“care” in English) • -er (“air” in English • Querer. Care-air. (rhymes with “Care Bear”) ...
The Correct Use of Pronouns
... The forms mine, yours, hers, ours and theirs functions as pronouns (that is, they may be subjects, direct objects, predicate nominatives, etc.) ...
... The forms mine, yours, hers, ours and theirs functions as pronouns (that is, they may be subjects, direct objects, predicate nominatives, etc.) ...
to Romanid grammar!
... Digraph ll represents sound l pronounced on the palate18. Its rough English equivalent is the sound cluster l+y in phrase will you. It occurs only in a few words, e.g. batalla battle, palla straw. Letter cluster ng is not a grapheme, it is pronounced always as two sounds IPA [ŋg] as in jungle (never ...
... Digraph ll represents sound l pronounced on the palate18. Its rough English equivalent is the sound cluster l+y in phrase will you. It occurs only in a few words, e.g. batalla battle, palla straw. Letter cluster ng is not a grapheme, it is pronounced always as two sounds IPA [ŋg] as in jungle (never ...
English - Appendix 2: Vocabulary, grammar and punctuation
... important, as it gives us more conscious control and choice in our language. Building this knowledge is best achieved through a focus on grammar within the teaching of reading, writing and speaking. Once pupils are familiar with a grammatical concept [for example ‘modal verb’], they should be encour ...
... important, as it gives us more conscious control and choice in our language. Building this knowledge is best achieved through a focus on grammar within the teaching of reading, writing and speaking. Once pupils are familiar with a grammatical concept [for example ‘modal verb’], they should be encour ...
Verbs with two objects Source
... I asked Peter. (Here the verb asked is followed by an indirect object.) I asked a question. (Here the verb asked is followed by a direct object.) I asked Peter a question. (Here the verb asked is followed by both a direct object and an indirect object.) Other verbs that can be used like this are: te ...
... I asked Peter. (Here the verb asked is followed by an indirect object.) I asked a question. (Here the verb asked is followed by a direct object.) I asked Peter a question. (Here the verb asked is followed by both a direct object and an indirect object.) Other verbs that can be used like this are: te ...
English Review Test Preparation
... A pronoun must agree in number with the word or words it replaces. If the word a pronoun refers to is singular, the pronoun must be singular; if the word is plural, the pronoun must be plural. The word to which a pronoun refers is its antecedent. Who and whom usually refer to human beings; which and ...
... A pronoun must agree in number with the word or words it replaces. If the word a pronoun refers to is singular, the pronoun must be singular; if the word is plural, the pronoun must be plural. The word to which a pronoun refers is its antecedent. Who and whom usually refer to human beings; which and ...
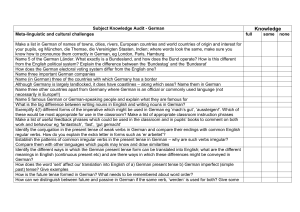
Subject Knowledge Audit German
... Which common verbs take ‘sein’ rather than ‘haben’ in their compound past tense and why? What is the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? How can pupils be helped to understand? Give examples of some verbs which might be able to form their past tense with both haben and sein and exp ...
... Which common verbs take ‘sein’ rather than ‘haben’ in their compound past tense and why? What is the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? How can pupils be helped to understand? Give examples of some verbs which might be able to form their past tense with both haben and sein and exp ...
Pronoun Study Sheet:
... What is the largest planet in our solar system? asks a question; is a pronoun Singular Indefinite Pronouns anybody, anyone, each, either, everybody, everyone, neither, nobody, no one, one, somebody, someone Pronouns like each and one are frequently followed by prepositional phrases. Remember that th ...
... What is the largest planet in our solar system? asks a question; is a pronoun Singular Indefinite Pronouns anybody, anyone, each, either, everybody, everyone, neither, nobody, no one, one, somebody, someone Pronouns like each and one are frequently followed by prepositional phrases. Remember that th ...
The national curriculum in England - English
... important, as it gives us more conscious control and choice in our language. Building this knowledge is best achieved through a focus on grammar within the teaching of reading, writing and speaking. Once pupils are familiar with a grammatical concept [for example ‘modal verb’], they should be encour ...
... important, as it gives us more conscious control and choice in our language. Building this knowledge is best achieved through a focus on grammar within the teaching of reading, writing and speaking. Once pupils are familiar with a grammatical concept [for example ‘modal verb’], they should be encour ...
Modifiers - NUAST Moodle
... “He pushed on and ran quickly through the rain” You can have nouns which modify nouns and verbs which modify verbs, the goal is when you look at a sentence is to spot what the main noun and main verb are, what the sentence is about, don’t worry if in a complex sentence there are more than one. ...
... “He pushed on and ran quickly through the rain” You can have nouns which modify nouns and verbs which modify verbs, the goal is when you look at a sentence is to spot what the main noun and main verb are, what the sentence is about, don’t worry if in a complex sentence there are more than one. ...
More nouns (Nominative, direct object, and indirect object)
... Most common errors: Points were deducted if you capitalized a common noun. Be INTENTIONAL about your academic writing (that’s the dif ference between normal and academic writing). Pre- AP English: “English” is a proper noun. Languages, ethnicities, and races are always capitalized (for fear of ...
... Most common errors: Points were deducted if you capitalized a common noun. Be INTENTIONAL about your academic writing (that’s the dif ference between normal and academic writing). Pre- AP English: “English” is a proper noun. Languages, ethnicities, and races are always capitalized (for fear of ...
DGP Notes 10
... everybody, anybody, more, much, another, both, any, other, etc. ADJECTIVE modifies nouns (green pen.) and pronouns (They are happy.) tells Which one? What kind? How many? ...
... everybody, anybody, more, much, another, both, any, other, etc. ADJECTIVE modifies nouns (green pen.) and pronouns (They are happy.) tells Which one? What kind? How many? ...
e-Course [1432] - Advanced Languages - Spanish II
... tense, the preterit perfect and pluperperfect tenses, the future perfect tense, the conditional perfect, the present perfect and pluperperfect subjunctive, and the perfect participle. e-Unit [14324] - Advanced Languages - Spanish II - Quarter 4: Learn to identify, pronounce, write and correctly use ...
... tense, the preterit perfect and pluperperfect tenses, the future perfect tense, the conditional perfect, the present perfect and pluperperfect subjunctive, and the perfect participle. e-Unit [14324] - Advanced Languages - Spanish II - Quarter 4: Learn to identify, pronounce, write and correctly use ...






















![e-Course [1432] - Advanced Languages - Spanish II](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009059633_1-dfe6690fd9f1cd5d8714ab3ad8a1a8fb-300x300.png)