THE NOTION OF INSTRUMENT IN MALAY LANGUAGE
... All these expressions show some constraints on the type of nouns that are used as instrument. This study has two main related goals. The first objective is to establish a semantic typology of nouns that are used as instrument for each of the five expressions of instrumentality. The second objective ...
... All these expressions show some constraints on the type of nouns that are used as instrument. This study has two main related goals. The first objective is to establish a semantic typology of nouns that are used as instrument for each of the five expressions of instrumentality. The second objective ...
Can you find the adjectives?
... Can you find the adjectives? First find the nouns and/or pronouns… ...
... Can you find the adjectives? First find the nouns and/or pronouns… ...
5. Pronoun
... A verb is used to show an action or a state of being go, write, exist, be 2. Noun A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, events, ideas and feelings. John, lion, table, freedom, love ... 3. Adjective Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun good, beautiful, ni ...
... A verb is used to show an action or a state of being go, write, exist, be 2. Noun A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, events, ideas and feelings. John, lion, table, freedom, love ... 3. Adjective Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun good, beautiful, ni ...
Direct object pronouns
... Direct object pronouns have the same gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural) as the nouns they replace. They come right before the conjugated verb. ¿Devolviste los libros a la biblioteca? No, no los ...
... Direct object pronouns have the same gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural) as the nouns they replace. They come right before the conjugated verb. ¿Devolviste los libros a la biblioteca? No, no los ...
Direct object pronouns
... Direct object pronouns have the same gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural) as the nouns they replace. They come right before the conjugated verb. ¿Devolviste los libros a la biblioteca? No, no los ...
... Direct object pronouns have the same gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural) as the nouns they replace. They come right before the conjugated verb. ¿Devolviste los libros a la biblioteca? No, no los ...
Grammar terms - St. Andrew`s and St. Mark`s
... a big dog (a phrase - this refers to ‘a big dog’ but doesn’t say what the dog did or what happened to it) a big dog chased me (a clause - the dog did something) A sentence is made up of one or more clauses: It was raining (one clause) It was raining and we were cold. (two main clauses joined by and ...
... a big dog (a phrase - this refers to ‘a big dog’ but doesn’t say what the dog did or what happened to it) a big dog chased me (a clause - the dog did something) A sentence is made up of one or more clauses: It was raining (one clause) It was raining and we were cold. (two main clauses joined by and ...
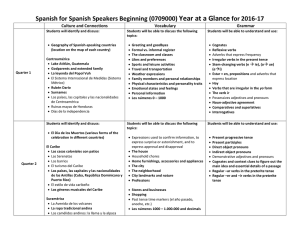
Spanish for Spanish Speakers Beginning (0709000) Year at a
... vocabulary give great opportunities to practice reading and listening using authentic texts and resources. Also, include opportunities for discussion and interpersonal speaking, as well as oral and written presentations to prepare for Pre-AP. ...
... vocabulary give great opportunities to practice reading and listening using authentic texts and resources. Also, include opportunities for discussion and interpersonal speaking, as well as oral and written presentations to prepare for Pre-AP. ...
The aims of the theoretical course of Grammar
... “substance or thingness”. It is the main nominative unit of speech. As any other part of speech, the noun can be characterised by three criteria: semantic (the meaning), morphological (the form and grammatical categories) and syntactical (functions, distribution). Semantic features of the noun. The ...
... “substance or thingness”. It is the main nominative unit of speech. As any other part of speech, the noun can be characterised by three criteria: semantic (the meaning), morphological (the form and grammatical categories) and syntactical (functions, distribution). Semantic features of the noun. The ...
Chapter 1 Subjects and Verbs
... The student ran from the parking lot to his class. (ran = physical action) Steve sits in bed and reads his book. (sits, reads = physical action) The student knew the answers to the test questions. (knew = mental action) Practice 5: Underline the physical or mental action verbs in the following sente ...
... The student ran from the parking lot to his class. (ran = physical action) Steve sits in bed and reads his book. (sits, reads = physical action) The student knew the answers to the test questions. (knew = mental action) Practice 5: Underline the physical or mental action verbs in the following sente ...
081124reg
... A phrase is a group of related words that lacks both a subject and a predicate. Because it lacks a subject and a predicate it cannot act as a sentence. A phrase typically functions as a single part of speech in a sentence (e.g., noun, adjective, adverb). There are five types of phrases: 1. Preposit ...
... A phrase is a group of related words that lacks both a subject and a predicate. Because it lacks a subject and a predicate it cannot act as a sentence. A phrase typically functions as a single part of speech in a sentence (e.g., noun, adjective, adverb). There are five types of phrases: 1. Preposit ...
PowerPoint
... The English pronouns make several distinctions over and above a singular/plural distinction. One distinction is in person, which is sensitive to who is talking and to whom. English (and most languages) distinguish three persons. first person second person third person ...
... The English pronouns make several distinctions over and above a singular/plural distinction. One distinction is in person, which is sensitive to who is talking and to whom. English (and most languages) distinguish three persons. first person second person third person ...
The Parts of a Sentence
... An object complement is similar to a subject complement, except that (obviously) it modifies an object rather than a subject. Consider this example of a subject complement: The driver seems tired. In this case, as explained above, the adjective "tired" modifies the noun "driver," which is the subjec ...
... An object complement is similar to a subject complement, except that (obviously) it modifies an object rather than a subject. Consider this example of a subject complement: The driver seems tired. In this case, as explained above, the adjective "tired" modifies the noun "driver," which is the subjec ...
CAS LX 522 Syntax I
... Gender often comes in 2-3 flavors (masculine, feminine, neuter) which often corresponds roughly to biological gender where applicable. ...
... Gender often comes in 2-3 flavors (masculine, feminine, neuter) which often corresponds roughly to biological gender where applicable. ...
Lecture 1
... a few, a little, all, another, any, both, each, either, enough, every, fewer, less, many, no, neither, other, several.... ...
... a few, a little, all, another, any, both, each, either, enough, every, fewer, less, many, no, neither, other, several.... ...
11.10 More Uses of the Infinitive Language Lesson
... You are already familiar with using the infinitive form of a verb after words like poder, saber, and querer. (Examples include: "Puedo hacerlo," "Sé nadar," and "Quiero ir.") However, did you know that sensory verbs like to hear, to see, or to feel, are also followed by an infinitive? Watch out for ...
... You are already familiar with using the infinitive form of a verb after words like poder, saber, and querer. (Examples include: "Puedo hacerlo," "Sé nadar," and "Quiero ir.") However, did you know that sensory verbs like to hear, to see, or to feel, are also followed by an infinitive? Watch out for ...
Document
... • The English word will can refer either to future time or to someone’s willingness to do something. To express willingness, Spanish uses the verb querer + [infinitive], not the future tense. ¿Quieres contribuir a la protección del medio ambiente? ...
... • The English word will can refer either to future time or to someone’s willingness to do something. To express willingness, Spanish uses the verb querer + [infinitive], not the future tense. ¿Quieres contribuir a la protección del medio ambiente? ...
I, he, she - beverlyfrederick
... The PrA and PrN are also called Subject Complements. **** The linking verbs appear, feel, grow, look, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn can be either action or linking depending on their use in the sentence. If you can replace the verb with seem and not alter the meaning of your sentence, ...
... The PrA and PrN are also called Subject Complements. **** The linking verbs appear, feel, grow, look, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn can be either action or linking depending on their use in the sentence. If you can replace the verb with seem and not alter the meaning of your sentence, ...
To use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity
... A proper noun starts with a capital letter. Determiners before nouns place a limit ...
... A proper noun starts with a capital letter. Determiners before nouns place a limit ...
Full poster
... 1. How are uncountable nouns, such as advice and furniture, treated in authentic usage? I have a feeling that constructions of type a piece of furniture and a word of advice actually are very infrequent. 2. I learnt about logical plurals at school: My children have good appetites etc. Do native spea ...
... 1. How are uncountable nouns, such as advice and furniture, treated in authentic usage? I have a feeling that constructions of type a piece of furniture and a word of advice actually are very infrequent. 2. I learnt about logical plurals at school: My children have good appetites etc. Do native spea ...
Words and morphemes
... • This just means taking a word or phrase you are sure of, and inserting it in place • If you end up with a grammatical sentence, you know the category of the item you’re working with • If not, try something else (morphosyntactic evidence, semantic or phonological information, educated ...
... • This just means taking a word or phrase you are sure of, and inserting it in place • If you end up with a grammatical sentence, you know the category of the item you’re working with • If not, try something else (morphosyntactic evidence, semantic or phonological information, educated ...
EE3 2.1 COMMANDS Nombre___________________________
... formal, a group of people or a group including yourself (Let's!) to do or not to do something. There is no difference between these +/- commands, just add NO to make it negative. Endings - go from the yo, drop the o, & add the opposite ending! *(shoe verb rules apply and the sole change of e-i & o-u ...
... formal, a group of people or a group including yourself (Let's!) to do or not to do something. There is no difference between these +/- commands, just add NO to make it negative. Endings - go from the yo, drop the o, & add the opposite ending! *(shoe verb rules apply and the sole change of e-i & o-u ...
MORPHOLOGY - introduction
... they are joined together to make words. The term morpheme is used to refer to the smallest, indivisible units of semantic content or grammatical function which words are made up of. As the smallest linguistic units they have both form and meaning. The meaning of the morpheme is called sememe. The fo ...
... they are joined together to make words. The term morpheme is used to refer to the smallest, indivisible units of semantic content or grammatical function which words are made up of. As the smallest linguistic units they have both form and meaning. The meaning of the morpheme is called sememe. The fo ...
Macedonian grammar
The grammar of Macedonian is, in many respects, similar to that of some other Balkan languages (constituent languages of the Balkan sprachbund), especially Bulgarian. Macedonian exhibits a number of grammatical features that distinguish it from most other Slavic languages, such as the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of an infinitival verb, among others.The first printed Macedonian grammar was published by Gjorgjija Pulevski in 1880.