THE PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE
... 16. Dick always tries to do his best. 17. Sarah tried to paint the ceiling of her room. 18. The lecturer was asked to speak for half an hour. 19. Our plan is to go to Tennessee in October. 20. To play tennis every day is Jim's ambition for the summer. ...
... 16. Dick always tries to do his best. 17. Sarah tried to paint the ceiling of her room. 18. The lecturer was asked to speak for half an hour. 19. Our plan is to go to Tennessee in October. 20. To play tennis every day is Jim's ambition for the summer. ...
Diagraming Basic Sentence Parts
... complements—are diagramed in different ways. A direct object is placed on the same horizontal line as the subject and the verb. It follows the verb and is separated from it by a vertical line. An indirect object is placed on a short horizontal line extending from a slanted line directly below the ve ...
... complements—are diagramed in different ways. A direct object is placed on the same horizontal line as the subject and the verb. It follows the verb and is separated from it by a vertical line. An indirect object is placed on a short horizontal line extending from a slanted line directly below the ve ...
Prepositions - Columbia College
... word that the preposition is in relation to). In addition to the preposition and its object, the prepositional phrase also contains those words that modify the preposition's object. In the following examples, the prepositions are printed in italics, the prepositions' objects (what the prepositions a ...
... word that the preposition is in relation to). In addition to the preposition and its object, the prepositional phrase also contains those words that modify the preposition's object. In the following examples, the prepositions are printed in italics, the prepositions' objects (what the prepositions a ...
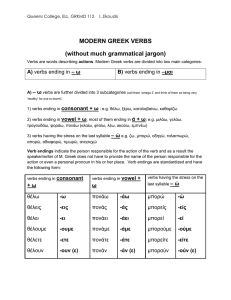
MODERN GREEK VERBS (without much grammatical jargon)
... Tenses are called here ‘Continuous’ (others call them ‘Imperfective’) and characteristically leave the action of the verb open in time, incomplete, repeated constantly or simply going on forever and ever. Such Tenses are the Future Cont., Subjunctive Cont., Continuous Negative Command and Past Conti ...
... Tenses are called here ‘Continuous’ (others call them ‘Imperfective’) and characteristically leave the action of the verb open in time, incomplete, repeated constantly or simply going on forever and ever. Such Tenses are the Future Cont., Subjunctive Cont., Continuous Negative Command and Past Conti ...
Paper 1 Task 2
... Introduction to Paper 1 Tasks One and Two Tasks One and Two test your understanding of key ELT terminology, focusing on a broad spectrum of the syllabus: knowledge of language systems and skills; methodology and approaches and assessment. Whilst knowledge of terminology may not be a valid aim in its ...
... Introduction to Paper 1 Tasks One and Two Tasks One and Two test your understanding of key ELT terminology, focusing on a broad spectrum of the syllabus: knowledge of language systems and skills; methodology and approaches and assessment. Whilst knowledge of terminology may not be a valid aim in its ...
The Logic of Turkish
... cube. I propose to understand all of the vowels as deviations from the dotless letter ı; so I place this vowel at the origin of Cartesian -space. As fits its simple written form, ı is pronounced by relaxing the mouth completely, but keeping the teeth nearly clenched: the opening of the mouth will th ...
... cube. I propose to understand all of the vowels as deviations from the dotless letter ı; so I place this vowel at the origin of Cartesian -space. As fits its simple written form, ı is pronounced by relaxing the mouth completely, but keeping the teeth nearly clenched: the opening of the mouth will th ...
Direct Objects and Indirect Objects Study Guide
... screamed what?” We can’t answer that question, so screamed does not have a direct object.) An INDIRECT OBJECT is a noun or pronoun that tells to whom, for whom, to what, or for what the action of the verb is being done. In order to have a sentence with an indirect object, you must also have a direct ...
... screamed what?” We can’t answer that question, so screamed does not have a direct object.) An INDIRECT OBJECT is a noun or pronoun that tells to whom, for whom, to what, or for what the action of the verb is being done. In order to have a sentence with an indirect object, you must also have a direct ...
teaching latin to students with an african home language
... singular or plural, words change the ‘front parts’ (i.e. prefixes) of their nouns, adjectives and verbs, Latin changes the endings (suffixes). What does need careful elucidation for all students, however, is case usage, and we need a slightly different approach for speakers of an African home langua ...
... singular or plural, words change the ‘front parts’ (i.e. prefixes) of their nouns, adjectives and verbs, Latin changes the endings (suffixes). What does need careful elucidation for all students, however, is case usage, and we need a slightly different approach for speakers of an African home langua ...
ON THE FUNCTIONS OF SOME DEVERBATIVE NOUNS IN
... and-SojThe man in the photograph above is no respeclor of reputations. Similarly Ex. 26 could be extended into Madame Cliquot is the bringer of the bubbly, more precisely Madame Cliquot tvas the person who brought the bubbly, as we learn from the article on the beginnings of champagne production ab ...
... and-SojThe man in the photograph above is no respeclor of reputations. Similarly Ex. 26 could be extended into Madame Cliquot is the bringer of the bubbly, more precisely Madame Cliquot tvas the person who brought the bubbly, as we learn from the article on the beginnings of champagne production ab ...
Where does Verb Bias Come From?
... events as well as linguistic information. However, Wonnacott et al. took care that no covert semantic or event categories differentiated the verbs that selected different word orders in their experiment; therefore they argued that their verbbias effects primarily reflected linguistic distributional ...
... events as well as linguistic information. However, Wonnacott et al. took care that no covert semantic or event categories differentiated the verbs that selected different word orders in their experiment; therefore they argued that their verbbias effects primarily reflected linguistic distributional ...
English 10 Grammar PowerPoint
... ex: The man (who, whom) she thought was perfect jilted her. (who, whom) was perfect b. Substitute the word he for who and him for whom. he was perfect or him was perfect c. Since he was perfect makes sense, you would use who. d. Sometimes you will have to rearrange the clause into normal word order. ...
... ex: The man (who, whom) she thought was perfect jilted her. (who, whom) was perfect b. Substitute the word he for who and him for whom. he was perfect or him was perfect c. Since he was perfect makes sense, you would use who. d. Sometimes you will have to rearrange the clause into normal word order. ...
ppt
... Important idea: The observable word order speakers produce is the result of a system of unconscious word order rules. (This linguistic system is called “syntax”.) ...
... Important idea: The observable word order speakers produce is the result of a system of unconscious word order rules. (This linguistic system is called “syntax”.) ...
Clauses.08.28.14.blog
... have a grandson? 2. Why was Zeus so drawn to Danae? How did Zeus get to her? 3. Is this a realistic story? Why or why not? 4. How was the prophecy from the beginning of the story fulfilled? 5. Is Perseus a hero? What evidence supports ...
... have a grandson? 2. Why was Zeus so drawn to Danae? How did Zeus get to her? 3. Is this a realistic story? Why or why not? 4. How was the prophecy from the beginning of the story fulfilled? 5. Is Perseus a hero? What evidence supports ...
English_10_Grammar_PowerPoint
... ex: The man (who, whom) she thought was perfect jilted her. (who, whom) was perfect b. Substitute the word he for who and him for whom. he was perfect or him was perfect c. Since he was perfect makes sense, you would use who. d. Sometimes you will have to rearrange the clause into normal word order. ...
... ex: The man (who, whom) she thought was perfect jilted her. (who, whom) was perfect b. Substitute the word he for who and him for whom. he was perfect or him was perfect c. Since he was perfect makes sense, you would use who. d. Sometimes you will have to rearrange the clause into normal word order. ...
Difference between gerund and participle worksheet
... State whether the –ing forms given in the following sentences are participles or gerunds. In the case of participles, name the noun or pronoun they qualify. In.Aug 22, 2013 . It's tough to know the difference between gerunds and present participles in English just by looking because they both consis ...
... State whether the –ing forms given in the following sentences are participles or gerunds. In the case of participles, name the noun or pronoun they qualify. In.Aug 22, 2013 . It's tough to know the difference between gerunds and present participles in English just by looking because they both consis ...
16. THE SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD.
... 1. On the referential level: time as a line, on which past and future defined as the one that is behind and the one that is ahead of the present. 2. On the semantic level present is general and unmarked. 3. On the grammatical level: English has no future form of the verb. Present is unmarked tense t ...
... 1. On the referential level: time as a line, on which past and future defined as the one that is behind and the one that is ahead of the present. 2. On the semantic level present is general and unmarked. 3. On the grammatical level: English has no future form of the verb. Present is unmarked tense t ...
The ACS Style Guide
... Incorrect: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in the leaves and/or roots. Correct: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in the leaves and roots. Also correct: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in either the leaves or the roots. Also correct: Our g ...
... Incorrect: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in the leaves and/or roots. Correct: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in the leaves and roots. Also correct: Our goal was to confirm the presence of the alkaloid in either the leaves or the roots. Also correct: Our g ...
INTRODUCING PHONOLOGY Underlying representations
... This model implies that the output of one component forms the input to the next component, so the phonological component starts with whatever the morphological component gives it, and applies its own rules (which are then subject to principles of physical interpretation in the phonetic component). T ...
... This model implies that the output of one component forms the input to the next component, so the phonological component starts with whatever the morphological component gives it, and applies its own rules (which are then subject to principles of physical interpretation in the phonetic component). T ...
do not work. - WordPress.com
... what clues you might use to help you locate the answer. For example, if you were looking for a certain date, you would quickly read the paragraph looking only for numbers. ...
... what clues you might use to help you locate the answer. For example, if you were looking for a certain date, you would quickly read the paragraph looking only for numbers. ...
It is infinitive
... How many kinds of infinitive are there in English ? What is bare infinitive? Where is gerundial infinitive used? Write an example of split infinitive. ...
... How many kinds of infinitive are there in English ? What is bare infinitive? Where is gerundial infinitive used? Write an example of split infinitive. ...
Figurative Language
... moral of the story that the author wants you to learn after reading. Foreshadowing-When an author hints at things that might happen later in the story. Flashback-When the author switches from the present to tell about something that has already happened. Suspense-A feeling of uncertainty or anxiety ...
... moral of the story that the author wants you to learn after reading. Foreshadowing-When an author hints at things that might happen later in the story. Flashback-When the author switches from the present to tell about something that has already happened. Suspense-A feeling of uncertainty or anxiety ...
Verb Wars Episode #1: A New Gerund
... main purpose, but they can also serve other functions. • This trimester we’ll talk about three different types of verbs and their uses for enhancing communication. – Gerunds – Participles – Infinitives ...
... main purpose, but they can also serve other functions. • This trimester we’ll talk about three different types of verbs and their uses for enhancing communication. – Gerunds – Participles – Infinitives ...
VERB TENSES
... past tense, and future tense with their variations to express the exact time of action as to an event happening, having happened, or yet to happen. • There are six common types of Verb Tenses ...
... past tense, and future tense with their variations to express the exact time of action as to an event happening, having happened, or yet to happen. • There are six common types of Verb Tenses ...