MONOLITHIC PHASE LOCKED LOOPS (PLL IC 565)
... The center frequency of the PLL is determined by the free running frequency of the VCO, which is given by ...
... The center frequency of the PLL is determined by the free running frequency of the VCO, which is given by ...
Tie-Line Error
... PID based LFC of single area power system PID controller has been broadly used for decades as the load frequency controllers. PID controller is simple to implement however, there are fundamental technical limitations in the existing PID framework, including the following: 1) the error computation ...
... PID based LFC of single area power system PID controller has been broadly used for decades as the load frequency controllers. PID controller is simple to implement however, there are fundamental technical limitations in the existing PID framework, including the following: 1) the error computation ...
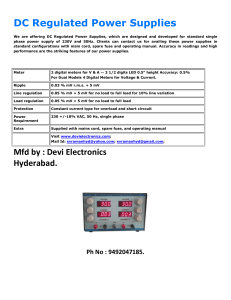
DC Regulated Power Supplies
... DC Regulated Power Supplies We are offering DC Regulated Power Supplies, which are designed and developed for standard single phase power supply of 230V and 50Hz. Clients can contact us for availing these power supplies in standard configurations with main cord, spare fuse and operating manual. Accu ...
... DC Regulated Power Supplies We are offering DC Regulated Power Supplies, which are designed and developed for standard single phase power supply of 230V and 50Hz. Clients can contact us for availing these power supplies in standard configurations with main cord, spare fuse and operating manual. Accu ...
PowerPoint-presentation
... • The DFT gives some information about the content of high frequency distortion but the time-domain information is “lost” • The STFT seems like a suitable analysing method but in this case when many of the high frequency components are synchronized with the fundamental it is impossible to get an go ...
... • The DFT gives some information about the content of high frequency distortion but the time-domain information is “lost” • The STFT seems like a suitable analysing method but in this case when many of the high frequency components are synchronized with the fundamental it is impossible to get an go ...
T3000 Frequency Relay
... frequencies higher than the preset value, while the output relay for over frequency is activated at frequencies lower than the preset value. This means that both output relays are activated at frequencies within the interval between the under and over frequency scale range. ...
... frequencies higher than the preset value, while the output relay for over frequency is activated at frequencies lower than the preset value. This means that both output relays are activated at frequencies within the interval between the under and over frequency scale range. ...
instructions to tenderers
... of the phase voltage LIN(A, B, C) from the line-to line voltages; channel E switched into channel D for multiplexing. •Filter: Low pass active filter of the 2° order required for the recovery of the fundamental wave out of the PWM signals. Cut-off frequency: 1 kHz. Space vector indicator: •Voltage v ...
... of the phase voltage LIN(A, B, C) from the line-to line voltages; channel E switched into channel D for multiplexing. •Filter: Low pass active filter of the 2° order required for the recovery of the fundamental wave out of the PWM signals. Cut-off frequency: 1 kHz. Space vector indicator: •Voltage v ...
High Frequency Power Converters for Utility Applications
... High Frequency Power Converters for Utility Applications In the modern power electronics converter applications, the demands for reaching higher efficiency and higher power density are aligned with higher switching frequency over range of 1 MHz. Compared to silicon-based devices, GaN and SiC power c ...
... High Frequency Power Converters for Utility Applications In the modern power electronics converter applications, the demands for reaching higher efficiency and higher power density are aligned with higher switching frequency over range of 1 MHz. Compared to silicon-based devices, GaN and SiC power c ...
7 With the protective cover closed, it is not possible to set the
... transformation ratio between the primary and secondary voltages of the transformer. Note that if Digipact display modules are used, the rated distribution-system voltage must be entered. ...
... transformation ratio between the primary and secondary voltages of the transformer. Note that if Digipact display modules are used, the rated distribution-system voltage must be entered. ...
LX-1020/5 SPECIAL VIDEO TRANSMITTER FOR WIDE RANGE OF
... The new Audio/Video transmitter is a special design for Military applications capable to work in extremely low or high temperature range. This transmitter has wide range of frequencies from 1000 MHz- 2000 MHz with no gaps or limits. This transmitter has digital display. It is easy to change channels ...
... The new Audio/Video transmitter is a special design for Military applications capable to work in extremely low or high temperature range. This transmitter has wide range of frequencies from 1000 MHz- 2000 MHz with no gaps or limits. This transmitter has digital display. It is easy to change channels ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.