* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint-presentation
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
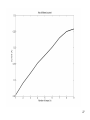
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
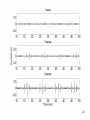
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
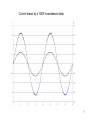
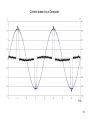
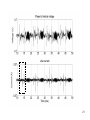
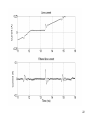
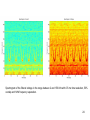
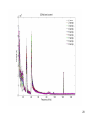
High Frequency Distortion in Power Grids due to Electronic Equipment Anders Larsson Luleå University of Technology Outline of the presentation • Background and motivation of the work • Waveform distortion – Low-frequency distortion (harmonics) – High-frequency distortion • Results and analysing methods of measurements – Measurement on fluorescent tube power by a high frequency ballast – Measurement on multiple fluorescent lamps 2 – Long term measurement at different locations Background and motivation of the work 3 • New technology has changed our lifestyle, we use more electronic product in our life than ever • Electronic equipment is often served by a regulated power supply • New technology has made it possible to build more energy efficient power supplies • Often are this type of power supplies nonlinear • This new technology has brought new distortions phenomena to the power grid • New measurement technology has made it easier and cheaper to measure 4 Some questions brought up in the beginning of the project • What types of signals can be found in this frequency range? • How do we observe these types of signals? • What happens when a large number of equipments are connected together? • How does these signals propagate in the LV net work? • Can these signals lead to a barrier to the introduction of other equipments such as PLC, home care equipments, alarms, audio equipments etc? • Can high frequency distortion lead to deterioration of other equipments? 5 Waveform distortion Low frequency distortion (harmonics) 6 Current drawn by a 100W incandescent lamp 7 How do we analyze waveform distortion? • If the current is not sinusoidal it contains other frequencies than the fundamental at 50 or 60 Hz • One way to analyze the signal is to use the Discreet Fourier Transform (DFT) to transfers the signal from the time- to the frequencydomain • There are two reasons to transform the signal; to quantify the waveform distortion and to determent the propagation of the signal 8 Harmonic content of the current drawn by the incandescent lamp 9 Current drawn by a Computer 10 Harmonic content of the Current drawn by a Computer 11 Current drawn by a HFFluorescent Light 12 Current drawn by a HFFluorescent Light 13 High frequency distortion 14 • Almost all new electronic equipments has SMPS that uses switching technology in the frequency range from about 20 to 80 kHz • The product standards covering harmonic set limits up to about 2 or 3 kHz • Radio disturbances standards mainly sets limits from 150 kHz and up • High frequency distortion is in this case defined from 2 kHz up to about 1 MHz 15 Sources • • • • • Switch Mode Power Supplies HF-ballasts Active Power Factor Correction Power Line Communications Other loads containing power electronics e.g. converters, dimmers etc. 16 Fluorescent lamps powered by high frequency ballast 19 20 21 22 Annex B in IEC 61000-4-7 Gb b 100Hz C b 90Hz 2 f 23 Spectrogram of the filtered voltage in the range between 2 and 150 kHz with 0.5 ms time resolution, 50% overlap and 1kHz frequency separation. 24 Multiple lamps 25 26 27 28 29 • Some examples of measurement at different locations 30 31 32 33 Some conclusion • The lamp adds extra high frequency components • The high frequency components are often synchronized with the fundamental frequency • One lamp generate high frequency notches which repeats synchronized with the power system frequency • Published papers describing “zero-crossing distortion” generated by the APFC circuit reminds of “high frequency notches” • High frequency notches increases with the number of lamps but the increase seems not to be linear. The STFT shows that these signals is found in the lower frequency range 34 • The DFT gives some information about the content of high frequency distortion but the time-domain information is “lost” • The STFT seems like a suitable analysing method but in this case when many of the high frequency components are synchronized with the fundamental it is impossible to get an good frequency resolution in the lower frequency range • There are large deviations between different locations and quite surprisingly the highest amplitudes were found at the resident • There is an change of in amplitude of the high frequency distortion over time. Some frequencies seems to be attenuated by loads coming on while other frequencies is generated by the loads 35 Thanks for your attention 36