4040
... with power consumption over 75 watts. This essentially requires power factor correction (PFC). Additionally, a standby power dissipation limit is set to conserve power when a load is OFF. “80 PLUS” is an initiative funded by electric utilities to integrate more energy efficient Power Supply Units (P ...
... with power consumption over 75 watts. This essentially requires power factor correction (PFC). Additionally, a standby power dissipation limit is set to conserve power when a load is OFF. “80 PLUS” is an initiative funded by electric utilities to integrate more energy efficient Power Supply Units (P ...
LT5519 - 0.7GHz to 1.4GHz High Linearity
... VCC1 (Pin 6): Power Supply Pin for the Bias Circuits. Typical current consumption is about 2mA. This pin should be externally connected to VCC and have appropriate RF bypass capacitors. ...
... VCC1 (Pin 6): Power Supply Pin for the Bias Circuits. Typical current consumption is about 2mA. This pin should be externally connected to VCC and have appropriate RF bypass capacitors. ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... winding-to-winding and winding-to-core dielectric breakdown, and acceptable thermal management. The inductor was designed using AMCC1000 cores due to their high saturation flux density, high permeability, window size, and availability. These cores are manufactured with iron-based METGLASS 2605 SA1 a ...
... winding-to-winding and winding-to-core dielectric breakdown, and acceptable thermal management. The inductor was designed using AMCC1000 cores due to their high saturation flux density, high permeability, window size, and availability. These cores are manufactured with iron-based METGLASS 2605 SA1 a ...
AN 574: Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Power Delivery Network
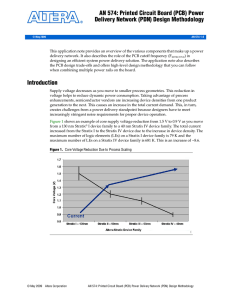
... at the FEFFECTIVE frequency reported by the tool. As shown in the following example, over-designing the PCB by adding capacitors with a SRF beyond FEFFECTIVE results in additional build of materials (BOM) cost without performance improvements. Two designs (A are B) are studied. All the parameters of ...
... at the FEFFECTIVE frequency reported by the tool. As shown in the following example, over-designing the PCB by adding capacitors with a SRF beyond FEFFECTIVE results in additional build of materials (BOM) cost without performance improvements. Two designs (A are B) are studied. All the parameters of ...
Doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) as a hybrid of asynchronous
... electrical radian/s, the rotor resistance Rr is modified as Rr /s where s = (1 − ωm /ωS ) is the slip. The rotor-side VSC of Fig. 1 injects balanced three-phase voltages (vRa , vRb , vRc ) at slip frequency ωr = sωs , voltage magnitude VR and voltage angle δ. Because Fig. 2 is based on the stator-si ...
... electrical radian/s, the rotor resistance Rr is modified as Rr /s where s = (1 − ωm /ωS ) is the slip. The rotor-side VSC of Fig. 1 injects balanced three-phase voltages (vRa , vRb , vRc ) at slip frequency ωr = sωs , voltage magnitude VR and voltage angle δ. Because Fig. 2 is based on the stator-si ...
SNC1D0 How Nikola Tesla Changed the Way we Use Energy
... with just the right formula: an AC system based on three-phase, 60-cycle current. Today, almost all power companies in the United States and Canada supply 60-cycle current, which means the AC completes 60 changes of direction in one second. This is known as the frequency of the system. By the early ...
... with just the right formula: an AC system based on three-phase, 60-cycle current. Today, almost all power companies in the United States and Canada supply 60-cycle current, which means the AC completes 60 changes of direction in one second. This is known as the frequency of the system. By the early ...
LM2907/LM2917 Frequency to Voltage Converter
... swing above and below ground and exceed the input thresholds to produce an output. This is offered specifically for magnetic variable reluctance pickups which typically provide a single-ended ac output. This single input is also fully protected against voltage swings to g 28V, which are easily attai ...
... swing above and below ground and exceed the input thresholds to produce an output. This is offered specifically for magnetic variable reluctance pickups which typically provide a single-ended ac output. This single input is also fully protected against voltage swings to g 28V, which are easily attai ...
RF Power Measurements and Control
... Next, the preamp was not cooperating with my potentiometer. I had to replace the serial potentiometer with a manually adjustable one to get results. And even then we did not achieve the full range of 0 to 1 and we only achieved about half of this gain. It will work for our purposes but I do see room ...
... Next, the preamp was not cooperating with my potentiometer. I had to replace the serial potentiometer with a manually adjustable one to get results. And even then we did not achieve the full range of 0 to 1 and we only achieved about half of this gain. It will work for our purposes but I do see room ...
Tracing Network flows due to Sources/Sinks using Virtual flow Concept
... of transmission charges allocation and to make up the loss component. System losses are associated with power transfer in the network. In the interconnected system, determination of the lines involved in providing transmission services for a given transaction period among the various entities is to ...
... of transmission charges allocation and to make up the loss component. System losses are associated with power transfer in the network. In the interconnected system, determination of the lines involved in providing transmission services for a given transaction period among the various entities is to ...
In a typical DC motor, there are permanent magnets on the outside
... Building Energy Systems, 2009 Fall. Electric Motor Supplemental Notes ...
... Building Energy Systems, 2009 Fall. Electric Motor Supplemental Notes ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.