The grammaticalization of mood and modality in Omotic
... Whereas the two grammatical domains of modality and clause type clearly do not necessarily coincide in Indo-European languages, Omotic languages do occasionally provide almost perfect matches between the two, as we shall see below. Interestingly, the strong link between sentence structure and illocu ...
... Whereas the two grammatical domains of modality and clause type clearly do not necessarily coincide in Indo-European languages, Omotic languages do occasionally provide almost perfect matches between the two, as we shall see below. Interestingly, the strong link between sentence structure and illocu ...
The Syntax of Valuation in Auxiliary–participle
... modal soe () to value the uT:__ of the modal want (), which results in an infinitive on want. But since the structure is not spelled-out at this point, valuation is not necessary but can be postponed. Since the verbs of a verb cluster in Frisian must appear in inverted (i.e., 3–2–1…) order, syntac ...
... modal soe () to value the uT:__ of the modal want (), which results in an infinitive on want. But since the structure is not spelled-out at this point, valuation is not necessary but can be postponed. Since the verbs of a verb cluster in Frisian must appear in inverted (i.e., 3–2–1…) order, syntac ...
The History of the Gerund in English and Its Structural Precursors
... samaritanisc and eart wod.10 ...
... samaritanisc and eart wod.10 ...
dependent clauses
... Note: It is important to always place an adjective clause pronoun as close as possible to the noun it modifies. If you place the adjective clause beside a noun it is not meant to modify, you will create a “misplaced modifier” error, which could change the meaning of your sentence and cause confusion ...
... Note: It is important to always place an adjective clause pronoun as close as possible to the noun it modifies. If you place the adjective clause beside a noun it is not meant to modify, you will create a “misplaced modifier” error, which could change the meaning of your sentence and cause confusion ...
view/Open[13801982] - S
... For exa mple, the to-be-deletion tran sformatio n is optiona ll y applicable when the main verb is seem, appear, a nd turn out, but not when it is happen or chance . John seems to be tired. John seems tired, John turned out to be a successf ul ca ndida te. ...
... For exa mple, the to-be-deletion tran sformatio n is optiona ll y applicable when the main verb is seem, appear, a nd turn out, but not when it is happen or chance . John seems to be tired. John seems tired, John turned out to be a successf ul ca ndida te. ...
An Introduction to Clauses - Johnson County Community College
... Clauses Handout created by Dr. M. Dickerson ...
... Clauses Handout created by Dr. M. Dickerson ...
The Preterite Tense of Regular –AR verbs
... Number your paper 1-4. As you listen to each conversation, jot down as much information as you can from each. You may hear info about what the person is shopping for, where they are shopping, how much the items cost, as well as other related info. ...
... Number your paper 1-4. As you listen to each conversation, jot down as much information as you can from each. You may hear info about what the person is shopping for, where they are shopping, how much the items cost, as well as other related info. ...
PART B - Academic Skills
... to have at least an independent (or main) clause. A complex sentence made up of several clauses can be co-joined to form one sentence (e.g. two independent clauses joined by ‘ and’, ‘ or’, ‘ but’). It can also be made up of an independent clause and several dependent ones. Dependent clauses cannot f ...
... to have at least an independent (or main) clause. A complex sentence made up of several clauses can be co-joined to form one sentence (e.g. two independent clauses joined by ‘ and’, ‘ or’, ‘ but’). It can also be made up of an independent clause and several dependent ones. Dependent clauses cannot f ...
On flexible and rigid nouns
... traditional (rigid) word classes like Verb, Noun or Adjective. This is captured in Hengeveld’s classification of parts of speech (PoS) systems, which has a major division between languages with a flexible PoS system and languages with a rigid PoS system (Figure 1). A simplified version of this class ...
... traditional (rigid) word classes like Verb, Noun or Adjective. This is captured in Hengeveld’s classification of parts of speech (PoS) systems, which has a major division between languages with a flexible PoS system and languages with a rigid PoS system (Figure 1). A simplified version of this class ...
lecture3
... 5. (4pts) What syntactic situations would force a parser to decide to analyze “stop” in “… the bus stop?” as a noun (vs. a verb)? In English, verbs don’t normally appear at the end of the sentence. To end in an uninflected verb (stop), we can form a question… 1. yes/no question 2. object wh-question ...
... 5. (4pts) What syntactic situations would force a parser to decide to analyze “stop” in “… the bus stop?” as a noun (vs. a verb)? In English, verbs don’t normally appear at the end of the sentence. To end in an uninflected verb (stop), we can form a question… 1. yes/no question 2. object wh-question ...
On the Origin and History of the English Prepositional Type A
... There seems to be common agreement in ascribing the origins of the phrase a-hunting in English to a prepositional pattern of the type on + verbal noun in -ing l-ung, which, apparently, was already in use from OE times. Van der Gaaf (202) holds that there is a prepositional construction of the type o ...
... There seems to be common agreement in ascribing the origins of the phrase a-hunting in English to a prepositional pattern of the type on + verbal noun in -ing l-ung, which, apparently, was already in use from OE times. Van der Gaaf (202) holds that there is a prepositional construction of the type o ...
Penn Treebank Tagset
... diagnostic tests for the distinction between prepositions and particles. As noted above (\IN or RB"), prepositions are generally associated with an immediately following noun phrase. However, they may be \stranded," i.e. their object may occur at the beginning of a clause rather than immediately fol ...
... diagnostic tests for the distinction between prepositions and particles. As noted above (\IN or RB"), prepositions are generally associated with an immediately following noun phrase. However, they may be \stranded," i.e. their object may occur at the beginning of a clause rather than immediately fol ...
Surprise: Spanish FrameNet! Carlos Subirats and Miriam R.L.
... simpler parts of the complex event. In addition, they are formed by adding linguistic material to the simpler form: the reflexive clitic pronoun se is added to sorprender to form sorprenderse; and the past participle suffix -(i)da is added to sorprender to form the past participle used in constructi ...
... simpler parts of the complex event. In addition, they are formed by adding linguistic material to the simpler form: the reflexive clitic pronoun se is added to sorprender to form sorprenderse; and the past participle suffix -(i)da is added to sorprender to form the past participle used in constructi ...
Basic Punctuation Help Tips
... In this simple sentence the verb ‘work’ becomes ‘works’ because the subject is ‘she’. Remember to add ‘s’ to a regular verb (verb that follows the typical grammar rule) when the subject is he, she, it or a single noun (person, place or thing). ...
... In this simple sentence the verb ‘work’ becomes ‘works’ because the subject is ‘she’. Remember to add ‘s’ to a regular verb (verb that follows the typical grammar rule) when the subject is he, she, it or a single noun (person, place or thing). ...
Topic 7
... can all be directly nested (embedded) inside main clauses (i.e. comprise a whole SPOCA element within the main clause). We also need to take account of the fact that clauses can be indirectly nested inside main clauses. By 'indirect nesting' we mean that the nested clauses do not form a whole SPOCA ...
... can all be directly nested (embedded) inside main clauses (i.e. comprise a whole SPOCA element within the main clause). We also need to take account of the fact that clauses can be indirectly nested inside main clauses. By 'indirect nesting' we mean that the nested clauses do not form a whole SPOCA ...
dependent clauses
... When the relative pronoun is used as the object of a preposition, the adjective clause can take several forms. The most formal way to express these ideas is to place the preposition at the beginning of the adjective clause as in Sentences 1 and 2 (below). In this type of sentence construction, if th ...
... When the relative pronoun is used as the object of a preposition, the adjective clause can take several forms. The most formal way to express these ideas is to place the preposition at the beginning of the adjective clause as in Sentences 1 and 2 (below). In this type of sentence construction, if th ...
IntEx: A Syntactic Role Driven Protein-Protein
... complete interactions by analyzing the matching contents of syntactic roles and their linguistically significant combinations. The novel aspects of our system are its ability to handle complex sentence structures using the Complex Sentence Processor (CSP) and to extract multiple and nested interacti ...
... complete interactions by analyzing the matching contents of syntactic roles and their linguistically significant combinations. The novel aspects of our system are its ability to handle complex sentence structures using the Complex Sentence Processor (CSP) and to extract multiple and nested interacti ...
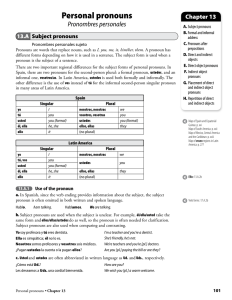
Personal pronouns - Vista Higher Learning
... d. In all voseo regions, vos adopted the direct and indirect object pronouns of tú (Te digo a vos. I tell you.) as well as its possessive and reflexive pronouns (Vos te sentás en tu silla. You sit in your chair.). 13.B.3 Vosotros/as - ustedes a. In Spain, there are two plural address forms: the in ...
... d. In all voseo regions, vos adopted the direct and indirect object pronouns of tú (Te digo a vos. I tell you.) as well as its possessive and reflexive pronouns (Vos te sentás en tu silla. You sit in your chair.). 13.B.3 Vosotros/as - ustedes a. In Spain, there are two plural address forms: the in ...
Basic Grammar Skills
... choose, use, and spell the right word. When in doubt about what word to use or the meaning of a word that you are reading, look it up in your dictionary. A good dictionary gives the following information on a word (usually in this order): 1. The word correctly spelled and with hyphens to show syllab ...
... choose, use, and spell the right word. When in doubt about what word to use or the meaning of a word that you are reading, look it up in your dictionary. A good dictionary gives the following information on a word (usually in this order): 1. The word correctly spelled and with hyphens to show syllab ...
1 Construction Morphology and the Parallel Architecture of grammar
... particular language construct. Correspondence relations may also be referred to as interface relations. In the default case, the lexical specification of a word comprises these three levels; hence, each word is a specification of interfaces between three pieces of information. The same holds for con ...
... particular language construct. Correspondence relations may also be referred to as interface relations. In the default case, the lexical specification of a word comprises these three levels; hence, each word is a specification of interfaces between three pieces of information. The same holds for con ...
Grace Theological Journal 5.2 (1984) 163
... or substantival, even without the article. Most of these function as anarthrous nouns. Some stand in agreement with some other substantive word in the sentence, such as a pronoun, a numerical adjective, or with the subject implied in the person and number inflection of the verb. Anarthrous participl ...
... or substantival, even without the article. Most of these function as anarthrous nouns. Some stand in agreement with some other substantive word in the sentence, such as a pronoun, a numerical adjective, or with the subject implied in the person and number inflection of the verb. Anarthrous participl ...
The Classification of Participles: A Statistical Study
... or substantival, even without the article. Most of these function as anarthrous nouns. Some stand in agreement with some other substantive word in the sentence, such as a pronoun, a numerical adjective, or with the subject implied in the person and number inflection of the verb. Anarthrous participl ...
... or substantival, even without the article. Most of these function as anarthrous nouns. Some stand in agreement with some other substantive word in the sentence, such as a pronoun, a numerical adjective, or with the subject implied in the person and number inflection of the verb. Anarthrous participl ...
3 Speech act distinctions in syntax
... of features that recur from language to language. They typically have first person singular subjects and second person indirect objects, and they usually look like positive declarative sentences, as in English. As for tense and aspect, they have a neutral form whose meaning covers present time. ln E ...
... of features that recur from language to language. They typically have first person singular subjects and second person indirect objects, and they usually look like positive declarative sentences, as in English. As for tense and aspect, they have a neutral form whose meaning covers present time. ln E ...
1. the language of mathematics - One Mathematical Cat, Please!
... that the name 121 inches convert units of inches to units of feet. • PREFERRED STYLE/FORMAT: Finally, ‘simpler’ often means in a preferred style or format. For example, 24 (two-fourths) and 12 (one-half) are both names for the same number, but people usually prefer the name 12 ; it is said to be in ...
... that the name 121 inches convert units of inches to units of feet. • PREFERRED STYLE/FORMAT: Finally, ‘simpler’ often means in a preferred style or format. For example, 24 (two-fourths) and 12 (one-half) are both names for the same number, but people usually prefer the name 12 ; it is said to be in ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.




![view/Open[13801982] - S](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016785878_1-5416959276f3d4c19425d527f23d48a6-300x300.png)