Warley Town School Explanation of Terms Used in English KS1
... punctuation is to indicate sentence boundaries. A suffix is an ‘ending’, used at the end of one word to turn it into another word. Unlike root words, suffixes cannot stand on their own as a complete word. Two words are synonyms if they have the same meaning, or similar meanings In English, tense is ...
... punctuation is to indicate sentence boundaries. A suffix is an ‘ending’, used at the end of one word to turn it into another word. Unlike root words, suffixes cannot stand on their own as a complete word. Two words are synonyms if they have the same meaning, or similar meanings In English, tense is ...
Pronouns A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun or
... In each of the following sentences, the verb or compound verb is highlighted: Dracula bites his victims on the neck. The verb "bites" describes the action Dracula takes. In early October, Giselle will plant twenty tulip bulbs. Here the compound verb "will plant" describes an action that will take pl ...
... In each of the following sentences, the verb or compound verb is highlighted: Dracula bites his victims on the neck. The verb "bites" describes the action Dracula takes. In early October, Giselle will plant twenty tulip bulbs. Here the compound verb "will plant" describes an action that will take pl ...
verb
... Participles and Participial Phrases • A participle is a verbal used as an ADJECTIVE. • Participles modify NOUNS or PRONOUNS only. • A participle will answer the adjective questions “Which one?” and “What kind?” • Participles are either PRESENT or PAST --• Present participles end in –ing • Past part ...
... Participles and Participial Phrases • A participle is a verbal used as an ADJECTIVE. • Participles modify NOUNS or PRONOUNS only. • A participle will answer the adjective questions “Which one?” and “What kind?” • Participles are either PRESENT or PAST --• Present participles end in –ing • Past part ...
Selection: Blancaflor Grammar: Linking Verbs Details: A linking verb
... Details: A linking verb links the subject of a sentence to a noun or an adjective. It does not show action. It tells what the subject is, was, or will be. Some examples are: am, is, are, was, were, will be, seem, appear, look, taste, feel, and felt. See for Help: Practice book pages 177-178 Example: ...
... Details: A linking verb links the subject of a sentence to a noun or an adjective. It does not show action. It tells what the subject is, was, or will be. Some examples are: am, is, are, was, were, will be, seem, appear, look, taste, feel, and felt. See for Help: Practice book pages 177-178 Example: ...
3rd lecture in grammar 2nd year feb.2013 1)Transitive verb While
... ditransitive. An example in English is the verb to give. There are also a few verbs, like "to trade" in the English language, that may be called "tritransitive" because they take three objects.[1] In contrast to transitive verbs, some verbs take zero objects. Verbs that do not require an object are ...
... ditransitive. An example in English is the verb to give. There are also a few verbs, like "to trade" in the English language, that may be called "tritransitive" because they take three objects.[1] In contrast to transitive verbs, some verbs take zero objects. Verbs that do not require an object are ...
Verbs that can be followed by both an infinitive and a gerund
... 4- After some expressions : It's no use ..., It's no good ..., There's no point in ..., I can't help..., I don't mind..., I can't stand/bear..., Example: " It's no use convincing him to meet her. " ...
... 4- After some expressions : It's no use ..., It's no good ..., There's no point in ..., I can't help..., I don't mind..., I can't stand/bear..., Example: " It's no use convincing him to meet her. " ...
Reported Speech-12º
... “I suppose you have heard the latest news about Lampedusa ”, she said. Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, clai ...
... “I suppose you have heard the latest news about Lampedusa ”, she said. Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, clai ...
Grammar Rocks worksheet
... 22) What is the predicate of a sentence? Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words for the following sentences. 23) Students who begin studying a week before a test are more likely to do better than those who only study the day before the test. 24) Raul wanted to do well on his test, but ...
... 22) What is the predicate of a sentence? Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words for the following sentences. 23) Students who begin studying a week before a test are more likely to do better than those who only study the day before the test. 24) Raul wanted to do well on his test, but ...
parts of speech packet - Copley
... An adverb is a word used to modify a verb, adjective, or another adverb. An adverb answers the following questions: how? when? where? or to what extent? Ex: We stayed inside. [The adverb inside modifies the verb stayed and tells where.] Ex: It was an unusually quiet morning. [The adverb unusually mo ...
... An adverb is a word used to modify a verb, adjective, or another adverb. An adverb answers the following questions: how? when? where? or to what extent? Ex: We stayed inside. [The adverb inside modifies the verb stayed and tells where.] Ex: It was an unusually quiet morning. [The adverb unusually mo ...
Sentence Patterns - Tidewater Community College
... Fax: 757-427-0327 http://www.tcc.edu/writing December 18, 2006 ...
... Fax: 757-427-0327 http://www.tcc.edu/writing December 18, 2006 ...
What are Infinitives?
... • The infinitive is a type of verbal noun, similar to a gerund. • It is usually preceded by the particle “to” in English, such as: “to be”, “to have”, “to go”, “to see”, etc. • “Infinitive” comes from the Latin word infinitīvus (“unlimited”) since it is often used to express the basic meaning of a v ...
... • The infinitive is a type of verbal noun, similar to a gerund. • It is usually preceded by the particle “to” in English, such as: “to be”, “to have”, “to go”, “to see”, etc. • “Infinitive” comes from the Latin word infinitīvus (“unlimited”) since it is often used to express the basic meaning of a v ...
Lecture 2: 13/3/2006
... – Articles (the, a, an) – Demonstratives (this, that, these, those) – Possessives (‘s, her, my, whose, etc) – Wh-determiners (which, what –in questions) – Quantifying determiners (some, every, most, no, any etc) ...
... – Articles (the, a, an) – Demonstratives (this, that, these, those) – Possessives (‘s, her, my, whose, etc) – Wh-determiners (which, what –in questions) – Quantifying determiners (some, every, most, no, any etc) ...
appendix Xii uK vs. us english
... In the English of the United Kingdom, collective nouns can take either the singular or plural verb forms, depending on whether the emphasis is on the collective as a whole or on the individual members respectively. Some collective nouns, such as the Government or staff, nearly always take the plural ...
... In the English of the United Kingdom, collective nouns can take either the singular or plural verb forms, depending on whether the emphasis is on the collective as a whole or on the individual members respectively. Some collective nouns, such as the Government or staff, nearly always take the plural ...
Introduction to Phrases
... pronoun in a sentence. We know that predicate nominatives can do this. This is an extension of that idea. Using appositive phrases allows writers to be concise in their language and helps not to be “wordy.” Punctuation is important. The ACT loves to assess on simple things like punctuation. This ...
... pronoun in a sentence. We know that predicate nominatives can do this. This is an extension of that idea. Using appositive phrases allows writers to be concise in their language and helps not to be “wordy.” Punctuation is important. The ACT loves to assess on simple things like punctuation. This ...
Unit 3: Grammar and Usage - Ms. De masi Teaching website
... happened before another time or event. The present perfect tense tells about something that happened at an indefinite time in the past. The present perfect tense consists of has or have + past participle. ...
... happened before another time or event. The present perfect tense tells about something that happened at an indefinite time in the past. The present perfect tense consists of has or have + past participle. ...
English 1 for Management (1EA)
... – This book is not as exciting as the last one. – It's much colder today than it was yesterday. – Our car is bigger than your car. ...
... – This book is not as exciting as the last one. – It's much colder today than it was yesterday. – Our car is bigger than your car. ...
2014 Grammar progress appendix 1
... • To use adverbs to describe verbs Adverbs describe verbs. They tell you in more detail how something is done. e.g. He ran quickly. She danced beautifully. The baby ate slowly. They often end in “ly” • To begin to use paragraphs to group sentences with the same information • To extend the range of ...
... • To use adverbs to describe verbs Adverbs describe verbs. They tell you in more detail how something is done. e.g. He ran quickly. She danced beautifully. The baby ate slowly. They often end in “ly” • To begin to use paragraphs to group sentences with the same information • To extend the range of ...
Adjectives & Verbs
... For verbs of the senses, try this technique to distinguish whether the verb is action or linking: Replace the verb in the sentence with the linking verb seem. If the sentence makes clear sense with the word seem as a substitute, then the verb is linking. If the sentence makes no sense with ...
... For verbs of the senses, try this technique to distinguish whether the verb is action or linking: Replace the verb in the sentence with the linking verb seem. If the sentence makes clear sense with the word seem as a substitute, then the verb is linking. If the sentence makes no sense with ...
nouns, verbs, adjectives…
... Pronouns substitute for nouns, noun phrases, or other pronouns, and can also refer to people (I, you), places (that), things ...
... Pronouns substitute for nouns, noun phrases, or other pronouns, and can also refer to people (I, you), places (that), things ...
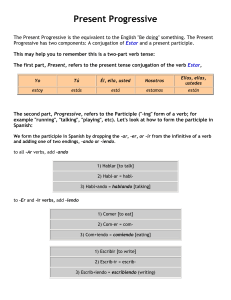
PRESENT PROGRESSIVE notes
... We combine these participles with a form of Estar to form the Present Progressive to describe what people are smack in the middle of doing: ...
... We combine these participles with a form of Estar to form the Present Progressive to describe what people are smack in the middle of doing: ...
VERB - Minooka Community High School
... Noun: everyday names of people, places, things, or ideas ...
... Noun: everyday names of people, places, things, or ideas ...
File
... Infinitives are verbals made up of the word “to” + a verb. Infinitives may function as nouns, adjectives or adverbs. When infinitives function as adjectives and adverbs, they are usually found preceding nouns and pronouns in sentences, and when they function as nouns, they are used as subjects, dire ...
... Infinitives are verbals made up of the word “to” + a verb. Infinitives may function as nouns, adjectives or adverbs. When infinitives function as adjectives and adverbs, they are usually found preceding nouns and pronouns in sentences, and when they function as nouns, they are used as subjects, dire ...
Chapter 1/2 Sentence types, nom, and acc. cases Chapter 4
... 2nd declension nouns, with nominative ending -us, follow this pattern: nominative (subject) colön-us pu-er ag-er accusative (object) colön-um puer-um agr-um Notice that there are two types of nouns ending -er; one type keeps the e of the nominative in the other cases, e.g., puer, puer-um; the other ...
... 2nd declension nouns, with nominative ending -us, follow this pattern: nominative (subject) colön-us pu-er ag-er accusative (object) colön-um puer-um agr-um Notice that there are two types of nouns ending -er; one type keeps the e of the nominative in the other cases, e.g., puer, puer-um; the other ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... There and here are never considered subjects. In sentences that begin with these words, the subject is usually found after the verb. ...
... There and here are never considered subjects. In sentences that begin with these words, the subject is usually found after the verb. ...
FREE ebook — an English Handbook
... There are a few more things to know about verbs: linking verbs cannot be transitive and do not have active or passive voice. Below are several charts that will be a help in understanding the difference between action and linking, transitive and intransitive, and active and passive voice. Take your ...
... There are a few more things to know about verbs: linking verbs cannot be transitive and do not have active or passive voice. Below are several charts that will be a help in understanding the difference between action and linking, transitive and intransitive, and active and passive voice. Take your ...