on fuzzy intuitionistic logic
... The value T(a) € L is the degree of truth of a in interpretation T. If T(a) = 1 we say that T is a model of a. If T(a) = 0, then a is false in interpretation T. By semantics Sx with respect to some set of formulae X, we understand the set of all models of X. Similarly, as in classical logic, it is r ...
... The value T(a) € L is the degree of truth of a in interpretation T. If T(a) = 1 we say that T is a model of a. If T(a) = 0, then a is false in interpretation T. By semantics Sx with respect to some set of formulae X, we understand the set of all models of X. Similarly, as in classical logic, it is r ...
ARTS LANGUAGE
... The most obvious aspect of any language is its vocabulary. All languages are made up of consonant and vowel combinations with meanings agreed upon by their users. These meaningful sound clusters (words) symbolize things, actions, concepts, and relationships. You might think that the words in any giv ...
... The most obvious aspect of any language is its vocabulary. All languages are made up of consonant and vowel combinations with meanings agreed upon by their users. These meaningful sound clusters (words) symbolize things, actions, concepts, and relationships. You might think that the words in any giv ...
Dever-clever
... root) – hospital (Lat) – hostel (Norm. Fr) – hotel (Par. Fr). Translation-Loans. This term is equivalent to borrowing. They are not taken into the vocabulary of another language more or less in the same phonetic shape in which they have been functioning in their own language, but undergo the process ...
... root) – hospital (Lat) – hostel (Norm. Fr) – hotel (Par. Fr). Translation-Loans. This term is equivalent to borrowing. They are not taken into the vocabulary of another language more or less in the same phonetic shape in which they have been functioning in their own language, but undergo the process ...
Chapter 1 Logic and Set Theory
... in dealing with sets are derived from established axioms. At some point of your academic career, you may wish to study set theory and logic in greater detail. Our main purpose here is to learn how to state mathematical results clearly and how to prove them. ...
... in dealing with sets are derived from established axioms. At some point of your academic career, you may wish to study set theory and logic in greater detail. Our main purpose here is to learn how to state mathematical results clearly and how to prove them. ...
grammar - Cambridge University Press
... on. Whether or not one thinks these are good pieces of advice, we do not take them to fall within the realm of grammar. A sentence like In this day and age one must circle round and explore every avenue may be loaded with careworn verbiage, or it may even be arrant nonsense, but there is absolutely ...
... on. Whether or not one thinks these are good pieces of advice, we do not take them to fall within the realm of grammar. A sentence like In this day and age one must circle round and explore every avenue may be loaded with careworn verbiage, or it may even be arrant nonsense, but there is absolutely ...
Chapter 1 - National Taiwan University
... write system specifications. Additionally, we mentioned that system specifications should be consistent. That is, we should be able to assign truth values to propositions such that all requirements are satisfied. In Example 2, we are lucky to have simple requirements where there are only 2 propositions ...
... write system specifications. Additionally, we mentioned that system specifications should be consistent. That is, we should be able to assign truth values to propositions such that all requirements are satisfied. In Example 2, we are lucky to have simple requirements where there are only 2 propositions ...
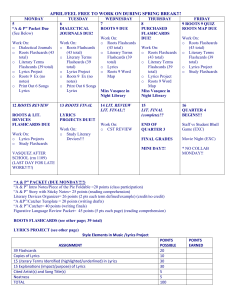
APRIL2010Reminders
... of that is more than its basic meaning Denotation: dictionary definition; the exact meaning of a word, without the feelings or suggestions that the word may imply. It is the opposite of “connotation Dialect: a form of a language which is spoken only in one area, with words or grammar that are slight ...
... of that is more than its basic meaning Denotation: dictionary definition; the exact meaning of a word, without the feelings or suggestions that the word may imply. It is the opposite of “connotation Dialect: a form of a language which is spoken only in one area, with words or grammar that are slight ...
On Verbal Competence - Journal of Arts and Humanities
... The intentional notion is the very idea or feeling that you intend to get across to the listener, but it is not yet verbalized. It is a notion that the speaker intends to convey. This is why it is called intentional notion. The intentional notion is nonverbal by nature, and can be verbalized in diff ...
... The intentional notion is the very idea or feeling that you intend to get across to the listener, but it is not yet verbalized. It is a notion that the speaker intends to convey. This is why it is called intentional notion. The intentional notion is nonverbal by nature, and can be verbalized in diff ...
Structuralism 1. The nature of meaning or understanding.
... particular relationship within a society (e.g., between a male offspring and his maternal uncle) can only be understood in the context of the whole system of kinship. Structuralism holds that, according to the human way of understanding things, particular elements have no absolute meaning or value: ...
... particular relationship within a society (e.g., between a male offspring and his maternal uncle) can only be understood in the context of the whole system of kinship. Structuralism holds that, according to the human way of understanding things, particular elements have no absolute meaning or value: ...
Topic 2
... subjects – lexicology, phonology, morphology, syntax, and even philosophy and psychology. As a result there exist many definitions of the term “word”, they are specific for each field of study and are considered one-sided by the representatives of all other domains (область знаний). But in our pract ...
... subjects – lexicology, phonology, morphology, syntax, and even philosophy and psychology. As a result there exist many definitions of the term “word”, they are specific for each field of study and are considered one-sided by the representatives of all other domains (область знаний). But in our pract ...
Dowload PowerPoint
... process of extracting the commonality inherent in multiple experiences to arrive at a conception representing a higher level of abstraction” (Langacker, 17). ...
... process of extracting the commonality inherent in multiple experiences to arrive at a conception representing a higher level of abstraction” (Langacker, 17). ...
Propositional Logic: Part I - Semantics
... Propositional logic is a formal mathematical system for reasoning about such statements. The first statement p is an atomic proposition. It cannot be further subdivided. The 2nd statement q is a compound proposition that’s truth depends upon the value of the two atomic propositions: 1. h:“We are hun ...
... Propositional logic is a formal mathematical system for reasoning about such statements. The first statement p is an atomic proposition. It cannot be further subdivided. The 2nd statement q is a compound proposition that’s truth depends upon the value of the two atomic propositions: 1. h:“We are hun ...
Topic 2
... phonology, morphology, syntax, and even philosophy and psychology. As a result there exist many definitions of the term “word”, they are specific for each field of study and are considered one-sided by the representatives of all ...
... phonology, morphology, syntax, and even philosophy and psychology. As a result there exist many definitions of the term “word”, they are specific for each field of study and are considered one-sided by the representatives of all ...