THE DEFENITION OF SEMANTICS
... This discipline, of which hakia.com's ontological semantics is the most advanced school, studies the meaning of sentences and texts as they are understood intuitively by native speakers. Because native speakers have internalized large lexicons, based presumably on a large ontology, as well as the ru ...
... This discipline, of which hakia.com's ontological semantics is the most advanced school, studies the meaning of sentences and texts as they are understood intuitively by native speakers. Because native speakers have internalized large lexicons, based presumably on a large ontology, as well as the ru ...
Hermeneutics - New Life Apostolic Church
... • Definition: a sum or stock of words employed by a language, group, individuals, or work or in a field of knowledge. • There are four essential elements • Etymology (history), comparative study, cultural meaning and the cognate (equivalent) of the words being studied. ...
... • Definition: a sum or stock of words employed by a language, group, individuals, or work or in a field of knowledge. • There are four essential elements • Etymology (history), comparative study, cultural meaning and the cognate (equivalent) of the words being studied. ...
4. Overview of Meaning Proto
... • They argued that all significant statements are either – Analy6c or contradictory (e.g., they are logic); or – Can be tested by experience. ...
... • They argued that all significant statements are either – Analy6c or contradictory (e.g., they are logic); or – Can be tested by experience. ...
miss-freys-back-to-school-night-presentation
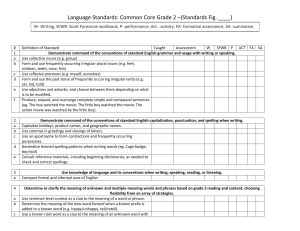
... • Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies • Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. • Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a kn ...
... • Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies • Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. • Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a kn ...
Slide 1
... Language is very difficult to put into words. -- Voltaire What do we mean by “language”? A system used to convey meaning made up of arbitrary elements that are organized using a set of rules. -- Rader ...
... Language is very difficult to put into words. -- Voltaire What do we mean by “language”? A system used to convey meaning made up of arbitrary elements that are organized using a set of rules. -- Rader ...