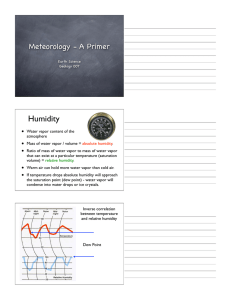
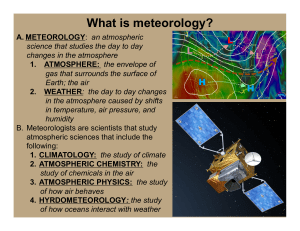
Study guide for Atmosphere, Weather, and Climate Test (Chap 24)
... _________(a) Snow melts in a narrow warm air layer aloft, but has time to refreeze before hitting the ground _________(b) Snow melts in a deep (thick) warm air layer aloft, but does not have time to refreeze while falling. So this type of precip freezes on the ground and on surfaces. _________(c) Th ...
... _________(a) Snow melts in a narrow warm air layer aloft, but has time to refreeze before hitting the ground _________(b) Snow melts in a deep (thick) warm air layer aloft, but does not have time to refreeze while falling. So this type of precip freezes on the ground and on surfaces. _________(c) Th ...
Meteorology Test On a July day large cumulonimbus clouds are
... d. In the Arctic Ocean north of Canada 8. In some years there are more hurricanes than usual. This is probably because a. The ocean is warmer than usual b. The ozone layer is very thin c. The gravitational pull of the Moon is stronger d. There are more windy days 9. An air mass gets its temperature ...
... d. In the Arctic Ocean north of Canada 8. In some years there are more hurricanes than usual. This is probably because a. The ocean is warmer than usual b. The ozone layer is very thin c. The gravitational pull of the Moon is stronger d. There are more windy days 9. An air mass gets its temperature ...
Meteorology Test On a July day large cumulonimbus clouds are
... d. In the Arctic Ocean north of Canada 8. In some years there are more hurricanes than usual. This is probably because a. The ocean is warmer than usual b. The ozone layer is very thin c. The gravitational pull of the Moon is stronger d. There are more windy days 9. An air mass gets its temperature ...
... d. In the Arctic Ocean north of Canada 8. In some years there are more hurricanes than usual. This is probably because a. The ocean is warmer than usual b. The ozone layer is very thin c. The gravitational pull of the Moon is stronger d. There are more windy days 9. An air mass gets its temperature ...
File - Winnipeg Ground School
... **HINT** We know that winds will increase during the day... remember diurnal variation and the “convective link” between the upper winds and the surface winds... well also remember that when the winds increase in speed, they also usually veer! ...
... **HINT** We know that winds will increase during the day... remember diurnal variation and the “convective link” between the upper winds and the surface winds... well also remember that when the winds increase in speed, they also usually veer! ...
Weather Tools and Symbols - Milton 7th Grade Advanced Science
... condense, and form clouds. Severe weather could result. ...
... condense, and form clouds. Severe weather could result. ...
Section 6.2
... 6.2 Rain • Rain is the result of a cooling air mass. • Cooling an air mass is like wringing out a wet sponge. • Tiny droplets form a cloud or fog. • Larger droplets fall as rain. ...
... 6.2 Rain • Rain is the result of a cooling air mass. • Cooling an air mass is like wringing out a wet sponge. • Tiny droplets form a cloud or fog. • Larger droplets fall as rain. ...
6.2 Cloud formation
... 6.2 Rain • Rain is the result of a cooling air mass. • Cooling an air mass is like wringing out a wet sponge. • Tiny droplets form a cloud or fog. • Larger droplets fall as rain. ...
... 6.2 Rain • Rain is the result of a cooling air mass. • Cooling an air mass is like wringing out a wet sponge. • Tiny droplets form a cloud or fog. • Larger droplets fall as rain. ...
Thermosphere
... 18. How is the pH of acid rain different from the pH of normal rain? • pH of acid rain is lower than normal rain 19. Explain the negative affects of acid rain. Can affect crops, organisms living in the water, damage buildings 20. How is smog formed? • Pollutants in the air react with sunlight ...
... 18. How is the pH of acid rain different from the pH of normal rain? • pH of acid rain is lower than normal rain 19. Explain the negative affects of acid rain. Can affect crops, organisms living in the water, damage buildings 20. How is smog formed? • Pollutants in the air react with sunlight ...
WEATHER
... a. reflection – light bounces off a surface; ex. oceans reflect light - albedo effect – reflectiveness of a surface; ex. snow & white shirt – high ...
... a. reflection – light bounces off a surface; ex. oceans reflect light - albedo effect – reflectiveness of a surface; ex. snow & white shirt – high ...
Meteorology_Study_Guide
... ______ 4. The layer above the stratosphere where temperature begins to fall again ______ 5. The boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere ______ 6. This layer shields life from ultraviolet radiation from the Sun ______ 7. This layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer ______ 8. The mi ...
... ______ 4. The layer above the stratosphere where temperature begins to fall again ______ 5. The boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere ______ 6. This layer shields life from ultraviolet radiation from the Sun ______ 7. This layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer ______ 8. The mi ...
Meteorology
... Low clouds are mostly formed of water droplets since their bases lie below 6,500 feet (2,000 meters). However, these clouds may also contain ice particles and snow. Vertical clouds form by thermal convection or frontal lifting and can grow to heights in excess of 39,000 feet (12,000 meters). ...
... Low clouds are mostly formed of water droplets since their bases lie below 6,500 feet (2,000 meters). However, these clouds may also contain ice particles and snow. Vertical clouds form by thermal convection or frontal lifting and can grow to heights in excess of 39,000 feet (12,000 meters). ...
43 Weather
... water gets warmer, some of it evaporates, which means it changes from a li'luid to water vapor in the air. ...
... water gets warmer, some of it evaporates, which means it changes from a li'luid to water vapor in the air. ...
ExamView Pro - Untitled.tst
... 33. the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place 34. Climate refers to weather patterns that have been observed over many years. 35. air temperature, humidity, type and amount of precipitation, air pressure, and the speed and direction of the wind 36. Seasons occur because Earth’s axis is ...
... 33. the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place 34. Climate refers to weather patterns that have been observed over many years. 35. air temperature, humidity, type and amount of precipitation, air pressure, and the speed and direction of the wind 36. Seasons occur because Earth’s axis is ...
Meteorology Unit Test Study Guide
... 32. Which type of cloud is puffy and white and has a flat base? cumulus. 33. Which type of clouds are low and sheet like? Stratus They form layers in the sky. 34. What type of cloud is fog? stratus 35. Which cloud prefix means “high?” cirro 36. Which cloud prefix means “low?” strato 37. Which cloud ...
... 32. Which type of cloud is puffy and white and has a flat base? cumulus. 33. Which type of clouds are low and sheet like? Stratus They form layers in the sky. 34. What type of cloud is fog? stratus 35. Which cloud prefix means “high?” cirro 36. Which cloud prefix means “low?” strato 37. Which cloud ...
Chapter 16 Outline (Weather) fill in PART 1
... i. Barometer (tool used to measure pressure) 1. Mercury (less common) 2. Aneroid “without liquid” (more current tool) d. Weather related air pressure (generally speaking) i. Air pressure rises as __________________________of air come together in upper atmosphere ______________________________ on low ...
... i. Barometer (tool used to measure pressure) 1. Mercury (less common) 2. Aneroid “without liquid” (more current tool) d. Weather related air pressure (generally speaking) i. Air pressure rises as __________________________of air come together in upper atmosphere ______________________________ on low ...
Weather
... • In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right. • In the Southern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the left. ...
... • In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right. • In the Southern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the left. ...
Worksheet 2
... The (14) _______________________ deflects moving air to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The cause of this is Earth’s (15) __________________. Each hemisphere has three basic wind systems. The first, at 30O latitude north and south, is known as the (16 ...
... The (14) _______________________ deflects moving air to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The cause of this is Earth’s (15) __________________. Each hemisphere has three basic wind systems. The first, at 30O latitude north and south, is known as the (16 ...
Chapter 19 Test Review Notes
... three-celled model of Earth’s wind patterns. • The circulation at mid-latitudes has been simplified. • Continents and seasons are not taken into account. • Upper-level winds have been simplified. ...
... three-celled model of Earth’s wind patterns. • The circulation at mid-latitudes has been simplified. • Continents and seasons are not taken into account. • Upper-level winds have been simplified. ...
Weather/Climate Vocabulary Matching
... #45 seasons #46 climate zone #47 microclimate #48 rain shadows ...
... #45 seasons #46 climate zone #47 microclimate #48 rain shadows ...
Study Guide for Weather Test :(gases, air pressure, layers of
... Normal greenhouse effect—a natural process. Keeps Earth warm. (See pollution section at bottom of page.) Gases: Nitrogen 78 % Oxygen 21% Trace gases 1% (know some of them too!) What is Ozone (O3) and what does it do? (good and bad) Water vapor- runs from 0%- 5% ( 0%= desert, 5%= rainforest) Other ga ...
... Normal greenhouse effect—a natural process. Keeps Earth warm. (See pollution section at bottom of page.) Gases: Nitrogen 78 % Oxygen 21% Trace gases 1% (know some of them too!) What is Ozone (O3) and what does it do? (good and bad) Water vapor- runs from 0%- 5% ( 0%= desert, 5%= rainforest) Other ga ...
Meteorology_Practice_Test
... d. Impossible to detect 13. What is an air mass? a. A large body of air that has similar characteristics throughout it b. Pressure exerted by a mass of air at a given point c. A boundary that separates a warm air mass from a dry air mass 14. The bending of light as it passes from one medium to anoth ...
... d. Impossible to detect 13. What is an air mass? a. A large body of air that has similar characteristics throughout it b. Pressure exerted by a mass of air at a given point c. A boundary that separates a warm air mass from a dry air mass 14. The bending of light as it passes from one medium to anoth ...
what to know about meteorology list
... 3. Remember: “The flow will go from high to low”. 4. As moisture increases, air pressure decreases (“wet” air is less dense/lighter than “dry” air). 5. Air pressure decreases with altitude; temperature does too! 6. Highs are cool and dry; lows are warm and wet. Remember: “High and Dry”. 7. Wind blow ...
... 3. Remember: “The flow will go from high to low”. 4. As moisture increases, air pressure decreases (“wet” air is less dense/lighter than “dry” air). 5. Air pressure decreases with altitude; temperature does too! 6. Highs are cool and dry; lows are warm and wet. Remember: “High and Dry”. 7. Wind blow ...