Verb Review Sheet
... Directions: Underline the linking verb and circle the predicate word. Label the predicate word with a PA for predicate adjective or PN for predicate noun. 11. Not all snakes are poisonous. 12. About a dozen snake species are rare. 13. One endangered snake is the indigo. 14. Indigos seem very friendl ...
... Directions: Underline the linking verb and circle the predicate word. Label the predicate word with a PA for predicate adjective or PN for predicate noun. 11. Not all snakes are poisonous. 12. About a dozen snake species are rare. 13. One endangered snake is the indigo. 14. Indigos seem very friendl ...
THE PARTS OF SPEECH (BASIC OVERVIEW)
... ADJECTIVE: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a noun. i.e. blue, sharp, scary, happy, his, Jennifer’s, old ARTICLE: a specific kind of adjective meaning “this, specific, singular.” i.e. the, a, an ADVERB: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a verb, an a ...
... ADJECTIVE: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a noun. i.e. blue, sharp, scary, happy, his, Jennifer’s, old ARTICLE: a specific kind of adjective meaning “this, specific, singular.” i.e. the, a, an ADVERB: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a verb, an a ...
1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order
... 1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order pattern: subject + ( frequency adverb ) + verb + indirect object + direct object + manner + place + time adverbials 2- SUBJECT – VERB AGREEMENT: “People are friendly” 3- ADJECTIVES: Adjectives come before nouns and don’t change form: “She ha ...
... 1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order pattern: subject + ( frequency adverb ) + verb + indirect object + direct object + manner + place + time adverbials 2- SUBJECT – VERB AGREEMENT: “People are friendly” 3- ADJECTIVES: Adjectives come before nouns and don’t change form: “She ha ...
Word Structure
... Use of the suffixes –er and –est to form comparisons of adverbs and adjectives. ...
... Use of the suffixes –er and –est to form comparisons of adverbs and adjectives. ...
Verb Tense Exercises
... • Past perfect has particular uses, and we do not see it as often as the other tenses. It is used for a point in time earlier than another moment. • We had been at the restaurant for over an hour when James finally arrived at 8:15. (We were there at 7:00; James showed up at 8:15). ...
... • Past perfect has particular uses, and we do not see it as often as the other tenses. It is used for a point in time earlier than another moment. • We had been at the restaurant for over an hour when James finally arrived at 8:15. (We were there at 7:00; James showed up at 8:15). ...
Parts of Speech - s3.amazonaws.com
... An adverb can modify (describe) a verb, an adjective, another adverb. The ...
... An adverb can modify (describe) a verb, an adjective, another adverb. The ...
The dreaded grammar cards
... A Clause is group of words with a subject and a predicate. 1) An Independent Clause can stand alone as a sentence and is a complete thought: I ride my bike to ...
... A Clause is group of words with a subject and a predicate. 1) An Independent Clause can stand alone as a sentence and is a complete thought: I ride my bike to ...
Introduction to Phrases
... is an extension of that idea. Using appositive phrases allows writers to be concise in their language and helps not to be “wordy.” Punctuation is important. The ACT loves to assess on simple things like punctuation. This falls under the “pick the BEST answer.” ...
... is an extension of that idea. Using appositive phrases allows writers to be concise in their language and helps not to be “wordy.” Punctuation is important. The ACT loves to assess on simple things like punctuation. This falls under the “pick the BEST answer.” ...
GRAMMAR STUDY-4 - ITS
... used to show similarity between two or more noun structures. It usually follows the noun structures it describes. (UN)LIKE means not like and is a preposition which must be followed by an object. My brother and my sister are very much alike. Like my brother, my sister enjoys playing chess. • ALMOST ...
... used to show similarity between two or more noun structures. It usually follows the noun structures it describes. (UN)LIKE means not like and is a preposition which must be followed by an object. My brother and my sister are very much alike. Like my brother, my sister enjoys playing chess. • ALMOST ...
Guidelines for preparing parts of speech
... Germans, Kennedys, 1970's or 1970s Pronoun It, I, she, themselves, ours, mine Type Examples Adjective five cents, quick man, largest tree Article the, a, an Verb acting as an adjective Striped shirt, stinking (ex. gerunds) badges Determiner This chair, each man, another win, that dog Type Examples V ...
... Germans, Kennedys, 1970's or 1970s Pronoun It, I, she, themselves, ours, mine Type Examples Adjective five cents, quick man, largest tree Article the, a, an Verb acting as an adjective Striped shirt, stinking (ex. gerunds) badges Determiner This chair, each man, another win, that dog Type Examples V ...
practical assignment
... three grammatical genders: masculine, feminine, neuter. For nouns with clear sexual gender, the grammatical gender generally agrees with the sexual gender. For example, qēns “woman” is feminine, so that natural gender and grammatical gender agree; but graba “ditch” is also feminine, though the refer ...
... three grammatical genders: masculine, feminine, neuter. For nouns with clear sexual gender, the grammatical gender generally agrees with the sexual gender. For example, qēns “woman” is feminine, so that natural gender and grammatical gender agree; but graba “ditch” is also feminine, though the refer ...
Glossary of grammatical terms for parents
... We can use a conjunction to join these sentences together: She went to the shops and bought a box of chocolates. Other conjunctions include: but, as, so, or, because, if, … ...
... We can use a conjunction to join these sentences together: She went to the shops and bought a box of chocolates. Other conjunctions include: but, as, so, or, because, if, … ...
The verbal system in Old English (grammatical categories
... Like the Dat. case of nouns the inflected Infinitive with the preposition tō could be used to indicate the direction or purpose of an action. The uninflected Infinitive was used in verb phrases with modal verbs or other verbs of incomplete predication. The Participle was a kind of verbal adjective w ...
... Like the Dat. case of nouns the inflected Infinitive with the preposition tō could be used to indicate the direction or purpose of an action. The uninflected Infinitive was used in verb phrases with modal verbs or other verbs of incomplete predication. The Participle was a kind of verbal adjective w ...
Adjectives, Nouns, Verbs,
... Examples of words that are verbs are: run, walk, jump, swing, swim Verbs can change to show past, present, & future action. Examples are: run, hopped, sleep Check out this example of a verb in a sentence: ...
... Examples of words that are verbs are: run, walk, jump, swing, swim Verbs can change to show past, present, & future action. Examples are: run, hopped, sleep Check out this example of a verb in a sentence: ...
DOC
... 4. She is washing her face. 5. They were going home. 6. We were playing on the lawn. 7. Ellie and Zoe were singing out of tune. 8. Emily and Maddy were singing in the choir. 9. She was not working hard. 10.They are coming home with us. 11. Zara is feeling ill. 12. Kate is running in the last race. 1 ...
... 4. She is washing her face. 5. They were going home. 6. We were playing on the lawn. 7. Ellie and Zoe were singing out of tune. 8. Emily and Maddy were singing in the choir. 9. She was not working hard. 10.They are coming home with us. 11. Zara is feeling ill. 12. Kate is running in the last race. 1 ...
seventh grade notes
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
Parts of Speech
... Subordinating conjunctions (SC) introduce subordinate clauses and indicate the relation of the clause to the rest of the sentence: after, although, because, before, though, unless, until, where, whether, while SC ...
... Subordinating conjunctions (SC) introduce subordinate clauses and indicate the relation of the clause to the rest of the sentence: after, although, because, before, though, unless, until, where, whether, while SC ...
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, SRINAGAR REVISION WORKSHEET
... Examples: Delhi, table, cat, Manoj etc. 2. Common Nouns are names of people, places, animals or things of same kind. Examples: Girl, car, pen etc. 3. Proper Noun are special names of people, places, animals or things. Proper nouns always ...
... Examples: Delhi, table, cat, Manoj etc. 2. Common Nouns are names of people, places, animals or things of same kind. Examples: Girl, car, pen etc. 3. Proper Noun are special names of people, places, animals or things. Proper nouns always ...
Parts of Speech - Rocky View Schools
... Action verbs can be active (Joel hit the ball) or passive (The ball was hit by Joel). Indicate whether the verb in each sentence is active or passive. (a) The moose ran into the street. ______________________________________________________________ (b) The bus was struck by the moose. ______________ ...
... Action verbs can be active (Joel hit the ball) or passive (The ball was hit by Joel). Indicate whether the verb in each sentence is active or passive. (a) The moose ran into the street. ______________________________________________________________ (b) The bus was struck by the moose. ______________ ...
The Grammar Book, Chapter 2, part 2
... It is best “to think of a particular part of speech as being determined by a cluster of criteria . . . . it is not simple to define even the most elemental building blocks of grammar, the parts of speech.” – Linguistics often prefer to use the terms lexical category ...
... It is best “to think of a particular part of speech as being determined by a cluster of criteria . . . . it is not simple to define even the most elemental building blocks of grammar, the parts of speech.” – Linguistics often prefer to use the terms lexical category ...
Infinitives vs. Gerunds An infinitive is the full form of a
... A gerund looks like a verb with the progressive “-ing” ending but really functions as a noun instead: How do you know which one to use? First, use these two general principles: 1. In general, when you want to use a verb as the subject, use the gerund form. (Using the infinitive is acceptable in writ ...
... A gerund looks like a verb with the progressive “-ing” ending but really functions as a noun instead: How do you know which one to use? First, use these two general principles: 1. In general, when you want to use a verb as the subject, use the gerund form. (Using the infinitive is acceptable in writ ...
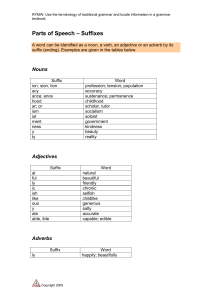
Parts of Speech – Suffixes
... Adding suffixes to words can change or add to their meaning, but most importantly they show how a word will be used in a sentence and what part of speech (e.g. noun, verb, adjective) the word belongs to. Creating words banks is one way of helping learners build their vocabulary base. Look at the exa ...
... Adding suffixes to words can change or add to their meaning, but most importantly they show how a word will be used in a sentence and what part of speech (e.g. noun, verb, adjective) the word belongs to. Creating words banks is one way of helping learners build their vocabulary base. Look at the exa ...
Week 21
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...