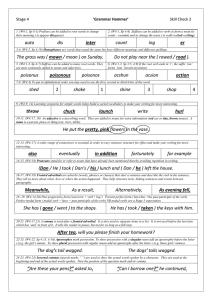
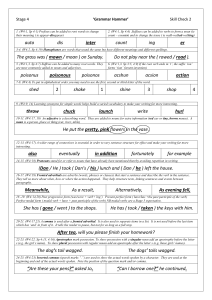
sub inter super play er ing The ( poor / pour ) child was lost. She
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
Verb Review
... b. asks students to review those verbs (either individually or in groups) c. writes a sentence on the board that describes a group of those verbs i. Things we do with our feet ii. Things we do alone, etc. d. asks students to make a list of the verbs that fit into that sentence (either individually o ...
... b. asks students to review those verbs (either individually or in groups) c. writes a sentence on the board that describes a group of those verbs i. Things we do with our feet ii. Things we do alone, etc. d. asks students to make a list of the verbs that fit into that sentence (either individually o ...
Stage 4 Check 2 – Answers
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
Stage 4 Check 2 – Answers
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
VERBS
... relation to another event in the past. Uses had and past participle form of main verb ...
... relation to another event in the past. Uses had and past participle form of main verb ...
Sentence Structure
... (In this example, the answer to the question who? or what? after the verb is the job. Shag answers to the question to whom?) Josephine gave Shag the job. S + V + indO + dirO We can rephrase the sentence as: Josephine gave the job to Shag. S + V + dirO + indO Note: Some other verbs which take an indi ...
... (In this example, the answer to the question who? or what? after the verb is the job. Shag answers to the question to whom?) Josephine gave Shag the job. S + V + indO + dirO We can rephrase the sentence as: Josephine gave the job to Shag. S + V + dirO + indO Note: Some other verbs which take an indi ...
Parts of Speech- Verbs - VCC Library
... Some verbs do not describe actions. These verbs talk about how things exist, or what they are similar to. These are called verbs of being. Some examples are be (is, are, were, …), have, seem, feel, sound, and taste. Example: ...
... Some verbs do not describe actions. These verbs talk about how things exist, or what they are similar to. These are called verbs of being. Some examples are be (is, are, were, …), have, seem, feel, sound, and taste. Example: ...
Chapter 12 Parts of Speech Overview
... is a verb that expresses a state of being. It connects, or links, the subject to a word or word group that identifies or describes the ...
... is a verb that expresses a state of being. It connects, or links, the subject to a word or word group that identifies or describes the ...
Actividad 3
... 1. a. The reflexive forms of poner mean “____________” and “_____________”. b. For leer, influir, and contribuir the i becomes a ____ in the _____________ & _____________ forms. c. Other verbs that follow the same pattern in the Preterite are ___________, ___________, __________& ____________. For t ...
... 1. a. The reflexive forms of poner mean “____________” and “_____________”. b. For leer, influir, and contribuir the i becomes a ____ in the _____________ & _____________ forms. c. Other verbs that follow the same pattern in the Preterite are ___________, ___________, __________& ____________. For t ...
Unit 1 * the 8 Parts of Speech
... B. State of being verbs 1. These verbs do not express an action. 2. They do all of the following: state that something exists, show time, and establish relationships. ...
... B. State of being verbs 1. These verbs do not express an action. 2. They do all of the following: state that something exists, show time, and establish relationships. ...
Verb - WordPress.com
... sentence because a sentence can not convey its meaning without a verb. It makes the fragments a meaningful whole. For example: He and his brother Lahore The use of went makes the sentence meaningful ad combine these fragments. ...
... sentence because a sentence can not convey its meaning without a verb. It makes the fragments a meaningful whole. For example: He and his brother Lahore The use of went makes the sentence meaningful ad combine these fragments. ...
parts of speech here
... 6. Prepositions – words which begin a phrase that shows the relation of a noun to another word in the sentence preposition + noun (object of preposition) = prepositional phrase about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, betw ...
... 6. Prepositions – words which begin a phrase that shows the relation of a noun to another word in the sentence preposition + noun (object of preposition) = prepositional phrase about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, betw ...
Verbs
... – Linking verbs are either forms of “be”, or show a condition Forms of be: is, am, are, was, were, been, being Condition: look, smell, feel, sound, taste, grow, appear, become, seem, remain ...
... – Linking verbs are either forms of “be”, or show a condition Forms of be: is, am, are, was, were, been, being Condition: look, smell, feel, sound, taste, grow, appear, become, seem, remain ...
HELPING VERBS
... The winner of the weekly lottery is determined by a drawing. The Thompsons are arriving at eight o’clock. What was delivered this afternoon? The children were beginning to fall asleep when the phone rang. I will be finished in about an hour. They have been gone a long time. ...
... The winner of the weekly lottery is determined by a drawing. The Thompsons are arriving at eight o’clock. What was delivered this afternoon? The children were beginning to fall asleep when the phone rang. I will be finished in about an hour. They have been gone a long time. ...
What is a verb?
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The most common linking verbs are: Be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being, appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, ...
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The most common linking verbs are: Be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being, appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, ...
AHSGE Test Vocabulary
... made when two independent clauses are connected (spliced) with only a comma. ...
... made when two independent clauses are connected (spliced) with only a comma. ...
AHSGE Test Vocabulary - Tarrant City Schools
... made when two independent clauses are connected (spliced) with only a comma. ...
... made when two independent clauses are connected (spliced) with only a comma. ...
NOUNS-VERBS-ADJECTIVES
... 6. If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again. 7. Bill is a fast learner who eats chocolate ice cream in large buckets. 8. Every April Fools’ Day we look for Easter eggs under the Christmas tree. 9. I work out at the gym every Thursday of every other month. 10. Black onions are rotten to the core ...
... 6. If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again. 7. Bill is a fast learner who eats chocolate ice cream in large buckets. 8. Every April Fools’ Day we look for Easter eggs under the Christmas tree. 9. I work out at the gym every Thursday of every other month. 10. Black onions are rotten to the core ...
Phrases - Huber Heights City Schools
... Phrases- a group of related words without a verb and subject which also serves as an entire unit and acts as one part of speech [Verb phrase- consists of a main verb and helping verbs but all serve together as one verb] [Absolute phrase – consists of a n or pron modified by a participle and has no g ...
... Phrases- a group of related words without a verb and subject which also serves as an entire unit and acts as one part of speech [Verb phrase- consists of a main verb and helping verbs but all serve together as one verb] [Absolute phrase – consists of a n or pron modified by a participle and has no g ...
Verbs Verbs are word which describes the action in a sentence (the
... Verbs are word which describes the action in a sentence (the doing word) Verb: the most important component of any sentence. These words talk about the action or the state of any noun or subject. This means that verbs show what the subject is doing or what is the state or situation of the subject. E ...
... Verbs are word which describes the action in a sentence (the doing word) Verb: the most important component of any sentence. These words talk about the action or the state of any noun or subject. This means that verbs show what the subject is doing or what is the state or situation of the subject. E ...
to pdf lesson
... the present and was and were in the past. They combine with the present participle form of the verb. ...
... the present and was and were in the past. They combine with the present participle form of the verb. ...
Lexical semantics

Lexical semantics (also known as lexicosemantics), is a subfield of linguistic semantics. The units of analysis in lexical semantics are lexical units which include not only words but also sub-words or sub-units such as affixes and even compound words and phrases. Lexical units make up the catalogue of words in a language, the lexicon. Lexical semantics looks at how the meaning of the lexical units correlates with the structure of the language or syntax. This is referred to as syntax-semantic interface.The study of lexical semantics looks at: the classification and decomposition of lexical items the differences and similarities in lexical semantic structure cross-linguistically the relationship of lexical meaning to sentence meaning and syntax.Lexical units, also referred to as syntactic atoms, can stand alone such as in the case of root words or parts of compound words or they necessarily attach to other units such as prefixes and suffixes do. The former are called free morphemes and the latter bound morphemes. They fall into a narrow range of meanings (semantic fields) and can combine with each other to generate new meanings.