The Eight Parts of Speech
... Definition: A word used in the place of a noun ◦ all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, ...
... Definition: A word used in the place of a noun ◦ all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, ...
Part of Speech PowerPoint Presentation
... -Definition: A word that shows the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word. - ANYWHERE A MOUSE COULD GO! - Examples: Aboard, below, from, since, about, beneath, throughout, concerning, past, and ...
... -Definition: A word that shows the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word. - ANYWHERE A MOUSE COULD GO! - Examples: Aboard, below, from, since, about, beneath, throughout, concerning, past, and ...
Grammar and Usage Student Help Desk
... Adverbs answer HOW?, WHEN?, WHERE?, or TO WHAT EXTENT?. Adverbs can appear in several different positions. Shari completed the exam quickly. Shari quickly completed the exam. Quickly, Shari completed the exam. Intensifiers: Adverbs that modify adjectives or other adverbs. They are usually placed dir ...
... Adverbs answer HOW?, WHEN?, WHERE?, or TO WHAT EXTENT?. Adverbs can appear in several different positions. Shari completed the exam quickly. Shari quickly completed the exam. Quickly, Shari completed the exam. Intensifiers: Adverbs that modify adjectives or other adverbs. They are usually placed dir ...
basic terms used in english
... 5. He sees a bear. 6. The bear walks on its hind legs. 7. People hold a festival in South Korea. 8. This festival is special. 9. It is a mud festival. 10. It is held every year. 11. Korean people are known for strange things. 12. it's not surprising for me that this annual event hold in south Korea. ...
... 5. He sees a bear. 6. The bear walks on its hind legs. 7. People hold a festival in South Korea. 8. This festival is special. 9. It is a mud festival. 10. It is held every year. 11. Korean people are known for strange things. 12. it's not surprising for me that this annual event hold in south Korea. ...
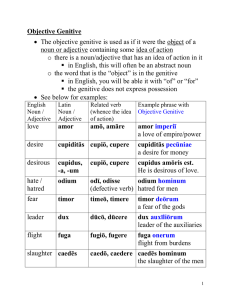
Objective Genitive + Ablative Separation
... Objective Genitive The objective genitive is used as if it were the object of a noun or adjective containing some idea of action o there is a noun/adjective that has an idea of action in it in English, this will often be an abstract noun o the word that is the “object” is in the genitive in En ...
... Objective Genitive The objective genitive is used as if it were the object of a noun or adjective containing some idea of action o there is a noun/adjective that has an idea of action in it in English, this will often be an abstract noun o the word that is the “object” is in the genitive in En ...
Language Arts Tutoring Referral Form
... In order to help you improve your skills and comprehension in this course, you are advised to seek a tutor’s assistance in the Learning Center (AD 232). Specific Topic / Assignment ________________________________________________ ...
... In order to help you improve your skills and comprehension in this course, you are advised to seek a tutor’s assistance in the Learning Center (AD 232). Specific Topic / Assignment ________________________________________________ ...
1 -2- Lexical word classes Lexical Words There are four main
... ( totally wrong) ( right now). As elements of clauses ( adverbials), adverbs and adverb phrases have a wide range of meanings: ...
... ( totally wrong) ( right now). As elements of clauses ( adverbials), adverbs and adverb phrases have a wide range of meanings: ...
Gerunds, participles, and infinitives
... Even when infinitives act like another part of speech, they keep their verb traits. Infinitives are still verbs. They express action or state of being, but they are never the main verb in a sentence. Infinitives can take a direct object and they can be modified by an adverb just like a regular verb. ...
... Even when infinitives act like another part of speech, they keep their verb traits. Infinitives are still verbs. They express action or state of being, but they are never the main verb in a sentence. Infinitives can take a direct object and they can be modified by an adverb just like a regular verb. ...
Chapter 6: Aspect (式、貌)
... Aspect is a morpheme used to signal the duration or completion of a reported event relative to other events. (aspect = the duration/completion of an acitivity) Four types of aspect markers in Mandarin 6.1 Perfective aspect: -le 6.1.1. Where to use –le: A bounded event Perfective -le is used in the f ...
... Aspect is a morpheme used to signal the duration or completion of a reported event relative to other events. (aspect = the duration/completion of an acitivity) Four types of aspect markers in Mandarin 6.1 Perfective aspect: -le 6.1.1. Where to use –le: A bounded event Perfective -le is used in the f ...
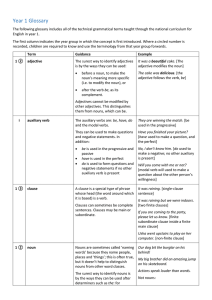
Year 1 Grammar glossary
... The following glossary includes all of the technical grammatical terms taught through the national curriculum for English in year 1. The first column indicates the year group in which the concept is first introduced. Where a circled number is recorded, children are required to know and use the termi ...
... The following glossary includes all of the technical grammatical terms taught through the national curriculum for English in year 1. The first column indicates the year group in which the concept is first introduced. Where a circled number is recorded, children are required to know and use the termi ...
Grammar Notes: ”Parts of Speech”
... COMMONLY USED PREPOSITIONS • about, before, down, in, of, since • above, behind, during, inside, off, through • across, beside, except, into, onto, toward • after, between, for, like, outside, until • at, by, from, near, over, without *** ____________ the lake (Phrase to help you) A Preposition wil ...
... COMMONLY USED PREPOSITIONS • about, before, down, in, of, since • above, behind, during, inside, off, through • across, beside, except, into, onto, toward • after, between, for, like, outside, until • at, by, from, near, over, without *** ____________ the lake (Phrase to help you) A Preposition wil ...
Parts of Speech PowerPoint
... As As if As long as As though Because Before Even if Even though Except If In order that ...
... As As if As long as As though Because Before Even if Even though Except If In order that ...
INFINITIVES vs. GERUNDS
... Afford, agree, ask, decide, demand, deserve, expect, hesitate, hope, intend, know how, learn, need, offer, plan, pretend, promise, refuse, want, would like o Verbs followed by a GERUND: Appreciate, avoid, can’t help, consider, delay, detest, discuss, dislike, dread, enjoy, finish, get through, g ...
... Afford, agree, ask, decide, demand, deserve, expect, hesitate, hope, intend, know how, learn, need, offer, plan, pretend, promise, refuse, want, would like o Verbs followed by a GERUND: Appreciate, avoid, can’t help, consider, delay, detest, discuss, dislike, dread, enjoy, finish, get through, g ...
Grammar Name Date A noun is a word that names a person, place
... 5. Collective nouns are nouns that name a group of persons and things, but are singular in form. Examples include herd, class, jury, audience, family, etc. And yes, there are also common nouns, but four of the five categories above take care of them. Unlike verbs, which appear only once in a simple ...
... 5. Collective nouns are nouns that name a group of persons and things, but are singular in form. Examples include herd, class, jury, audience, family, etc. And yes, there are also common nouns, but four of the five categories above take care of them. Unlike verbs, which appear only once in a simple ...
Parts of Speech - cloudfront.net
... Words, which are the building blocks of language, are used in eight different ways. They have, therefore, eight different names, called PARTS OF SPEECH. These parts of speech are: NOUN, PRONOUN, ADJECTIVE, VERB, ADVERB, PREPOSITION, CONJUNCTION, AND INTERJCTION. Each of these parts of speech can be ...
... Words, which are the building blocks of language, are used in eight different ways. They have, therefore, eight different names, called PARTS OF SPEECH. These parts of speech are: NOUN, PRONOUN, ADJECTIVE, VERB, ADVERB, PREPOSITION, CONJUNCTION, AND INTERJCTION. Each of these parts of speech can be ...
study guide
... C. Look at Lise’s schedule and decide whether each statement is a) vrai or b) faux Questions will involve the 24 hours clock. (16h00 = ?? :00) D. Read Jérôme’s letter and then underline the right word to complete each sentence. Vocabulaire E. Listen to the sentences and decide whether the speaker is ...
... C. Look at Lise’s schedule and decide whether each statement is a) vrai or b) faux Questions will involve the 24 hours clock. (16h00 = ?? :00) D. Read Jérôme’s letter and then underline the right word to complete each sentence. Vocabulaire E. Listen to the sentences and decide whether the speaker is ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... Here are some examples: A, An, The A book fell on the floor. An article is used before a noun. The test was easy. ...
... Here are some examples: A, An, The A book fell on the floor. An article is used before a noun. The test was easy. ...
LECTURE 10
... Note 1: The subjunctive present tense is the same as the indicative past tense. Note 2: The subjunctive past tense is the same as the indicative past perfect tense. Note 3: In the consequence clause, we use the conditional, which is formed with could or would. Infinitive mood ...
... Note 1: The subjunctive present tense is the same as the indicative past tense. Note 2: The subjunctive past tense is the same as the indicative past perfect tense. Note 3: In the consequence clause, we use the conditional, which is formed with could or would. Infinitive mood ...
Estructuras Gramaticales Leccion 6 with blanks
... iii. Adjectives that express a __________________________________ about the modified noun are usually placed before the noun. iv. __________, _____________, and ___________indefinite adjectives and ________ and _________ numbers are also placed before the noun. v. The adjectives _________ and ______ ...
... iii. Adjectives that express a __________________________________ about the modified noun are usually placed before the noun. iv. __________, _____________, and ___________indefinite adjectives and ________ and _________ numbers are also placed before the noun. v. The adjectives _________ and ______ ...
Grammar Study Guide 2013
... Pronouns Replace nouns (usually short words) Endings one, body, thing, self, and selves make words pronouns Antecedent – The noun the pronoun replaces Indefinite Pronouns (plus words ending in one, body, and thing) all both few more neither several another each little most none some any either many ...
... Pronouns Replace nouns (usually short words) Endings one, body, thing, self, and selves make words pronouns Antecedent – The noun the pronoun replaces Indefinite Pronouns (plus words ending in one, body, and thing) all both few more neither several another each little most none some any either many ...
Parts of Speech - Cloudfront.net
... here during a national tour. When: Will they be returning soon? How: Everyone played magnificently. To what extent: The auditorium was completely full. ...
... here during a national tour. When: Will they be returning soon? How: Everyone played magnificently. To what extent: The auditorium was completely full. ...
Grammar Objectives Overview
... Word families based on common words, showing how words are related in form and meaning (e.g. solve, solution, solver, dissolve, insoluble) The grammatical difference between plural and possessive –s Standard English forms for verb inflections instead of local spoken forms (e.g. we were instead of we ...
... Word families based on common words, showing how words are related in form and meaning (e.g. solve, solution, solver, dissolve, insoluble) The grammatical difference between plural and possessive –s Standard English forms for verb inflections instead of local spoken forms (e.g. we were instead of we ...
Sentence Coding sheet
... Order of Operations 1. Locate Subject 2. Find Simple predicate (Verb & Verb Phrase) Determine whether it is Action verb or Linking Verb. 3a. If Action verb Look for any Direct Objects If there is Direct Object, Check for Indirect objects OR 3b. If you have a linking verb Search for Predicate nom ...
... Order of Operations 1. Locate Subject 2. Find Simple predicate (Verb & Verb Phrase) Determine whether it is Action verb or Linking Verb. 3a. If Action verb Look for any Direct Objects If there is Direct Object, Check for Indirect objects OR 3b. If you have a linking verb Search for Predicate nom ...