Gender, Number, and Case
... certain properties. Aleph (alpha or “a”) was associated with women, bet (beta or “b”) was associated with men. In Latin, nouns that are characterized by –a in the endings are called “feminine” nouns. Once we started categorizing –a nouns as “feminine”, it made sense to categorize other nouns as “mas ...
... certain properties. Aleph (alpha or “a”) was associated with women, bet (beta or “b”) was associated with men. In Latin, nouns that are characterized by –a in the endings are called “feminine” nouns. Once we started categorizing –a nouns as “feminine”, it made sense to categorize other nouns as “mas ...
parts of speech
... Adverbs: Describe, qualify, or limit other elements in the sentence. They modify verbs. Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses. Coordinating Conjunction: Connect elements that are--grammatically speaking—of equal rank. (and, but, or, nor, for, and yet) Subordinating Conjunction: Introduce ...
... Adverbs: Describe, qualify, or limit other elements in the sentence. They modify verbs. Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses. Coordinating Conjunction: Connect elements that are--grammatically speaking—of equal rank. (and, but, or, nor, for, and yet) Subordinating Conjunction: Introduce ...
Slide 1 - Amy Benjamin
... take direct objects. (Direct objects answer “Who?” or “What?” They are used with action verbs only. S-V-SC: Subject-Verb-Subject Complement: This pattern uses a linking verb. Linking verbs require some kind of subject complement to finish the thought. Subject complements can be nouns, adjectives, or ...
... take direct objects. (Direct objects answer “Who?” or “What?” They are used with action verbs only. S-V-SC: Subject-Verb-Subject Complement: This pattern uses a linking verb. Linking verbs require some kind of subject complement to finish the thought. Subject complements can be nouns, adjectives, or ...
Noun Forms and Subject
... Making Them Agree with Verbs • Nouns refer to people, animals, places, or abstract ideas. They are the subjects and objects of verbs, and together with verbs they make up sentences. They are also the objects of prepositions and can be modified by adjectives and used with determiners. Without nouns, ...
... Making Them Agree with Verbs • Nouns refer to people, animals, places, or abstract ideas. They are the subjects and objects of verbs, and together with verbs they make up sentences. They are also the objects of prepositions and can be modified by adjectives and used with determiners. Without nouns, ...
6th grade- 2nd semester Language Arts Study Guide Nouns
... 6th grade- 2nd semester Language Arts Study Guide Nouns-A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what. Example: The dog ran after the ball. In this sentence, there are two nouns, dog and ball. A noun may be concrete (something you can ...
... 6th grade- 2nd semester Language Arts Study Guide Nouns-A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what. Example: The dog ran after the ball. In this sentence, there are two nouns, dog and ball. A noun may be concrete (something you can ...
Grammar Rocks worksheet
... 22) What is the predicate of a sentence? Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words for the following sentences. 23) Students who begin studying a week before a test are more likely to do better than those who only study the day before the test. 24) Raul wanted to do well on his test, but ...
... 22) What is the predicate of a sentence? Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words for the following sentences. 23) Students who begin studying a week before a test are more likely to do better than those who only study the day before the test. 24) Raul wanted to do well on his test, but ...
The plural form of most nouns is created simply by adding the letter s
... more than one cactus = cacti more than one thesis = theses ...
... more than one cactus = cacti more than one thesis = theses ...
act-nouns and their functions
... Direct address noun a the name of the person (normally) who is being directly spoken to. It is always a proper noun. It is set off by a comma or commas. Example: George, did you pay for the big salad? Subject complement the adjective, noun, or pronoun that follows a linking verb. The following verbs ...
... Direct address noun a the name of the person (normally) who is being directly spoken to. It is always a proper noun. It is set off by a comma or commas. Example: George, did you pay for the big salad? Subject complement the adjective, noun, or pronoun that follows a linking verb. The following verbs ...
THE NOTION OF INSTRUMENT IN MALAY LANGUAGE
... related goals. The first objective is to establish a semantic typology of nouns that are used as instrument for each of the five expressions of instrumentality. The second objective is to determine the semantic classes of verbs that cooccur with each of the defined class of nouns. We conduct the stu ...
... related goals. The first objective is to establish a semantic typology of nouns that are used as instrument for each of the five expressions of instrumentality. The second objective is to determine the semantic classes of verbs that cooccur with each of the defined class of nouns. We conduct the stu ...
Parts of Speech Review
... there, but you can’t see it or feel it in a physical way. Examples: love, kindness, sleep, day ...
... there, but you can’t see it or feel it in a physical way. Examples: love, kindness, sleep, day ...
review packet
... Make sure you know the verb aller (mentioned previously in the packet) Ex: I am going to speak French. = Je vais parler français You are going to go to Phoenix. = Tu vas aller à Phoenix. She is going to watch TV. = Elle va regarder la télé ...
... Make sure you know the verb aller (mentioned previously in the packet) Ex: I am going to speak French. = Je vais parler français You are going to go to Phoenix. = Tu vas aller à Phoenix. She is going to watch TV. = Elle va regarder la télé ...
Grammar Scavenger Hunt
... Grammar Review Scavenger Hunt The class is going to be divided into groups. Once you are in your groups, use your Holt Handbook, and whatever you remember from elementary school, to answer the questions about the eight parts of speech. If you are asked to write a sentence, you cannot use one of the ...
... Grammar Review Scavenger Hunt The class is going to be divided into groups. Once you are in your groups, use your Holt Handbook, and whatever you remember from elementary school, to answer the questions about the eight parts of speech. If you are asked to write a sentence, you cannot use one of the ...
Sentence Structure and development
... speech (also called word classes): nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections •the parts of speech come in many varieties and may show up just about anywhere in a sentence. •To know for sure what part of speech a word is, we have to look not only at th ...
... speech (also called word classes): nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections •the parts of speech come in many varieties and may show up just about anywhere in a sentence. •To know for sure what part of speech a word is, we have to look not only at th ...
The Verb Phrase
... Officer Carson was unmoved. Other times, the activity or condition continues over a long stretch of time, happens predictably, or occurs in relationship to other events. In these instances, a single-word verb like sobbed or was cannot accurately describe what happened, so writers use multipart verb ...
... Officer Carson was unmoved. Other times, the activity or condition continues over a long stretch of time, happens predictably, or occurs in relationship to other events. In these instances, a single-word verb like sobbed or was cannot accurately describe what happened, so writers use multipart verb ...
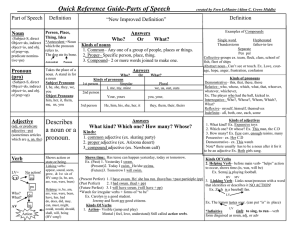
Describes a noun or a pronoun.
... Ex. Jumps across, over, around, near, on, off, under, toward, in, inside, from, against, behind, beneath *Beware! There are some prepositions that do not fit. Ex. of, for, at, after, except, instead of, about NOTE* The S of a sentence will never be in the prep. Phrase! ...
... Ex. Jumps across, over, around, near, on, off, under, toward, in, inside, from, against, behind, beneath *Beware! There are some prepositions that do not fit. Ex. of, for, at, after, except, instead of, about NOTE* The S of a sentence will never be in the prep. Phrase! ...
SUBJECT/VERB AGREEMENT ____________________________________________________________
... trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) 9. In sentences beginning with „there is‟ or „there are‟, the subject follows the verb. The verb agrees with the subject even if it is placed after the verb. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one pers ...
... trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) 9. In sentences beginning with „there is‟ or „there are‟, the subject follows the verb. The verb agrees with the subject even if it is placed after the verb. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one pers ...
Subject/Verb Agreement
... trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) 9. In sentences beginning with „there is‟ or „there are‟, the subject follows the verb. The verb agrees with the subject even if it is placed after the verb. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one pers ...
... trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) 9. In sentences beginning with „there is‟ or „there are‟, the subject follows the verb. The verb agrees with the subject even if it is placed after the verb. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one pers ...
writing cheat sheet
... A word that comes before a noun or pronoun, a preposition creates a phrase that modifies another word in the sentence. The noun or the pronoun is called the object of the preposition, and the phrase that is created is called a prepositional phrase. Example: She spilled the drink on him. Prepositions ...
... A word that comes before a noun or pronoun, a preposition creates a phrase that modifies another word in the sentence. The noun or the pronoun is called the object of the preposition, and the phrase that is created is called a prepositional phrase. Example: She spilled the drink on him. Prepositions ...
Jargon Busting Latin Terminology!
... 1. Present: The tense used when we want to show that an action is happening now. If you can put the word “now” after a doing word and the sentence still makes sense, then the verb must be in the present tense. For example, the phrases “he is walking (now)” and “he walks (now)” contain verbs in the p ...
... 1. Present: The tense used when we want to show that an action is happening now. If you can put the word “now” after a doing word and the sentence still makes sense, then the verb must be in the present tense. For example, the phrases “he is walking (now)” and “he walks (now)” contain verbs in the p ...
Miss Nicholls` GPS Dictionary Modal Verb A verb that shows how
... Hint: identify a preposition followed by a noun and this is called a prepositional phrase (it’s the language system being posh and giving this a name!) Coordinating Conjunctions ...
... Hint: identify a preposition followed by a noun and this is called a prepositional phrase (it’s the language system being posh and giving this a name!) Coordinating Conjunctions ...
Jordan - GEOCITIES.ws
... 3) The “zero” article is used with plural countable noun and with uncountable nouns. e.g The appointment of Ministers . 4) The definite article “The” is used when the noun is post modified by an of – phrase . e.g. He likes the mountain of Mo’ab . The history of the Arabs is interesting .(post – mod ...
... 3) The “zero” article is used with plural countable noun and with uncountable nouns. e.g The appointment of Ministers . 4) The definite article “The” is used when the noun is post modified by an of – phrase . e.g. He likes the mountain of Mo’ab . The history of the Arabs is interesting .(post – mod ...
Chapter 24
... Singular- and plural-count noun: These terms refer to words for people and things that can be counted. Use “a” or “an” before a singular-count noun when it refers to something in general. Use “the” when referring to something specifically. Noncount nouns name things that can’t be counted and take no ...
... Singular- and plural-count noun: These terms refer to words for people and things that can be counted. Use “a” or “an” before a singular-count noun when it refers to something in general. Use “the” when referring to something specifically. Noncount nouns name things that can’t be counted and take no ...
there was
... • ¡Atención! In affirmative commands, reflexive, indirect, and direct object pronouns are always attached to the end of the verb. In negative commands, these pronouns always precede the verb. ...
... • ¡Atención! In affirmative commands, reflexive, indirect, and direct object pronouns are always attached to the end of the verb. In negative commands, these pronouns always precede the verb. ...
1/13/11 #2 Noun Review
... Demonstrative adjectives: this that these, those 2/7 #7 Adverbs notes 5 pts. Adverb - a word that modifies a verb, and adjective or another adverb. Many adverbs end in -ly , answers question where? When? In what way? To what extent? Examples with Verbs 1. The student worked carefully on her book re ...
... Demonstrative adjectives: this that these, those 2/7 #7 Adverbs notes 5 pts. Adverb - a word that modifies a verb, and adjective or another adverb. Many adverbs end in -ly , answers question where? When? In what way? To what extent? Examples with Verbs 1. The student worked carefully on her book re ...