Indirect Object Pronouns
... affected by the verb’s action. It answers the question “to whom/what?” or “for whom/what?” For example: She gives the man the book. Who gives? - she - subject. Gives what? - book - direct object. To whom? - man - indirect object. ...
... affected by the verb’s action. It answers the question “to whom/what?” or “for whom/what?” For example: She gives the man the book. Who gives? - she - subject. Gives what? - book - direct object. To whom? - man - indirect object. ...
Presentation
... • The Past Participles of verbs that have an inseparable prefix do not add the prefix ge-: • These verbs will lose there –en ending and will have a –t put back in place of the original ending. • Besuchen (to visit, as in a person) besucht • Besichtigen (to visit, as in a place) besichtigt ...
... • The Past Participles of verbs that have an inseparable prefix do not add the prefix ge-: • These verbs will lose there –en ending and will have a –t put back in place of the original ending. • Besuchen (to visit, as in a person) besucht • Besichtigen (to visit, as in a place) besichtigt ...
MORE ON COMPLEMENTS
... They happen when an adjective phrase follows and modifies the object of a verb. 1. The IRS agent considered him very guilty . 2. His wife found him totally useless. ...
... They happen when an adjective phrase follows and modifies the object of a verb. 1. The IRS agent considered him very guilty . 2. His wife found him totally useless. ...
features
... number feature and stating a rule about agreement is about as simple as it can be. There’s pretty much no other way to describe this effect that isn’t just equivalent. So, if agreement is part of syntax (and let’s say that it is), we’re already off and running with rules/constraints sensitive to fea ...
... number feature and stating a rule about agreement is about as simple as it can be. There’s pretty much no other way to describe this effect that isn’t just equivalent. So, if agreement is part of syntax (and let’s say that it is), we’re already off and running with rules/constraints sensitive to fea ...
DGP Notes
... • tells How? When? Where? To what extent? • Not and never are always adverbs. PREPOSITION (prep) • shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence • across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, sinc ...
... • tells How? When? Where? To what extent? • Not and never are always adverbs. PREPOSITION (prep) • shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence • across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, sinc ...
Unit 5: NEGATIVE SENTENCES
... 2 Verbal nouns These are the –ing form of the verb (Unit 14) used as a noun. ...
... 2 Verbal nouns These are the –ing form of the verb (Unit 14) used as a noun. ...
Grammar - oaklandapsi2011
... • Create tone and mood: Verb Mood (Indicative, Imperative, Subjunctive) ...
... • Create tone and mood: Verb Mood (Indicative, Imperative, Subjunctive) ...
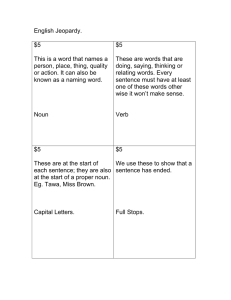
Parts of Speech Definition 1. NOUN Names a person
... 5. If you determine the simple predicate to be an action verb or a helping + action verb phrase, then ask yourself, “Subject + Verb + WHAT???” If you find a logical answer to this question, label that word as the direct object by writing “D.O.” above it. Then, only if you have already identified a d ...
... 5. If you determine the simple predicate to be an action verb or a helping + action verb phrase, then ask yourself, “Subject + Verb + WHAT???” If you find a logical answer to this question, label that word as the direct object by writing “D.O.” above it. Then, only if you have already identified a d ...
subjects, predicates, and sentences - Windsor C
... Victory goes to whoever makes more goals. (object of a preposition) This rink is where the teams play. (predicate noun) ...
... Victory goes to whoever makes more goals. (object of a preposition) This rink is where the teams play. (predicate noun) ...
January 13, 2004 Chapter 2.1-2.3 Sentence Structure, Word
... • They won’t get us very far in figuring out all the word classes we’ll need. • This is because word classes are fundamentally (morpho)syntactic. • Phonological and semantic facts reflect them only some of the time. • Thus inflectional and distributional evidence will be what we use to establish the ...
... • They won’t get us very far in figuring out all the word classes we’ll need. • This is because word classes are fundamentally (morpho)syntactic. • Phonological and semantic facts reflect them only some of the time. • Thus inflectional and distributional evidence will be what we use to establish the ...
Elevated Language
... Giving non-human qualities to inhuman things or inanimate objects. Ex) The dog spoke to me. This is personification because it give the inhuman dog the human ability to speak ...
... Giving non-human qualities to inhuman things or inanimate objects. Ex) The dog spoke to me. This is personification because it give the inhuman dog the human ability to speak ...
Predicate Nouns and Linking Verbs
... 11. Check again for prepositional phrases. 12. No prepositional phrases. 13. Period, statement, declarative sentence 14. Go back to the verb - divide the complete subject from the complete predicate. 15. Is there an adverb exception? No. 16. Is this sentence in a natural or inverted order? Natural ...
... 11. Check again for prepositional phrases. 12. No prepositional phrases. 13. Period, statement, declarative sentence 14. Go back to the verb - divide the complete subject from the complete predicate. 15. Is there an adverb exception? No. 16. Is this sentence in a natural or inverted order? Natural ...
File
... (“I know something.” The clause is a noun clause, direct object of the verb know.) Give a copy to whoever wants one. (“Give a copy to someone.” The clause is a noun clause, object of the preposition to.) ...
... (“I know something.” The clause is a noun clause, direct object of the verb know.) Give a copy to whoever wants one. (“Give a copy to someone.” The clause is a noun clause, object of the preposition to.) ...
Passato Prossimo
... Quando si usa? When does one use it? • Right after an action is finished (similar to English present perfect) • Ho appena mangiato una pizza. (I have just eaten a pizza) ...
... Quando si usa? When does one use it? • Right after an action is finished (similar to English present perfect) • Ho appena mangiato una pizza. (I have just eaten a pizza) ...
5. Pronoun
... A verb is used to show an action or a state of being go, write, exist, be 2. Noun A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, events, ideas and feelings. John, lion, table, freedom, love ... 3. Adjective Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun good, beautiful, ni ...
... A verb is used to show an action or a state of being go, write, exist, be 2. Noun A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, events, ideas and feelings. John, lion, table, freedom, love ... 3. Adjective Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun good, beautiful, ni ...
predicator - Rizka Safriyani
... two predicates can have nearly, if not exactly, the same sense but be of different grammatical part of speech Example: Jack is foolish, Jack is a fool Foolish and fool are predicate Foolish is an adjective Fool is a noun Both have different part of speech ...
... two predicates can have nearly, if not exactly, the same sense but be of different grammatical part of speech Example: Jack is foolish, Jack is a fool Foolish and fool are predicate Foolish is an adjective Fool is a noun Both have different part of speech ...
noun phrase - WordPress.com
... English places modifiers before a noun. Here we indicate the noun that is at the center of a noun phrase by an asterisk (*) and modifiers by arrows pointed toward the noun they modify. white house ...
... English places modifiers before a noun. Here we indicate the noun that is at the center of a noun phrase by an asterisk (*) and modifiers by arrows pointed toward the noun they modify. white house ...
linking verbs
... • These types of verbs do not show action but connects a subject with a word that describes or identifies it. • They connect nouns or pronouns to words that describe, label, or identify them. ...
... • These types of verbs do not show action but connects a subject with a word that describes or identifies it. • They connect nouns or pronouns to words that describe, label, or identify them. ...
Finding the Object - Savannah State University
... Intransitive verbs do not require an object. Linking verbs are one type of intransitive verbs. Though they do not take objects, linking verbs require subject complements. Subject complements are words or groups of words that complete the meaning of the subject by renaming or describing it. Subject c ...
... Intransitive verbs do not require an object. Linking verbs are one type of intransitive verbs. Though they do not take objects, linking verbs require subject complements. Subject complements are words or groups of words that complete the meaning of the subject by renaming or describing it. Subject c ...
1. Sentence fragment
... 13. Lack of agreement between subject and verb In Standard English verbs must agree with their subjects in number (singular or plural) and in person (first, second, third). Knowing the rules of agreement, being able to identify each subject, and recognizing the number of each subject are critical in ...
... 13. Lack of agreement between subject and verb In Standard English verbs must agree with their subjects in number (singular or plural) and in person (first, second, third). Knowing the rules of agreement, being able to identify each subject, and recognizing the number of each subject are critical in ...
C. Exam Questions, Grades and Time Allocated for Each Question
... 28. I wrapped the blanket around……………… a. my self c. I ...
... 28. I wrapped the blanket around……………… a. my self c. I ...
powerpoint jeopardy - Mr. Phillips` Classroom
... following sentence: • “We quickly ran out of ice cream on the hot, scorching day, but that did not matter after all.” ...
... following sentence: • “We quickly ran out of ice cream on the hot, scorching day, but that did not matter after all.” ...
Year 5 - Holbrook Primary School
... Build-up –develop suspense howled like an injured creature. techniques Problem /dilemma –may be Drop in –‘ed’ clause e.g. more than one problem to be Poor Tim, exhausted by so much resolved effort, ran home. Resolution –clear links with The lesser known Bristol dragon, dilemma recognised by pu ...
... Build-up –develop suspense howled like an injured creature. techniques Problem /dilemma –may be Drop in –‘ed’ clause e.g. more than one problem to be Poor Tim, exhausted by so much resolved effort, ran home. Resolution –clear links with The lesser known Bristol dragon, dilemma recognised by pu ...