Sentence Pattern Three: Subject–Verb–Indirect Object–Direct Object
... Sentence Pattern Three: Subject–Verb–Indirect Object–Direct Object (S-V-IO-DO) This pattern adds one more element to that of Sentence Pattern Two. That element is called the indirect object. The pattern is subject plus action verb plus indirect object plus direct object. Many times, the indirect obj ...
... Sentence Pattern Three: Subject–Verb–Indirect Object–Direct Object (S-V-IO-DO) This pattern adds one more element to that of Sentence Pattern Two. That element is called the indirect object. The pattern is subject plus action verb plus indirect object plus direct object. Many times, the indirect obj ...
Notes_Phrases_Sept 6
... relationship but can also show direction. (Examples: to, for, from, under, beside, on, in) ...
... relationship but can also show direction. (Examples: to, for, from, under, beside, on, in) ...
Phrases
... Infinitive: is a noun or modifier made from the to- form of the verb. To dream, to think, to snorkel. We think of an infinitive as one word, to wander, whereas a prepositional phrase like to Boston is two words. Avoid split infinitives. Splitting an infinitive means inserting an adverb between the t ...
... Infinitive: is a noun or modifier made from the to- form of the verb. To dream, to think, to snorkel. We think of an infinitive as one word, to wander, whereas a prepositional phrase like to Boston is two words. Avoid split infinitives. Splitting an infinitive means inserting an adverb between the t ...
Modal verbs
... most European languages, are ‘to be’ and ‘to have’. Along with ‘to do’, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
... most European languages, are ‘to be’ and ‘to have’. Along with ‘to do’, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
Verbs
... most European languages, are ‗to be‘ and ‗to have‘. Along with ‗to do‘, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
... most European languages, are ‗to be‘ and ‗to have‘. Along with ‗to do‘, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
Modal verbs
... most European languages, are ‘to be’ and ‘to have’. Along with ‘to do’, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
... most European languages, are ‘to be’ and ‘to have’. Along with ‘to do’, these three are known as the primary verbs, so important are they. We can begin our understanding of their uses by considering the features called aspect and voice. Aspect The basic auxiliary use of to have (it also has a use as ...
The Derivational Morphology of Totonac
... The inflectional categories for verbs are person (both subject and object), number, tense, aspect and mood. Third person singular, subject or object, is always marked with a zero morpheme. For nominals, number inflection is optional except with human nouns, and possession is obligatorily marked with ...
... The inflectional categories for verbs are person (both subject and object), number, tense, aspect and mood. Third person singular, subject or object, is always marked with a zero morpheme. For nominals, number inflection is optional except with human nouns, and possession is obligatorily marked with ...
1. Language change and variation in English
... • have gone through a process of language contact, e.g. as honest as an elephant • have been progressively acknowledged as local standards, e.g. Indian English, Caribbean English, East-African English • share common features that are different from native standard varieties ...
... • have gone through a process of language contact, e.g. as honest as an elephant • have been progressively acknowledged as local standards, e.g. Indian English, Caribbean English, East-African English • share common features that are different from native standard varieties ...
Part-of-Speech Tagging with Hidden Markov Models
... examples are directional or locative (here, downhill), others are to do with degree (very, somewhat), and others are temporal (yesterday). There are many more closed classes, including: Determiners modify nouns to make reference to an instance or instances of the noun e.g. a, the, some Pronouns subs ...
... examples are directional or locative (here, downhill), others are to do with degree (very, somewhat), and others are temporal (yesterday). There are many more closed classes, including: Determiners modify nouns to make reference to an instance or instances of the noun e.g. a, the, some Pronouns subs ...
ЗАВДАННЯ ДЛЯ САМОСТІЙНОГО ОПРАЦЮВАННЯ З КУРСУ
... It is a non-finite form of the verb which has a verbal and an adjectival or an adverbial character. There are two Participles in English: Participle I and Participle II, traditionally called The Present Participle and The Past Participle. I. 1. PARTICIPLE I ...
... It is a non-finite form of the verb which has a verbal and an adjectival or an adverbial character. There are two Participles in English: Participle I and Participle II, traditionally called The Present Participle and The Past Participle. I. 1. PARTICIPLE I ...
Future Tense
... The Conditional Tense expresses time in the future, but with a condition or a contrary situation. In English this is done through the word "would". I would be there tomorrow if I could. What would he say if he knew? I would see you at the party, but I can't make it. We would wait for five minutes, b ...
... The Conditional Tense expresses time in the future, but with a condition or a contrary situation. In English this is done through the word "would". I would be there tomorrow if I could. What would he say if he knew? I would see you at the party, but I can't make it. We would wait for five minutes, b ...
6. Past Tense Verbs and Past Participles
... how to speak Spanish when they were children. how to speak Spanish for many years. ...
... how to speak Spanish when they were children. how to speak Spanish for many years. ...
W98-1014 - Association for Computational Linguistics
... types. These are no classification errors when either a function or a verb word was not classified, and misclassification when a verb word was classified as an adjective or noun, and viceversa. The results gave errors of the first type whenever the corresponding stem was not in the database. Errors ...
... types. These are no classification errors when either a function or a verb word was not classified, and misclassification when a verb word was classified as an adjective or noun, and viceversa. The results gave errors of the first type whenever the corresponding stem was not in the database. Errors ...
Aim: How do we identify common problems in grammar and usage?
... Simple Sentence: Kendra and I have taken the SAT but have not received our scores. (compound subject and compound verb – NO COMMA: ONE INDEPENDENT SENTENCE) Compound Sentence: Kendra and I have taken the SAT, but we have not received our scores. (compound subject and compound verb Note: compound se ...
... Simple Sentence: Kendra and I have taken the SAT but have not received our scores. (compound subject and compound verb – NO COMMA: ONE INDEPENDENT SENTENCE) Compound Sentence: Kendra and I have taken the SAT, but we have not received our scores. (compound subject and compound verb Note: compound se ...
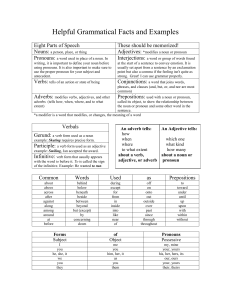
Helpful Grammatical Facts and Examples
... Stumbling and falling, the explorer found his way out of the forest. after an introductory word or phrase, to set it off from the main part of the sentence Ex. After dinner, Leo usually takes a walk. For example, this comma is needed to set off the introductory phrase. with an appositive (a word ...
... Stumbling and falling, the explorer found his way out of the forest. after an introductory word or phrase, to set it off from the main part of the sentence Ex. After dinner, Leo usually takes a walk. For example, this comma is needed to set off the introductory phrase. with an appositive (a word ...
Morphology – lecture script
... Derivational affixes (both prefixes and suffixes) change meaning, grammatical category or phonological form. English has only a few inflectional morphemes: On nouns: plural -s and possessive -s On verbs: 3rd person singular -s ...
... Derivational affixes (both prefixes and suffixes) change meaning, grammatical category or phonological form. English has only a few inflectional morphemes: On nouns: plural -s and possessive -s On verbs: 3rd person singular -s ...
(PS) rules - kuas.edu.tw
... string of random words? • If it is a sentence, does it have to be meaningful? ...
... string of random words? • If it is a sentence, does it have to be meaningful? ...
rules-grammar-3-t1
... Agreement: The noun and pronoun must agree on 1. Singular or plural 2. Boy or girl The girl is drawing, she has nice colors (Antecedent) ...
... Agreement: The noun and pronoun must agree on 1. Singular or plural 2. Boy or girl The girl is drawing, she has nice colors (Antecedent) ...
Lecture 5 X-bar Theory and the Structure of the Sentence
... significance to formal units of grammar. At this point, we may ask the reasonable question with respect to what significance we can attach to the features N and V. A part of speech is nominal if it can be the obligatory constituent, that is the argument (i.e. a participant in an event) of a predicat ...
... significance to formal units of grammar. At this point, we may ask the reasonable question with respect to what significance we can attach to the features N and V. A part of speech is nominal if it can be the obligatory constituent, that is the argument (i.e. a participant in an event) of a predicat ...
Writing Research
... Placing the grammatical subject at the start ensures the most efficient information delivery system. ...
... Placing the grammatical subject at the start ensures the most efficient information delivery system. ...
The Construction of the Sentence
... the sentence, “Spot gave Joe a chance,” Chance would be the direct object and Joe would be the indirect object since he is receiving the action. *Hint: Look for direct objects first. *Hint: A dir ...
... the sentence, “Spot gave Joe a chance,” Chance would be the direct object and Joe would be the indirect object since he is receiving the action. *Hint: Look for direct objects first. *Hint: A dir ...
JN2/3200 Public Relations JCU 2007
... • “…scientists believe in their existence.” (not of) • “…I was bored with that.” (not of) ...
... • “…scientists believe in their existence.” (not of) • “…I was bored with that.” (not of) ...
Grammar Guide HB
... A preposition usually comes before a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. Prepositions show how one thing is related to something else. Examples: to, of, if, on, in, by, with, under, through, at ...
... A preposition usually comes before a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. Prepositions show how one thing is related to something else. Examples: to, of, if, on, in, by, with, under, through, at ...
english language
... manner (slowly, quickly, willingly), or place (here, there, everywhere) in addition to a wide range of other meanings. An adverb (such as slowly or quickly) that describes how the action of a verb is carried out called an adverb of manner. An adverb (such as here, there, everywhere) that describ ...
... manner (slowly, quickly, willingly), or place (here, there, everywhere) in addition to a wide range of other meanings. An adverb (such as slowly or quickly) that describes how the action of a verb is carried out called an adverb of manner. An adverb (such as here, there, everywhere) that describ ...