1 Chap 14: Firms in Competitive Markets…
... • The competitive firm’s long-run supply curve is the portion of its marginal-cost curve that lies above average total cost. • Short-Run Supply Curve – The portion of its marginal cost curve that lies ...
... • The competitive firm’s long-run supply curve is the portion of its marginal-cost curve that lies above average total cost. • Short-Run Supply Curve – The portion of its marginal cost curve that lies ...
CHAPTER 6: The Competition Environment
... of competition will bring about lower prices and greater consumer choice. Where competition alone has not been sufficient to protect the consumers' interest, government has created a series of regulatory bodies which can determine the level and structure of charges made by these utilities. In util ...
... of competition will bring about lower prices and greater consumer choice. Where competition alone has not been sufficient to protect the consumers' interest, government has created a series of regulatory bodies which can determine the level and structure of charges made by these utilities. In util ...
Sales promotions
... A low price is charged initially to penetrate the market and build brand loyalty. The price is then increased e.g. introductory offers on magazines. ...
... A low price is charged initially to penetrate the market and build brand loyalty. The price is then increased e.g. introductory offers on magazines. ...
Word Document (download)
... seller’s actions affect the other sellers so that what is best for me to do depends on what the other firms do. In some industries with oligopoly firms have differentiated product, but in others they have homogeneous products. ...
... seller’s actions affect the other sellers so that what is best for me to do depends on what the other firms do. In some industries with oligopoly firms have differentiated product, but in others they have homogeneous products. ...
Oligopoly
... Let q2 = 0 units so that Q = q1—that is, seller 1 is a monopolist. Seller 1 should set its quantity supplied at the level corresponding to the equality of MR and MC. Let MR – MC = 0 100 – 2Q – 40 = 0 2Q = 60 Q = QM = 30 units Thus ...
... Let q2 = 0 units so that Q = q1—that is, seller 1 is a monopolist. Seller 1 should set its quantity supplied at the level corresponding to the equality of MR and MC. Let MR – MC = 0 100 – 2Q – 40 = 0 2Q = 60 Q = QM = 30 units Thus ...
Key to Microeconomics Test 1 Short answer essay and/or graph (55
... Absolute advantage: refers to a producer having higher efficiency of production. Efficiency refers to ability to produce more output with same resources. Comparative advantage: between two(or more) producers, a comparative advantage indicates lower relative opportunity costs. b) Why would a country ...
... Absolute advantage: refers to a producer having higher efficiency of production. Efficiency refers to ability to produce more output with same resources. Comparative advantage: between two(or more) producers, a comparative advantage indicates lower relative opportunity costs. b) Why would a country ...
The Role of Profits and Markets
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed ...
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed ...
profit and loss presentation
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2005 – Biz/ed ...
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2005 – Biz/ed ...
Session 1
... although demand may fall, the percentage fall in demand will be less than the percentage increase in price meaning that the firms revenue will increase as well as profit ...
... although demand may fall, the percentage fall in demand will be less than the percentage increase in price meaning that the firms revenue will increase as well as profit ...
oligopoly
... Each firm charging such a price gets 1/Ni of the total profits. If a firm were to undercut this price by a single penny, the total industry profits would change only by a very small amount (since P changes very little, total Q changes very little, which implies that total costs change very little). ...
... Each firm charging such a price gets 1/Ni of the total profits. If a firm were to undercut this price by a single penny, the total industry profits would change only by a very small amount (since P changes very little, total Q changes very little, which implies that total costs change very little). ...
Ch3 - YSU
... • Does the fact that a market automatically reach its equilibrium also guarantee the achievement of economic efficiency – all goods at their socially optimal levels? – Only if the benefits to buyers and/or the costs to sellers are not shared by others. (Efficiency Principle) – Buyers and sellers are ...
... • Does the fact that a market automatically reach its equilibrium also guarantee the achievement of economic efficiency – all goods at their socially optimal levels? – Only if the benefits to buyers and/or the costs to sellers are not shared by others. (Efficiency Principle) – Buyers and sellers are ...
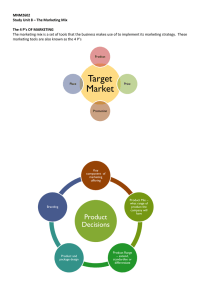
MNM2602 Study Unit 8 – The Marketing Mix The 4 P`s OF
... The 4 P’s OF MARKETING The marketing mix is a set of tools that the business makes use of to implement its marketing strategy. These marketing tools are also known as the 4 P’s ...
... The 4 P’s OF MARKETING The marketing mix is a set of tools that the business makes use of to implement its marketing strategy. These marketing tools are also known as the 4 P’s ...
Intro Micro Exam 2, Fall2003
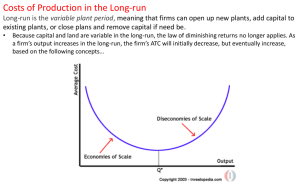
... 5. a. What is minimum efficient scale (MES)? How can this concept, combined with economies and diseconomies of scale, be used to describe the number and size of firms in an industry? Feel free to use a diagram if it helps your explanation. (6 points) ...
... 5. a. What is minimum efficient scale (MES)? How can this concept, combined with economies and diseconomies of scale, be used to describe the number and size of firms in an industry? Feel free to use a diagram if it helps your explanation. (6 points) ...
Practice Problem
... _____ 3. What is the marginal revenue product and the marginal factor cost of extra labor hired by this grower when hiring the profit maximizing number of workers. _____ 4. What is the marginal physical product of the last worker hired to pick cranberries. What is inefficient if this grower decides ...
... _____ 3. What is the marginal revenue product and the marginal factor cost of extra labor hired by this grower when hiring the profit maximizing number of workers. _____ 4. What is the marginal physical product of the last worker hired to pick cranberries. What is inefficient if this grower decides ...
Document
... any level of output it might produce, total cost is determined by (1) its technology of production and (2) the prices it must pay for its inputs. And for any level of output it might produce, the maximum price it can charge is determined by the market demand curve for its product. ...
... any level of output it might produce, total cost is determined by (1) its technology of production and (2) the prices it must pay for its inputs. And for any level of output it might produce, the maximum price it can charge is determined by the market demand curve for its product. ...
File
... The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor increases at first due to increased specialization, then diminishes as more labor is added to fixed land and capital. Mar ...
... The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor increases at first due to increased specialization, then diminishes as more labor is added to fixed land and capital. Mar ...
Answers to Homework #4
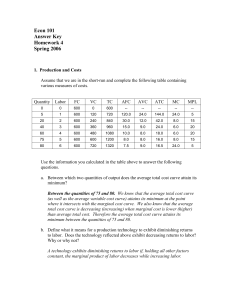
... The market for gasoline in the City of Madison is characterized by perfect competition. Firms and consumers are price takers and there is free entry and exit. Assume this industry is a constant cost industry. The total cost and marginal cost functions for an individual firm are given by the followin ...
... The market for gasoline in the City of Madison is characterized by perfect competition. Firms and consumers are price takers and there is free entry and exit. Assume this industry is a constant cost industry. The total cost and marginal cost functions for an individual firm are given by the followin ...
chap 1 - SFU.ca
... from the consumption of A is independent of the utility from consuming B (i.e., the quantity of A consumed does not affect the utility obtained from consuming B). Min spends all of her money on A and B (she does not save). The blank columns are for your convenience. a. Assume the price of A = $8, th ...
... from the consumption of A is independent of the utility from consuming B (i.e., the quantity of A consumed does not affect the utility obtained from consuming B). Min spends all of her money on A and B (she does not save). The blank columns are for your convenience. a. Assume the price of A = $8, th ...
ch03-qs - uob.edu.bh
... A. both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will increase. B. both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will decrease. C. equilibrium price will decrease but equilibrium quantity will increase. D. equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease. 13. The law of Sup ...
... A. both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will increase. B. both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will decrease. C. equilibrium price will decrease but equilibrium quantity will increase. D. equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease. 13. The law of Sup ...