Monopoly
... Where the demand curve is inelastic, a 1% increase in price leads to a fall in demanded quantity of less than 1%. ...
... Where the demand curve is inelastic, a 1% increase in price leads to a fall in demanded quantity of less than 1%. ...
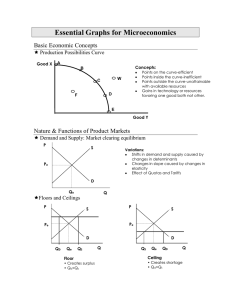
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
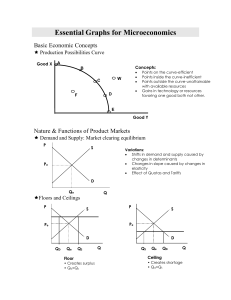
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
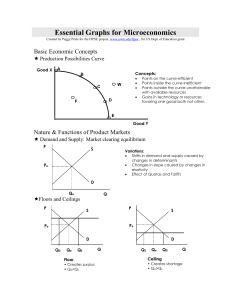
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1
... additional unit of labor added is done so at the same price the MC will fall as long as the MP is rising. This is because marginal cost is simply the (constant) price or cost of an extra worker divided by his or her marginal product. This means that as long as MP is rising the MC will be falling. Ho ...
... additional unit of labor added is done so at the same price the MC will fall as long as the MP is rising. This is because marginal cost is simply the (constant) price or cost of an extra worker divided by his or her marginal product. This means that as long as MP is rising the MC will be falling. Ho ...
ECON 3070-003 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... Difference with other sections: This section covers fewer topics and puts more emphasis on analysis than other sections. Problem sets: Problem sets are given out on a regular basis, and the answers are placed on reserve in the Norlin Library. The problem sets are an integral part of the course. They ...
... Difference with other sections: This section covers fewer topics and puts more emphasis on analysis than other sections. Problem sets: Problem sets are given out on a regular basis, and the answers are placed on reserve in the Norlin Library. The problem sets are an integral part of the course. They ...
Microeconomics Topic 7: “Contrast market outcomes under
... wheat of a particular grade is homogeneous (while ice cream is not). If the product is homogeneous, consumers don't care from which firm they buy the good because their products are identical. (3) Freedom of entry and exit. There are no barriers to enter the industry, so new firms can compete with o ...
... wheat of a particular grade is homogeneous (while ice cream is not). If the product is homogeneous, consumers don't care from which firm they buy the good because their products are identical. (3) Freedom of entry and exit. There are no barriers to enter the industry, so new firms can compete with o ...
Now
... b. McGraw-Hill and other publishers introduce online materials that can be used instead of a textbook c. The cost of paper increases d. College tuition increases 2. What is scarcity? Why is it relevant to economics? 3. Define opportunity cost. 4. Define elasticity of demand. If a good has an inelast ...
... b. McGraw-Hill and other publishers introduce online materials that can be used instead of a textbook c. The cost of paper increases d. College tuition increases 2. What is scarcity? Why is it relevant to economics? 3. Define opportunity cost. 4. Define elasticity of demand. If a good has an inelast ...
Lecture 04.2a
... – Are Total Revenues > Total Costs? • At point of entry -> all costs are variable • Costs also include opportunity costs – Opp. Costs for resources are signaled by market prices for inputs – Opp. Costs of money invested -> “normal rate of return” – Opp. Costs for your (owner’s) labor -> what you cou ...
... – Are Total Revenues > Total Costs? • At point of entry -> all costs are variable • Costs also include opportunity costs – Opp. Costs for resources are signaled by market prices for inputs – Opp. Costs of money invested -> “normal rate of return” – Opp. Costs for your (owner’s) labor -> what you cou ...
Externalities FRQs
... (c) Assume that the conversion of open-space land and farmland imposes costs on the general population, which can no longer enjoy the scenic vistas. (i) Indicate whether the marginal social cost of converting land is greater than, less than, or equal to the marginal private cost of converting land. ...
... (c) Assume that the conversion of open-space land and farmland imposes costs on the general population, which can no longer enjoy the scenic vistas. (i) Indicate whether the marginal social cost of converting land is greater than, less than, or equal to the marginal private cost of converting land. ...
Did you watch the Superbowl?
... the demand curve with higher price and quantity. If demand is inelastic, then percentage reduction is quantity is smaller than percentage increase in price. ...
... the demand curve with higher price and quantity. If demand is inelastic, then percentage reduction is quantity is smaller than percentage increase in price. ...
p($) - City University of Hong Kong
... Economists assume ALL firms maximize economic profits, R C As shown by the cost functions developed in the last chapter, total costs depends on quantity of output of the firm. To see how a firm’s revenue depends on its output level, we must look at the demand for the firm’s product, whic ...
... Economists assume ALL firms maximize economic profits, R C As shown by the cost functions developed in the last chapter, total costs depends on quantity of output of the firm. To see how a firm’s revenue depends on its output level, we must look at the demand for the firm’s product, whic ...
Managerial Economics
... price is $200; hence CS = $50 The marginal cost of producing a VCR is $130 and hence PS = $70 Consequently V = $50 + $70 = $120 ...
... price is $200; hence CS = $50 The marginal cost of producing a VCR is $130 and hence PS = $70 Consequently V = $50 + $70 = $120 ...
Competition And Market Structure
... products that are substitutes for each other but also differ from each other: -- attributes, -- performance characteristics, -- image, -- price. ...
... products that are substitutes for each other but also differ from each other: -- attributes, -- performance characteristics, -- image, -- price. ...
Oligopoly - ILM.COM.PK
... Quantity will be less than the competitive quantity. The monopolist sells the output at a price greater than marginal costs but the ...
... Quantity will be less than the competitive quantity. The monopolist sells the output at a price greater than marginal costs but the ...
Which of the following influences does NOT shift the supply curve?
... Equilibrium in the fish market is disturbed by two different events: (i) a report by the American Medical Association announces that increased consumption of fish is associated with lower heart disease, and (ii) fisherman are banned from fishing in environmentally sensitive areas that previously wer ...
... Equilibrium in the fish market is disturbed by two different events: (i) a report by the American Medical Association announces that increased consumption of fish is associated with lower heart disease, and (ii) fisherman are banned from fishing in environmentally sensitive areas that previously wer ...