Product Life Cycle (PLC)
... Low, reflecting heavy competition Greater number of channels and more incentives to resellers Messages focus on Aimed at early adopters; Aimed at wider audience; differentiating brand from messages designed to messages focus on its competitors; heavy educate about product type; brand benefits; for u ...
... Low, reflecting heavy competition Greater number of channels and more incentives to resellers Messages focus on Aimed at early adopters; Aimed at wider audience; differentiating brand from messages designed to messages focus on its competitors; heavy educate about product type; brand benefits; for u ...
AP_Micro_4-6_Unit_Summary
... Practice Question Assume there is a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
... Practice Question Assume there is a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
uwcmaastricht-econ
... Allocative efficiency occurs when the economy produces the combination of goods that are mostly wanted by society. That is, when the ‘what to produce’ question is answered in the best possible way. In a competitive market, allocative efficiency is achieved at the equilibrium point, where quantity de ...
... Allocative efficiency occurs when the economy produces the combination of goods that are mostly wanted by society. That is, when the ‘what to produce’ question is answered in the best possible way. In a competitive market, allocative efficiency is achieved at the equilibrium point, where quantity de ...
In a monopolistic market, there is only one firm in the market and the
... each firm must constantly determine how they will respond to price changes by the rival soft drink maker. To show how the previously discussed fundamentals could work in a real-world setting, assume that you are manager at Coca-Cola and have heard that Pepsi recently received damaging news from a su ...
... each firm must constantly determine how they will respond to price changes by the rival soft drink maker. To show how the previously discussed fundamentals could work in a real-world setting, assume that you are manager at Coca-Cola and have heard that Pepsi recently received damaging news from a su ...
Name Date Period _____ Unit 2: Microeconomics Review Part 1
... 17. What are positive externalities? How does the government try to promote positive externalities? Positive externalities refer to unintended consequences that benefit third parties. For example, the government subsidizes farmers. They do this to increase incentives for farmers to produce more food ...
... 17. What are positive externalities? How does the government try to promote positive externalities? Positive externalities refer to unintended consequences that benefit third parties. For example, the government subsidizes farmers. They do this to increase incentives for farmers to produce more food ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... 11. In the short run, the firm will stop production when the price falls below (A) 0A (B) 0B (C) 0C (D) 0D (E) 0E 12. If the chemical industry in an area has been dumping its toxic waste free of charge into a river, government action to ensure a more efficient use of resources would have which of th ...
... 11. In the short run, the firm will stop production when the price falls below (A) 0A (B) 0B (C) 0C (D) 0D (E) 0E 12. If the chemical industry in an area has been dumping its toxic waste free of charge into a river, government action to ensure a more efficient use of resources would have which of th ...
Click
... • In capitalism, what are the factors (forces) that help shape what is produced and consumed? Supply and Demand determines trade: Buyers purchase goods and services with money Sellers get money for selling goods and services The price is relative to the amount buyers are willing to trade and the amo ...
... • In capitalism, what are the factors (forces) that help shape what is produced and consumed? Supply and Demand determines trade: Buyers purchase goods and services with money Sellers get money for selling goods and services The price is relative to the amount buyers are willing to trade and the amo ...
Business Simulation Seminar - B-K
... Erect barriers to entry Make it difficult for new competitors to achieve compare awareness and accessibility ...
... Erect barriers to entry Make it difficult for new competitors to achieve compare awareness and accessibility ...
ECMA04H – Week 10
... The monopolist keeps all the 100 plants separate and operates as many as he needs to supply the good. In effect the SLR becomes the MC curve (and the AC curve) of the monopolist. ...
... The monopolist keeps all the 100 plants separate and operates as many as he needs to supply the good. In effect the SLR becomes the MC curve (and the AC curve) of the monopolist. ...
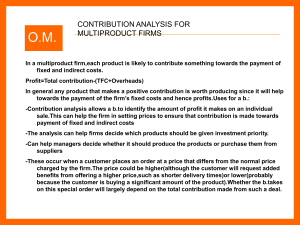
+ of operating cost and profit centres
... -Contribution analysis allows a b.to identify the amount of profit it makes on an individual sale.This can help the firm in setting prices to ensure that contribution is made towards payment of fixed and indirect costs -The analysis can help firms decide which products should be given investment pri ...
... -Contribution analysis allows a b.to identify the amount of profit it makes on an individual sale.This can help the firm in setting prices to ensure that contribution is made towards payment of fixed and indirect costs -The analysis can help firms decide which products should be given investment pri ...
Market Price Under Perfect Competition
... Costas Megalodrachmas is the owner of the monopoly operation. In a recent statement he said; “people in the Midwest are very price-conscious and our managers there know what to charge”. A. Are the demand curves in the two regions mentioned the same? If so why, If not how do they differ? B. CM also s ...
... Costas Megalodrachmas is the owner of the monopoly operation. In a recent statement he said; “people in the Midwest are very price-conscious and our managers there know what to charge”. A. Are the demand curves in the two regions mentioned the same? If so why, If not how do they differ? B. CM also s ...
Supply & Elasticity of Supply
... • Supply is the counterpart of demand • It also is a schedule of prices and quantities • Supply is driven by different factors • Together Supply & Demand determine the market prices and quantities ...
... • Supply is the counterpart of demand • It also is a schedule of prices and quantities • Supply is driven by different factors • Together Supply & Demand determine the market prices and quantities ...
PLC and Pricing
... •Disadvantages •High profits attract competition •Profit maximization is short term •Problematic if initial price is way to high ...
... •Disadvantages •High profits attract competition •Profit maximization is short term •Problematic if initial price is way to high ...
Chapter 14 - Powerpoint
... Each competitive firm is a price taker in that it will take the price as being given. Explanation: If a firm tries to charge a higher price, buyers will go to other sellers who they know are willing to sell the same product. A firm could sell at a lower price. However, since it can sell all units a ...
... Each competitive firm is a price taker in that it will take the price as being given. Explanation: If a firm tries to charge a higher price, buyers will go to other sellers who they know are willing to sell the same product. A firm could sell at a lower price. However, since it can sell all units a ...