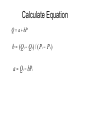* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply & Elasticity of Supply
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
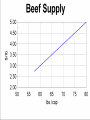
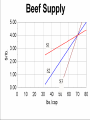
Supply & Elasticity of Supply AG BM 102 Introduction • Supply is the counterpart of demand • It also is a schedule of prices and quantities • Supply is driven by different factors • Together Supply & Demand determine the market prices and quantities Supply - A schedule of the quantities of product that producers will sell at various prices An Example – Beef Supply Price Quantity Price Quantity 3.00 60 4.25 72.5 3.25 62.5 4.50 75 3.50 65 4.75 77.5 3.75 67.5 5.00 80 4.00 70 5.25 82.5 Some Ideas • • • • • Time period important Short time – little adjustment possible Long time – lots of adjustment possible Medium – moderate adjustment possible Orchard Important Points • This assumes other determinants of supply are fixed • Input prices • Technology • If they change the line moves Upward sloping • Higher prices induce more production • Higher prices induce entry • Higher prices mean more profit Calculate Equation Q a bP b (Q1 Q2) / ( P1 P 2) a Q1 bP1 Values Q1 70lbs., P1 $4.00, Q2 80lbs. and b (70 80) / (4 5) 10 a 70 (10) 4 30 Q 30 10 P P 2 $5.00 Check to see if points are on line • P = 4, Q = 30 + 10 (4) = 70 • P = 5, Q = 30 + 10 (5) = 80 Elasticity of SupplyThe percentage change in quantity supplied in response to a one percent change in price Calculate Elasticity of Supply (Q Q1) / ( P P1) * ( P1) / (Q1) b( P / Q ) 2 2 1 1 b( P / Q ) (10)(4 / 70) (4 / 7) 0.57 1 1 Interpretation • Inelastic supply – between zero and 1 • Elastic supply – greater than 1 • Unitary elasticity - equal to 1 Discussion of Supply Elasticity • • • • Short run vs. long run Plant products vs. animal products Ag vs. non- ag (e.g., clothing) Perishable vs. storable Change in Supply or Quantity Supplied • Effect on beef market if feed price rises • Effect on beef market if chicken price falls • Effect on beef market if consumer income rises • Effect on beef market if hard winter kills a lot of cattle Concluding Comments • Understanding supply goes a long way toward understanding markets • Two parts- mechanical part & intuitive part • Second is more important – Think about what will suppliers do? – How fast can they adjust? – What holds them back? Same lists for demand • Intuition important • Comes from thinking systematically – What will demander do? – How fast will demander change? – Is habit an issue here? • Lots of variables, but most not important – Key is to know which is which