5.01G Supply and Demand - Lesson Plan
... price. The equilibrium price is the market price or the price that goods and services will sell for. The amount of goods and services businesses are able to supply depends on market supply. Market supply refers to the amount of raw materials and resources available at a given time. Limited resource ...
... price. The equilibrium price is the market price or the price that goods and services will sell for. The amount of goods and services businesses are able to supply depends on market supply. Market supply refers to the amount of raw materials and resources available at a given time. Limited resource ...
Chapter 5 short version
... Internet Stores • Many stores are using the Internet because the overhead, or the fixed cost of operation, is so low. • An individual engaged in e-commerce– electronic business or exchange conducted over the Internet–does not need to spend large sums of money to rent a building and stock it with ...
... Internet Stores • Many stores are using the Internet because the overhead, or the fixed cost of operation, is so low. • An individual engaged in e-commerce– electronic business or exchange conducted over the Internet–does not need to spend large sums of money to rent a building and stock it with ...
Slide 1
... uniform commodities where no single buyer or seller has much effect on market price. • Monopolistic competition is a market with many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices rather than a single market price with differentiated offers. • Oligopolistic competition is a market with few sel ...
... uniform commodities where no single buyer or seller has much effect on market price. • Monopolistic competition is a market with many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices rather than a single market price with differentiated offers. • Oligopolistic competition is a market with few sel ...
Midterm Questions and Answers, Spring 2004
... movement along the demand curve and a higher price. Rather, the demand curve was shifting out, moving along the supply curve to a higher price and a higher quantity. This was a time of increased in‡ationary expectations, and people thought that the price of gold was going to increase in the future. ...
... movement along the demand curve and a higher price. Rather, the demand curve was shifting out, moving along the supply curve to a higher price and a higher quantity. This was a time of increased in‡ationary expectations, and people thought that the price of gold was going to increase in the future. ...
Lecture 3
... Demand Curve: relationship between quantity demanded and price, other factors fixed Law of Demand: demand curves slope down Change in price causes movement along the demand curve Change in income or other background factor causes shift of demand curve A demand curve is hypothetical ...
... Demand Curve: relationship between quantity demanded and price, other factors fixed Law of Demand: demand curves slope down Change in price causes movement along the demand curve Change in income or other background factor causes shift of demand curve A demand curve is hypothetical ...
1 - Pomona College
... become unregulated, we would expect a. the price to rise and the quantity traded to fall. b. the price to fall and the quantity traded to rise. c. the price to fall but the quantity traded to be unchanged. d. both the price and quantity traded to fall. 16. Suppose that Sun City, Arizona adopted rent ...
... become unregulated, we would expect a. the price to rise and the quantity traded to fall. b. the price to fall and the quantity traded to rise. c. the price to fall but the quantity traded to be unchanged. d. both the price and quantity traded to fall. 16. Suppose that Sun City, Arizona adopted rent ...
Product Adaptation
... Deciding on the Global Marketing Program • Companies that operate in one or more foreign markets must decide how much, if at all, to adapt their marketing mixes to local conditions. • At one extreme are global companies that use a STANDARDADIZED MARKETING MIX, selling largely the same products and ...
... Deciding on the Global Marketing Program • Companies that operate in one or more foreign markets must decide how much, if at all, to adapt their marketing mixes to local conditions. • At one extreme are global companies that use a STANDARDADIZED MARKETING MIX, selling largely the same products and ...
Chapter 07 Key Question Solutions
... (b) Disagree. The marginal utility of a unit beyond the first may be sufficiently great (relative to product price) to make it a worthwhile purchase. Consumers are interested in maximizing total utility, not marginal utility. (c) Agree. This product’s price could be so high relative to the first uni ...
... (b) Disagree. The marginal utility of a unit beyond the first may be sufficiently great (relative to product price) to make it a worthwhile purchase. Consumers are interested in maximizing total utility, not marginal utility. (c) Agree. This product’s price could be so high relative to the first uni ...
Consumers Rule - Lampung University
... • You’re the marketing manager for a small securities firm (a firm that sells stocks and bonds) whose customers are primarily businesses and other organizations. Your company is considering using the Internet to provide information and service to its customers. • Outline the pros and cons of this mo ...
... • You’re the marketing manager for a small securities firm (a firm that sells stocks and bonds) whose customers are primarily businesses and other organizations. Your company is considering using the Internet to provide information and service to its customers. • Outline the pros and cons of this mo ...
Responding to Buyer Power
... revenue. • With price discrimination, the firm sells 30 units at $70 and 40 units at $30 for $3300 revenue. • As long as the cost of implementing price discrimination is less than $1200, profits are increased. David J. Bryce © 2002 ...
... revenue. • With price discrimination, the firm sells 30 units at $70 and 40 units at $30 for $3300 revenue. • As long as the cost of implementing price discrimination is less than $1200, profits are increased. David J. Bryce © 2002 ...
CONSUMER.PPT
... Prices convey information to producers about the benefits consumers receive from goods and services - and give information to consumers about the costs of producing goods and services. Given our assumptions that producers are maximizing profits and consumers are maximizing utility, we can infer that ...
... Prices convey information to producers about the benefits consumers receive from goods and services - and give information to consumers about the costs of producing goods and services. Given our assumptions that producers are maximizing profits and consumers are maximizing utility, we can infer that ...
Demand - OnCourse
... • Demand- the amount of a good or service a consumer is willing and able to buy at various possible prices during a given time period. • Quantity Demanded- amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at each particular price during a given time period. • Law of demand – De ...
... • Demand- the amount of a good or service a consumer is willing and able to buy at various possible prices during a given time period. • Quantity Demanded- amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at each particular price during a given time period. • Law of demand – De ...
Market Power and Monopoly
... The key difference between perfect competition and a market structure in which firms have pricing power is the presence of barriers to entry, or factors that prevent entry into the market with large producer surplus. • Normally, positive producer surplus in the long run will induce additional firms ...
... The key difference between perfect competition and a market structure in which firms have pricing power is the presence of barriers to entry, or factors that prevent entry into the market with large producer surplus. • Normally, positive producer surplus in the long run will induce additional firms ...
Production
... determining economic profit Implicit revenue includes the increases in the value of assets owned by the firm; implicit costs include opportunity cost of time and capital provided by owners of the firm In the long run a firm can choose among all possible production techniques; in the short run it ...
... determining economic profit Implicit revenue includes the increases in the value of assets owned by the firm; implicit costs include opportunity cost of time and capital provided by owners of the firm In the long run a firm can choose among all possible production techniques; in the short run it ...
Ppt
... Demand • Economists consistently will gather data and put it into a schedule and then to make it visually easier to understand put the schedule into graph form • Law of Demand: An increase in price will cause a decrease in quantity demanded – P ↑ Qd ↓ and P ↓ Qd ↑ ...
... Demand • Economists consistently will gather data and put it into a schedule and then to make it visually easier to understand put the schedule into graph form • Law of Demand: An increase in price will cause a decrease in quantity demanded – P ↑ Qd ↓ and P ↓ Qd ↑ ...
Competitive Advantage
... Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways: Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions ...
... Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways: Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions ...
PDF
... Since equation 15 is non-linear, the structural model is estimated using a Seemingly Unrelated Regression (SUR) approach in the SHAZAM econometric software. We test the null hypothesis that H0: Θ = 0 and measure the index of industry oligopoly power as defined by Ł = Θ / η. In addition, Θ and Ł are ...
... Since equation 15 is non-linear, the structural model is estimated using a Seemingly Unrelated Regression (SUR) approach in the SHAZAM econometric software. We test the null hypothesis that H0: Θ = 0 and measure the index of industry oligopoly power as defined by Ł = Θ / η. In addition, Θ and Ł are ...
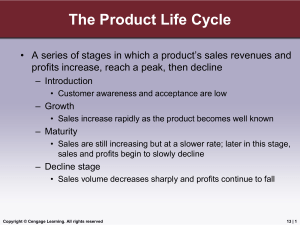
Product Life Cycle
... • Sales are still increasing but at a slower rate; later in this stage, sales and profits begin to slowly decline ...
... • Sales are still increasing but at a slower rate; later in this stage, sales and profits begin to slowly decline ...
PROCUREMENT - Poznań University of Technology
... function to equalize the quantity demanded by consumers, and the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in an economic equilibrium of price and quantity. An increase in the quantity produced or supplied will typically result in a reduction in price and vice-versa. Similarly, an increase in the nu ...
... function to equalize the quantity demanded by consumers, and the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in an economic equilibrium of price and quantity. An increase in the quantity produced or supplied will typically result in a reduction in price and vice-versa. Similarly, an increase in the nu ...
Consumer behaviour and Demand
... 24. Priya is indifferent to the bundle (4,7 and (4,8) indicate whether she has monotonic Preference or not. 25. A good may either be normal and inferior both True or False. Explain. 26. Distinguish between law of DD and ED. 27. Define those ED which has the same ED at the different point on the curv ...
... 24. Priya is indifferent to the bundle (4,7 and (4,8) indicate whether she has monotonic Preference or not. 25. A good may either be normal and inferior both True or False. Explain. 26. Distinguish between law of DD and ED. 27. Define those ED which has the same ED at the different point on the curv ...