Meteorology
... 2. Latitude The lower the latitutdethe higher the angle of insolation Equator= 0°; altitude of sun is high all year, warm temperatures Poles= 90° (North and South); altitude of sun is low all year, colder temperatures ...
... 2. Latitude The lower the latitutdethe higher the angle of insolation Equator= 0°; altitude of sun is high all year, warm temperatures Poles= 90° (North and South); altitude of sun is low all year, colder temperatures ...
MST DQ Week 3 Name: 3/31/2014 1. During which season does
... 2. At a certain time of year, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted toward the sun. Which of these describes how this tilt affects the Southern Hemisphere during this time of year? A The days will be longer in the Southern Hemisphere during this time of year. B. The nights will be longer in the Southern ...
... 2. At a certain time of year, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted toward the sun. Which of these describes how this tilt affects the Southern Hemisphere during this time of year? A The days will be longer in the Southern Hemisphere during this time of year. B. The nights will be longer in the Southern ...
Weather & Climate Chapter 1
... From pre-history Man has been directly and indirectly affected by environment --- nothing as much as weather --- Sun God; Rain God; omens; reward/punishment; etc --- SAD ...
... From pre-history Man has been directly and indirectly affected by environment --- nothing as much as weather --- Sun God; Rain God; omens; reward/punishment; etc --- SAD ...
Name:__________________ Date: Pre
... Positions 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram below represent the noon sun above the horizon on three different days during the year, as viewed from Binghamton, New York. 18. At which position was the noon Sun on January 21, as viewed from Binghamton? (1) above position 1 (2) below position 3 (3) between po ...
... Positions 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram below represent the noon sun above the horizon on three different days during the year, as viewed from Binghamton, New York. 18. At which position was the noon Sun on January 21, as viewed from Binghamton? (1) above position 1 (2) below position 3 (3) between po ...
Atmospheric heating
... • No well-defined upper limit • Fraction of atmosphere's mass • Gases moving at high speeds ...
... • No well-defined upper limit • Fraction of atmosphere's mass • Gases moving at high speeds ...
Earth and Space Science
... A) Heavier elements were created at the time of the big bang when the sphere of hydrogen exploded violently with great heat and pressure dispersing the matter which later cooled to form the universe as we know it. B) The hydrogen sphere erupted in a big bang and over time gases condensed and fused t ...
... A) Heavier elements were created at the time of the big bang when the sphere of hydrogen exploded violently with great heat and pressure dispersing the matter which later cooled to form the universe as we know it. B) The hydrogen sphere erupted in a big bang and over time gases condensed and fused t ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... provides light and heat. Several factors affect the amount of solar energy Earth receives. These are rotation, revolution, tilt, and latitude. Earth’s axis is an imaginary rod running from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth spins around on its axis. One complete rotation takes 24 hours, or one ...
... provides light and heat. Several factors affect the amount of solar energy Earth receives. These are rotation, revolution, tilt, and latitude. Earth’s axis is an imaginary rod running from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth spins around on its axis. One complete rotation takes 24 hours, or one ...
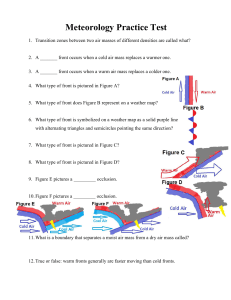
Meteorology Practice Test
... 56. In Figure I, position 1 marks the beginning of what season in the Northern Hemisphere? 57. In Figure I, which number refers to the position of the Earth during the Northern Hemisphere’s vernal equinox? 58. True or false: the Earth reaches perihelion in early January and aphelion in early July. 5 ...
... 56. In Figure I, position 1 marks the beginning of what season in the Northern Hemisphere? 57. In Figure I, which number refers to the position of the Earth during the Northern Hemisphere’s vernal equinox? 58. True or false: the Earth reaches perihelion in early January and aphelion in early July. 5 ...
Jeopardy Review mid
... During a windless summer day, the air inside this house is warmed by the Sun. In which cross section do the arrows show the most likely air movement when the windows are opened? ...
... During a windless summer day, the air inside this house is warmed by the Sun. In which cross section do the arrows show the most likely air movement when the windows are opened? ...
Natural Causes for Climate Change
... 1. Different layers of our atmosphere perform different functions related to heat balance (greenhouse gases) and weather. 2. Greenhouse gases have different warming potentials, which is a function of how much radiation they absorb and their residence time in the atmosphere. Changes in the amounts of ...
... 1. Different layers of our atmosphere perform different functions related to heat balance (greenhouse gases) and weather. 2. Greenhouse gases have different warming potentials, which is a function of how much radiation they absorb and their residence time in the atmosphere. Changes in the amounts of ...
Benchmark 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... is tilted towards the sun we receive more direct light and experience the warmer, longer days of summer and when we are tilted away from the sun we receive indirect light from the sun which causes days to be shorter and cooler_______________________ 32. When it is summer in the southern hemisphere, ...
... is tilted towards the sun we receive more direct light and experience the warmer, longer days of summer and when we are tilted away from the sun we receive indirect light from the sun which causes days to be shorter and cooler_______________________ 32. When it is summer in the southern hemisphere, ...
Meteorology Chapter 3 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... 30) The seasonal shift of isotherms is greater over the continents than over the ocean. 31) Isotherms are more irregular in the Southern Hemisphere than in the Northern Hemisphere. 32) Latitude is a major control of temperature since latitude determines the Sun angle. 33) The daily range of temper ...
... 30) The seasonal shift of isotherms is greater over the continents than over the ocean. 31) Isotherms are more irregular in the Southern Hemisphere than in the Northern Hemisphere. 32) Latitude is a major control of temperature since latitude determines the Sun angle. 33) The daily range of temper ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... Radiation from Earth's surface • Earth re-radiates radiation (terrestrial radiation) at the longer wavelengths • Longer wavelength terrestrial radiation is absorbed by • Carbon dioxide and • Water vapor in the atmosphere • Lower atmosphere is heated from Earth's surface ...
... Radiation from Earth's surface • Earth re-radiates radiation (terrestrial radiation) at the longer wavelengths • Longer wavelength terrestrial radiation is absorbed by • Carbon dioxide and • Water vapor in the atmosphere • Lower atmosphere is heated from Earth's surface ...
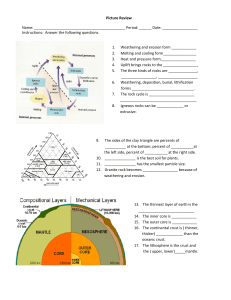
Picture Review Name
... 85. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 86. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 87. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 88. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 89. What is the relationship between o ...
... 85. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 86. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 87. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 88. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 89. What is the relationship between o ...
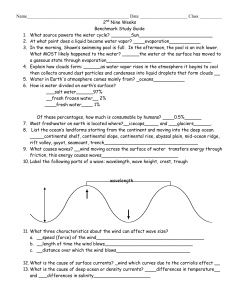
2nd Nine Weeks
... is tilted towards the sun we receive more direct light and experience the warmer, longer days of summer and when we are tilted away from the sun we receive indirect light from the sun which causes days to be shorter and cooler_______________________ 32. When it is summer in the southern hemisphere, ...
... is tilted towards the sun we receive more direct light and experience the warmer, longer days of summer and when we are tilted away from the sun we receive indirect light from the sun which causes days to be shorter and cooler_______________________ 32. When it is summer in the southern hemisphere, ...
Energy - eBoard
... east. Vertical ray located at the Tropic of Capricorn 23½ o south latitude. 32. Equinoxes (equal night) - September 23rd – Autumnal, March 21st – Vernal. Vertical ray located at the equator. 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness everywhere on earth. 33. The Equator always has 12 hours of day ...
... east. Vertical ray located at the Tropic of Capricorn 23½ o south latitude. 32. Equinoxes (equal night) - September 23rd – Autumnal, March 21st – Vernal. Vertical ray located at the equator. 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness everywhere on earth. 33. The Equator always has 12 hours of day ...
facts and concepts that you need to know to pass the earth science
... Summer Solstice: June 21 or 22, Sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Cancer 23.5 o N, first day of summer in the northern hemisphere and longest daylight hours Winter Solstice: Dec 21 or 22, Sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Capricorn 23.5 oS, first day of winter in the northern hemisphere an ...
... Summer Solstice: June 21 or 22, Sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Cancer 23.5 o N, first day of summer in the northern hemisphere and longest daylight hours Winter Solstice: Dec 21 or 22, Sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Capricorn 23.5 oS, first day of winter in the northern hemisphere an ...
Weather & Climate
... Some short-term changes may be the result of changes in ocean currents and global winds. Ocean currents help transfer heat to the atmosphere. This process generates global winds. The global winds help move ocean currents. Any major change in an ocean current can cause a change in climate. El Nino is ...
... Some short-term changes may be the result of changes in ocean currents and global winds. Ocean currents help transfer heat to the atmosphere. This process generates global winds. The global winds help move ocean currents. Any major change in an ocean current can cause a change in climate. El Nino is ...
Energy in Ecosystems
... Light Years are a measure of distance in space based on __how far light travels in 1 year If you turned on a HUGE spotlight and pointed it out into space, when would an alien see the spotlight if they were on a planet 300 light years away? _300 years Why do we use light years instead of km to measur ...
... Light Years are a measure of distance in space based on __how far light travels in 1 year If you turned on a HUGE spotlight and pointed it out into space, when would an alien see the spotlight if they were on a planet 300 light years away? _300 years Why do we use light years instead of km to measur ...
1 - Blinklearning
... the Northern and Southern hemispheres. We measure the latitude of a specific place on the Earth, depending on whether it is North or South of the Equator; longitude is measured in terms of East or West, depending on whether the place is East or West of the Prime Meridian. For example, Mount Everest ...
... the Northern and Southern hemispheres. We measure the latitude of a specific place on the Earth, depending on whether it is North or South of the Equator; longitude is measured in terms of East or West, depending on whether the place is East or West of the Prime Meridian. For example, Mount Everest ...
Study Island
... B. It generates winds. C. It causes tides. D. It influences ocean currents. 9. In mantle convection currents, hotter rock moves _______, while cooler rock moves _______. A. sideways; upward B. downward; upward C. upward; downward D. downward; sideways 10. The movement of Earth's tectonic plates rela ...
... B. It generates winds. C. It causes tides. D. It influences ocean currents. 9. In mantle convection currents, hotter rock moves _______, while cooler rock moves _______. A. sideways; upward B. downward; upward C. upward; downward D. downward; sideways 10. The movement of Earth's tectonic plates rela ...
Ltihosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere
... Temperature Changes with Latitude • Solar energy does not hit earth uniformly – This is due to earth’s spherical shape and tilt Equator (a) High concentration Little Reflection High Temperature ...
... Temperature Changes with Latitude • Solar energy does not hit earth uniformly – This is due to earth’s spherical shape and tilt Equator (a) High concentration Little Reflection High Temperature ...
Wind, Water, Weather and Seasons Test Review
... 28. How long is one full rotation? __________________________________________________________ 29. Why do different latitudes of Earth experience different hours of daylight throughout the year? _________________________________________ ...
... 28. How long is one full rotation? __________________________________________________________ 29. Why do different latitudes of Earth experience different hours of daylight throughout the year? _________________________________________ ...
Season
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology and hours of daylight. Seasons result from the yearly orbit of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis relative to the plane of the orbit. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to go into hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant.During May, June, and July, the northern hemisphere is exposed to more direct sunlight because the hemisphere faces the sun. The same is true of the southern hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is the tilt of the Earth that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months which increases the solar flux. However, due to seasonal lag, June, July, and August are the hottest months in the northern hemisphere and December, January, and February are the hottest months in the southern hemisphere.In temperate and subpolar regions, four calendar-based seasons (with their adjectives) are generally recognized: spring (vernal), summer (estival), autumn (autumnal) and winter (hibernal). In American English and Canadian English, fall is sometimes used as a synonym for both autumn and autumnal. Ecologists often use a six-season model for temperate climate regions that includes pre-spring (prevernal) and late summer (serotinal) as distinct seasons along with the traditional four.Various calendars used in South Asia define six seasons.Hot regions have two or three seasons; the rainy (or wet, or monsoon) season and the dry season, and, in some tropical areas, a cool or mild season.In some parts of the world, special ""seasons"" are loosely defined based on important events such as a hurricane season, tornado season, or a wildfire season.