synoptic and local weather conditions associated with pm2
... Daily PM2.5 data were obtained for the Imperial Court and Walnut Street monitoring sites. Data for the temporary DEP monitor at Walnut Street existed from May 2007 to September 2008. The permanent station at Imperial Court began monitoring in April 2001. To coincide with the Walnut Street data, Impe ...
... Daily PM2.5 data were obtained for the Imperial Court and Walnut Street monitoring sites. Data for the temporary DEP monitor at Walnut Street existed from May 2007 to September 2008. The permanent station at Imperial Court began monitoring in April 2001. To coincide with the Walnut Street data, Impe ...
Weather Influences on Carlisle`s Air Quality
... Daily PM2.5 data were obtained for the Imperial Court and Walnut Street monitoring sites. Data for the temporary DEP monitor at Walnut Street existed from May 2007 to September 2008. The permanent station at Imperial Court began monitoring in April 2001. To coincide with the Walnut Street data, Impe ...
... Daily PM2.5 data were obtained for the Imperial Court and Walnut Street monitoring sites. Data for the temporary DEP monitor at Walnut Street existed from May 2007 to September 2008. The permanent station at Imperial Court began monitoring in April 2001. To coincide with the Walnut Street data, Impe ...
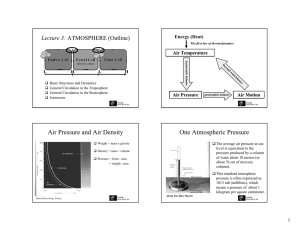
Air Pressure and Air Density One Atmospheric Pressure
... The Orbital Monsoon Hypothesis The 23,000-year cycle of orbital procession increases (decreases) summer insolation and at the same time decreases (increases) winter insolation at low and middle latitudes. Departures from the modern seasonal cycle of solar radiation have driven stronger monsoon c ...
... The Orbital Monsoon Hypothesis The 23,000-year cycle of orbital procession increases (decreases) summer insolation and at the same time decreases (increases) winter insolation at low and middle latitudes. Departures from the modern seasonal cycle of solar radiation have driven stronger monsoon c ...
The climatology, meteorology, and boundary layer structure of
... shows that this occurs almost as often in shoulder seasons as it does in winter, particularly in the ...
... shows that this occurs almost as often in shoulder seasons as it does in winter, particularly in the ...
Sec 14.3 - Highland High School
... Seasons are due to Earth’s tilt on its axis and revolution around the Sun which leads to regular variations in daylight, temperature, and weather patterns. ...
... Seasons are due to Earth’s tilt on its axis and revolution around the Sun which leads to regular variations in daylight, temperature, and weather patterns. ...
BataffoiiSp
... tiny glass prisms, ice crystals in the air bend sunlight, creating this colorful glow. The ice crystals are usually part of a thin layer of winter clouds that spread across the sky. Sundogs always appear in a position 22 degrees to the sides of the sun. To find a distance of 22 degrees, stretch your ...
... tiny glass prisms, ice crystals in the air bend sunlight, creating this colorful glow. The ice crystals are usually part of a thin layer of winter clouds that spread across the sky. Sundogs always appear in a position 22 degrees to the sides of the sun. To find a distance of 22 degrees, stretch your ...
atmospheric circulation
... 14. So as the Earth changes it's _____________to the _________ the seasons 2. The _________ provides all of the energy leading to _________________ in our weather. 3. ________________ shade the Earth and so keep our atmosphere ______________. 4. Sunlight warms the __________________ of the Earth whi ...
... 14. So as the Earth changes it's _____________to the _________ the seasons 2. The _________ provides all of the energy leading to _________________ in our weather. 3. ________________ shade the Earth and so keep our atmosphere ______________. 4. Sunlight warms the __________________ of the Earth whi ...
1. What are the two most abundant permanent gasses, and roughly
... 41.Which would have the greatest effect on the earth's greenhouse effect: Removing all of the CO2 from the atmosphere or removing all of the water vapour? 42.Explain why an increase in cloud cover would increase the greenhouse effect of the atmosphere, yet not necessarily lead to a lower earth surfa ...
... 41.Which would have the greatest effect on the earth's greenhouse effect: Removing all of the CO2 from the atmosphere or removing all of the water vapour? 42.Explain why an increase in cloud cover would increase the greenhouse effect of the atmosphere, yet not necessarily lead to a lower earth surfa ...
Quaternary Climate Change and Geomorphology
... (a) Glacial/Pluvial Lake development- concomitant with increased moisture/evaporation during glacial periods, along with melt water, more water was available on continents, thus large glacial lakes often form. (b) Western Interior U.S. = wetter during glacial climates, lake development in arid regi ...
... (a) Glacial/Pluvial Lake development- concomitant with increased moisture/evaporation during glacial periods, along with melt water, more water was available on continents, thus large glacial lakes often form. (b) Western Interior U.S. = wetter during glacial climates, lake development in arid regi ...
Sping-EXTREME WEATHER – Jigsaw Spring
... Countries that have the same seasons as us and those that are different. Southern hemisphere countries and how they have the opposite season to us. Weather diaries – starting point/introduction to. ...
... Countries that have the same seasons as us and those that are different. Southern hemisphere countries and how they have the opposite season to us. Weather diaries – starting point/introduction to. ...
SCIENCE PROJECT2 m and b
... summers. This climate is found in the polar air mass region. Very cold air masses from the arctic often move in. The temperature range is larger than any other climate. Rain increases during summer months, but annual rain is still small. Much of this climate is considered humid, but large areas in w ...
... summers. This climate is found in the polar air mass region. Very cold air masses from the arctic often move in. The temperature range is larger than any other climate. Rain increases during summer months, but annual rain is still small. Much of this climate is considered humid, but large areas in w ...
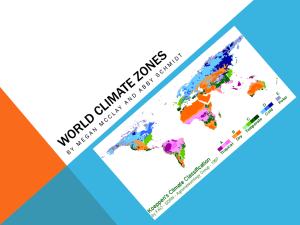
Global Climates and Biomes
... - air sinks, pressure increases decreasing in volume, and temperatures increase ...
... - air sinks, pressure increases decreasing in volume, and temperatures increase ...
Global Climates and Biomes
... - air sinks, pressure increases decreasing in volume, and temperatures increase ...
... - air sinks, pressure increases decreasing in volume, and temperatures increase ...
Lesson 6
... Meteorology: N. science dealing with weather and weather forecasting (You can learn about tornadoes in a class on meteorology.) Phenomenon: N. an unusual or significant occurrence (The return of Hailey’s comet every seventy-six years is a phenomenon of nature.) Refraction: N. bending or deflection o ...
... Meteorology: N. science dealing with weather and weather forecasting (You can learn about tornadoes in a class on meteorology.) Phenomenon: N. an unusual or significant occurrence (The return of Hailey’s comet every seventy-six years is a phenomenon of nature.) Refraction: N. bending or deflection o ...
PowerPoint Fill-in-the-Notes for Unit 2
... The Earth and the Sun Understanding Seasons Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • ___________________ ...
... The Earth and the Sun Understanding Seasons Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • ___________________ ...
Lecture 12 - Climate Regulation and Climate Change
... Earth’s axis tilt gives us the cause of the seasons. Tilt varies on a 41,000 cycle. Less tilt = milder seasonal variation More tilt = bigger seasonal variation ...
... Earth’s axis tilt gives us the cause of the seasons. Tilt varies on a 41,000 cycle. Less tilt = milder seasonal variation More tilt = bigger seasonal variation ...
Earth and Space Science Objective Booklet 4a. Compare and
... 1) What is a natural product and give 3 examples? 2) What is a synthetic product? 3) What are advantages and disadvantages of natural vs. synthetic products? 4) List five natural products, their sources and their uses. 5) What companies in Mississippi are involved with research and development of ne ...
... 1) What is a natural product and give 3 examples? 2) What is a synthetic product? 3) What are advantages and disadvantages of natural vs. synthetic products? 4) List five natural products, their sources and their uses. 5) What companies in Mississippi are involved with research and development of ne ...
The Biosphere - Del Mar College
... • Formed by interaction of pollutants (sulfur dioxides, nitrogen oxides) with moisture in the air • Corrodes metals, stone and other materials • Kills trees, fish and other organisms ...
... • Formed by interaction of pollutants (sulfur dioxides, nitrogen oxides) with moisture in the air • Corrodes metals, stone and other materials • Kills trees, fish and other organisms ...
Lafayette Parish School System 2013
... Moves (SI GLE: 2, 9, 12; PS GLE: 40; ESS GLE: 7) SI-9 Write and defend a conclusion based on logical analysis of experimental data (SI-H-A6) (SI-H-A2) ...
... Moves (SI GLE: 2, 9, 12; PS GLE: 40; ESS GLE: 7) SI-9 Write and defend a conclusion based on logical analysis of experimental data (SI-H-A6) (SI-H-A2) ...
Season
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology and hours of daylight. Seasons result from the yearly orbit of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis relative to the plane of the orbit. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to go into hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant.During May, June, and July, the northern hemisphere is exposed to more direct sunlight because the hemisphere faces the sun. The same is true of the southern hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is the tilt of the Earth that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months which increases the solar flux. However, due to seasonal lag, June, July, and August are the hottest months in the northern hemisphere and December, January, and February are the hottest months in the southern hemisphere.In temperate and subpolar regions, four calendar-based seasons (with their adjectives) are generally recognized: spring (vernal), summer (estival), autumn (autumnal) and winter (hibernal). In American English and Canadian English, fall is sometimes used as a synonym for both autumn and autumnal. Ecologists often use a six-season model for temperate climate regions that includes pre-spring (prevernal) and late summer (serotinal) as distinct seasons along with the traditional four.Various calendars used in South Asia define six seasons.Hot regions have two or three seasons; the rainy (or wet, or monsoon) season and the dry season, and, in some tropical areas, a cool or mild season.In some parts of the world, special ""seasons"" are loosely defined based on important events such as a hurricane season, tornado season, or a wildfire season.