Chapter 5, Section 2
... • Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs • Symbol is λ (pronounce lambda) • Number of waves per unit time • Usually waves/sec called hertz (Hz) ...
... • Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs • Symbol is λ (pronounce lambda) • Number of waves per unit time • Usually waves/sec called hertz (Hz) ...
Part51
... We can see that the crest of the wave is moving along the length of the slinky, and we can describe the crest with a phase angle (crest is where phase angle = 90o), so Speed of wave = phase speed = v = distance/time = /T = f = w/k. Note that the phase speed is not the same as the speed of material ...
... We can see that the crest of the wave is moving along the length of the slinky, and we can describe the crest with a phase angle (crest is where phase angle = 90o), so Speed of wave = phase speed = v = distance/time = /T = f = w/k. Note that the phase speed is not the same as the speed of material ...
Influence of the block-hierarchical structure of rocks on the
... nested blocks different in scales [1]. By analyzing dimensions of blocks, starting from scales of crystals to fractions of rock mass and geoblocks of the earth’s crust, it has been found that a ratio of sizes of blocks at neighboring scale levels, a = l N +1 / lN , exhibits a certain stability, viz, ...
... nested blocks different in scales [1]. By analyzing dimensions of blocks, starting from scales of crystals to fractions of rock mass and geoblocks of the earth’s crust, it has been found that a ratio of sizes of blocks at neighboring scale levels, a = l N +1 / lN , exhibits a certain stability, viz, ...
Topics 1, 2, 3, 4, 9 selected problems paper 1 take
... During the collision, the average force exerted by the truck on the car is FT and the average force exerted by the car on the truck is FC. Which one of the following statements is correct? A. ...
... During the collision, the average force exerted by the truck on the car is FT and the average force exerted by the car on the truck is FC. Which one of the following statements is correct? A. ...
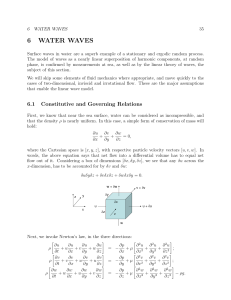
6 WATER WAVES - MIT OpenCourseWare
... of the displaced water: Am = πr2 ρ (per unit length). A very interesting and important aspect of added mass is its connection with the Archimedes force. We observe that the added mass force on a body accelerating in a still fluid is only onehalf that which is seen on a stationary body in an accelerat ...
... of the displaced water: Am = πr2 ρ (per unit length). A very interesting and important aspect of added mass is its connection with the Archimedes force. We observe that the added mass force on a body accelerating in a still fluid is only onehalf that which is seen on a stationary body in an accelerat ...
1st Semester Exam Review2
... Accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the accepted value. For example, we'd expect a balance to read 100.00 grams if we placed a standard100.00 g weight on the balance. If it does not, then the balance is inaccurate. ...
... Accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the accepted value. For example, we'd expect a balance to read 100.00 grams if we placed a standard100.00 g weight on the balance. If it does not, then the balance is inaccurate. ...
Monday, Apr. 6, 2015 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... 3) For finite potentials, the wave function and its derivatives must be continuous. This is required because the second-order derivative term in the wave equation must be single valued. (There are exceptions to this rule when V is infinite.) 4) In order to normalize the wave functions, they must app ...
... 3) For finite potentials, the wave function and its derivatives must be continuous. This is required because the second-order derivative term in the wave equation must be single valued. (There are exceptions to this rule when V is infinite.) 4) In order to normalize the wave functions, they must app ...
Canvas-j12 What`s the Frequency?
... On a Saturday night in October, 1986, at about 10:30pm, CBS anchorman Dan Rather was accosted in upper Manhattan by a well-dressed assailant who demanded an answer to a mysterious question. “Kenneth, what’s the frequency?” asked the anchorman’s antagonist. Rather, who had forgotten his high school p ...
... On a Saturday night in October, 1986, at about 10:30pm, CBS anchorman Dan Rather was accosted in upper Manhattan by a well-dressed assailant who demanded an answer to a mysterious question. “Kenneth, what’s the frequency?” asked the anchorman’s antagonist. Rather, who had forgotten his high school p ...
Unit Lesson Plan * Atomic Structure
... Waves spread out as they pass through an opening during diffraction. Waves can add up to become stronger and cancel each other out during constructive and destructive interference. Sound is caused by a vibrating object and requires a medium to move. Smaller objects produce higher pitched sounds. Lou ...
... Waves spread out as they pass through an opening during diffraction. Waves can add up to become stronger and cancel each other out during constructive and destructive interference. Sound is caused by a vibrating object and requires a medium to move. Smaller objects produce higher pitched sounds. Lou ...
Questions - HCC Learning Web
... released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed of the object. Where does this maximum speed occur? (d) Find the maximu ...
... released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed of the object. Where does this maximum speed occur? (d) Find the maximu ...
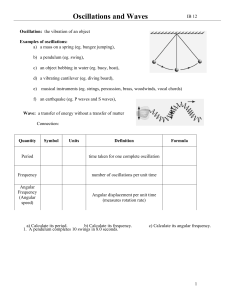
pkt 6 oscillations and waves
... Wavelength (λ, meters) – shortest distance along the wave between two points that are in phase -the distance a complete wave (cycle) travels in one period. Compare the motion of a single particle to the motion of the wave as a whole (the motion of the energy transfer). ...
... Wavelength (λ, meters) – shortest distance along the wave between two points that are in phase -the distance a complete wave (cycle) travels in one period. Compare the motion of a single particle to the motion of the wave as a whole (the motion of the energy transfer). ...
IPC Spring Final Exam Review Key MOTION
... clearly holding a frying pan without being burned. What can you infer about the material the pan is made out of? It must be made from a conductor. What can you infer about the material the handle of the pan is made out of? It must be made from an insulator. ...
... clearly holding a frying pan without being burned. What can you infer about the material the pan is made out of? It must be made from a conductor. What can you infer about the material the handle of the pan is made out of? It must be made from an insulator. ...
pkt 9 SHM and waves
... traveling wave. It has the same frequency, the same wavelength, and almost the same amplitude. These two traveling waves moving in opposite directions in the string are the component waves. These component waves interfere with each other creating the standing wave whose amplitude at any point is the ...
... traveling wave. It has the same frequency, the same wavelength, and almost the same amplitude. These two traveling waves moving in opposite directions in the string are the component waves. These component waves interfere with each other creating the standing wave whose amplitude at any point is the ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... A huge wave generated by an underwater earthquake or landslide is called a tsunami. The speed at which this wave travels can be about 700 ...
... A huge wave generated by an underwater earthquake or landslide is called a tsunami. The speed at which this wave travels can be about 700 ...
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications
... along its medium, but the individual particles just move around their equilibrium positions. ...
... along its medium, but the individual particles just move around their equilibrium positions. ...
Waves - Websupport1
... string above the equilibrium position Wavelength, λ, is the distance between two successive points that behave identically ...
... string above the equilibrium position Wavelength, λ, is the distance between two successive points that behave identically ...
Final exam review1
... A 0.250-kg ball sits on a vertical spring with a spring constant of 540 N/m. The ball is pushed downward, compressing the spring 0.10 m. When released, the ball leaves the spring and travels upward. How high does it rise above the point of ...
... A 0.250-kg ball sits on a vertical spring with a spring constant of 540 N/m. The ball is pushed downward, compressing the spring 0.10 m. When released, the ball leaves the spring and travels upward. How high does it rise above the point of ...
AS Revision Flash Cards File
... Wave motion A progressive wave transfers energy from one place to another, but the medium only vibrates or oscillates. All wave motions, including water waves, sound, light and microwaves can show reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. In transverse waves the vibration of the me ...
... Wave motion A progressive wave transfers energy from one place to another, but the medium only vibrates or oscillates. All wave motions, including water waves, sound, light and microwaves can show reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. In transverse waves the vibration of the me ...
PowerPoint - science
... of each wave is 0.25 m. Two waves pass the duck each second, so the frequency is 2 Hz. This means that the waves travel 0.5 m each second, so the speed of the waves is 0.5 m/s. From this example, the connection between speed, frequency and wavelength is: ...
... of each wave is 0.25 m. Two waves pass the duck each second, so the frequency is 2 Hz. This means that the waves travel 0.5 m each second, so the speed of the waves is 0.5 m/s. From this example, the connection between speed, frequency and wavelength is: ...
PSB Final Review
... 3. Displacement and velocity are examples of ____________________ because they have both magnitude and direction. 4. Speed is measured in units of _________________________. 5. A car’s speedometer measures _________________________. 6. The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity indic ...
... 3. Displacement and velocity are examples of ____________________ because they have both magnitude and direction. 4. Speed is measured in units of _________________________. 5. A car’s speedometer measures _________________________. 6. The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity indic ...
7.2.1 Seismic waves - The Berkeley Course in Applied Geophysics
... solution in time is sinusoidal and that the time dependence is given by eit, where is the angular frequency in radians/sec (equal to 2f, where f is the frequency in cycles per second or Hertz). With this solution in t the equation of motion becomes: 2u/x2 +2/K u = 0 or, with 2/K = k2 2u/ ...
... solution in time is sinusoidal and that the time dependence is given by eit, where is the angular frequency in radians/sec (equal to 2f, where f is the frequency in cycles per second or Hertz). With this solution in t the equation of motion becomes: 2u/x2 +2/K u = 0 or, with 2/K = k2 2u/ ...
Name - WordPress.com
... one period of the wave is used. Intensity can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "strength", "a ...
... one period of the wave is used. Intensity can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "strength", "a ...
AS Definitions
... distance from the pivot to the line of action of the force. Couple. Two forces which act on a body and are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction separated by a perpendicular distance. Torque of a couple. The product of ONE of the forces and the perpendicular distance between them. Equilibrium ...
... distance from the pivot to the line of action of the force. Couple. Two forces which act on a body and are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction separated by a perpendicular distance. Torque of a couple. The product of ONE of the forces and the perpendicular distance between them. Equilibrium ...
Waves and Vibrations - Cardinal Newman
... A wave travels along its medium, but the individual particles just move up and down. ...
... A wave travels along its medium, but the individual particles just move up and down. ...
Wave

In physics, a wave is an oscillation accompanied by a transfer of energy that travels through space or mass. Frequency refers to the addition of time. Wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, which may or may not displace particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass transport. Waves consist, instead, of oscillations or vibrations (of a physical quantity), around almost fixed locations.There are two main types of waves. Mechanical waves propagate through a medium, and the substance of this medium is deformed. The deformation reverses itself owing to restoring forces resulting from its deformation. For example, sound waves propagate via air molecules colliding with their neighbors. When air molecules collide, they also bounce away from each other (a restoring force). This keeps the molecules from continuing to travel in the direction of the wave.The second main type of wave, electromagnetic waves, do not require a medium. Instead, they consist of periodic oscillations of electrical and magnetic fields generated by charged particles, and can therefore travel through a vacuum. These types of waves vary in wavelength, and include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.Waves are described by a wave equation which sets out how the disturbance proceeds over time. The mathematical form of this equation varies depending on the type of wave. Further, the behavior of particles in quantum mechanics are described by waves. In addition, gravitational waves also travel through space, which are a result of a vibration or movement in gravitational fields.A wave can be transverse or longitudinal. Transverse waves occur when a disturbance creates oscillations that are perpendicular to the propagation of energy transfer. Longitudinal waves occur when the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy propagation. While mechanical waves can be both transverse and longitudinal, all electromagnetic waves are transverse in free space.