Routing protocol Chapter 4 4.1 Introduction
... switching system given that node's advertised additive link metrics. Performing GCAC will add complexity to the signalling protocol, and will heighten the risk that the real CAC performed by a switch further along the path (possibly in another area) may faiL This failure will introduce crankback. A ...
... switching system given that node's advertised additive link metrics. Performing GCAC will add complexity to the signalling protocol, and will heighten the risk that the real CAC performed by a switch further along the path (possibly in another area) may faiL This failure will introduce crankback. A ...
Introduction to Dynamic Routing
... How the ITaP Production Network Uses Dynamic Routing •Routing Protocols Used •Interior •EIGRP •OSPF •Static •Exterior •BGP ...
... How the ITaP Production Network Uses Dynamic Routing •Routing Protocols Used •Interior •EIGRP •OSPF •Static •Exterior •BGP ...
Koostada juurdepääsuvõrk, tagamaks kuni 30 terminaali
... Storage Temp. Relative Humidity Storage Humidity Operating Altitude ...
... Storage Temp. Relative Humidity Storage Humidity Operating Altitude ...
Implementing IPv6 as a Peer-to-Peer Overlay Network
... as are true peer-to-peer applications. • IPv6 features: Applications can take advantage of IPv6 features, such as multicast, anycast, mobile IP, and IPSec. Applications developed using the IPv6 API can run not only on our ON, but may continue to run as IPv6 is deployed in various other forms. • Robu ...
... as are true peer-to-peer applications. • IPv6 features: Applications can take advantage of IPv6 features, such as multicast, anycast, mobile IP, and IPSec. Applications developed using the IPv6 API can run not only on our ON, but may continue to run as IPv6 is deployed in various other forms. • Robu ...
Routing Protocols for Ad
... the last dest_sequence_# src_sequence_# used to maintain freshness information about the reverse route to the source dest_sequnece_# indicates how fresh a route must be, before it can be accepted by the source ...
... the last dest_sequence_# src_sequence_# used to maintain freshness information about the reverse route to the source dest_sequnece_# indicates how fresh a route must be, before it can be accepted by the source ...
Catalyst 3512 XL, 3524, and 3548 XL Stackable 10/100 and Gigabit
... Users can also implement higher levels of data security and boost LAN performance by deploying up to 250 virtual LANs ...
... Users can also implement higher levels of data security and boost LAN performance by deploying up to 250 virtual LANs ...
Week5 - University of Sydney
... • we need a metric, which one? – cost? not appropriate within enterprise but between; e.g., which long-distance company? – hop count - how many routers do we traverse – available bandwidth - go least congested route – speed of underlying network, use ATM as opposed to 1200 baud modem? – time: shorte ...
... • we need a metric, which one? – cost? not appropriate within enterprise but between; e.g., which long-distance company? – hop count - how many routers do we traverse – available bandwidth - go least congested route – speed of underlying network, use ATM as opposed to 1200 baud modem? – time: shorte ...
Chapter 4 slides
... 4.4.3 Datagram format 4.4.4 IP fragmentation 4.4.5 ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol ...
... 4.4.3 Datagram format 4.4.4 IP fragmentation 4.4.5 ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol ...
The Internet Underwater: An IP-compatible Protocol Stack for Commercial Undersea Modems
... (6LoWPAN) [2] became part of the Internet suite of standardized protocols. It is now essential to design, deploy, and test a standardized protocol stack that can efficiently provide interoperability for underwater networking devices. While one can envision a scenario where users can address and acce ...
... (6LoWPAN) [2] became part of the Internet suite of standardized protocols. It is now essential to design, deploy, and test a standardized protocol stack that can efficiently provide interoperability for underwater networking devices. While one can envision a scenario where users can address and acce ...
ECE544Lec3_15
... • ATM network moves cells (fixed length packets) with low delay and low delay variation at high speeds • Devices at ends translate (e.g., segment and reassemble) between cells and original traffic ...
... • ATM network moves cells (fixed length packets) with low delay and low delay variation at high speeds • Devices at ends translate (e.g., segment and reassemble) between cells and original traffic ...
Switching and Forwarding
... Cons 2: Full address for destination still required for connection. ...
... Cons 2: Full address for destination still required for connection. ...
Proceedings of USITS ’03: 4th USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems
... routing latency. The protocols for joining and leaving the network introduce complexity and require O(log2 n) messages each. A stabilization protocol is required to maintain network integrity. Viceroy [13] is the rst proposal that provides O(logn) routing latency with only a constant number of link ...
... routing latency. The protocols for joining and leaving the network introduce complexity and require O(log2 n) messages each. A stabilization protocol is required to maintain network integrity. Viceroy [13] is the rst proposal that provides O(logn) routing latency with only a constant number of link ...
Network Layer
... Q: How does an ISP get block of addresses? A: ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers o allocates addresses o manages DNS o assigns domain names, resolves disputes ...
... Q: How does an ISP get block of addresses? A: ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers o allocates addresses o manages DNS o assigns domain names, resolves disputes ...
Multicast Delivery of Broadband Multimedia Services
... Deployment Scenarios for broadband multimedia Stage 1: until 2003 Unicast only or local multicast only in private networks As shown in the current services Stage 2: until 2005 Hybrid delivery of unicast and multicast Seamless transport via Relay Agents Unicast over non-multicast region ...
... Deployment Scenarios for broadband multimedia Stage 1: until 2003 Unicast only or local multicast only in private networks As shown in the current services Stage 2: until 2005 Hybrid delivery of unicast and multicast Seamless transport via Relay Agents Unicast over non-multicast region ...
Ethernet over 4 E1 / 8 E1 / 16 E1 - IP over TDM
... Port based Ethernet limit allows user to provide different speed for the different customers to utilize bandwidth according to their requirement Supports differential delay of up to 120ms on E1 Links Complies with IEEE 802.3 specifications. ...
... Port based Ethernet limit allows user to provide different speed for the different customers to utilize bandwidth according to their requirement Supports differential delay of up to 120ms on E1 Links Complies with IEEE 802.3 specifications. ...
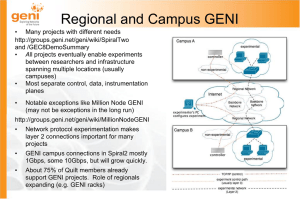
GENIConnections
... •Dynamic resource allocation via GMPLS-enabled control plane •MAX supports sliced edge compute resources (myPLC) and network virtualization with a GENI Aggregate Manager •Layer 2 Ethernet switches with dedicated 1 GbE and 10GbE connections •Layer 3 IP (management, control and general connectivity) • ...
... •Dynamic resource allocation via GMPLS-enabled control plane •MAX supports sliced edge compute resources (myPLC) and network virtualization with a GENI Aggregate Manager •Layer 2 Ethernet switches with dedicated 1 GbE and 10GbE connections •Layer 3 IP (management, control and general connectivity) • ...
Multicast Delivery of Broadband Multimedia Services
... Deployment Scenarios for broadband multimedia Stage 1: until 2003 Unicast only or local multicast only in private networks As shown in the current services Stage 2: until 2005 Hybrid delivery of unicast and multicast Seamless transport via Relay Agents Unicast over non-multicast region ...
... Deployment Scenarios for broadband multimedia Stage 1: until 2003 Unicast only or local multicast only in private networks As shown in the current services Stage 2: until 2005 Hybrid delivery of unicast and multicast Seamless transport via Relay Agents Unicast over non-multicast region ...
ch05 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... IP – Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) • Sets up virtual circuits for audio-video applications – Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) • Used after a virtual connection setup by RSVP or RTSP • Adds a sequence number and a timestamp for helping applications to synchronize delivery • Uses UDP (because ...
... IP – Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) • Sets up virtual circuits for audio-video applications – Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) • Used after a virtual connection setup by RSVP or RTSP • Adds a sequence number and a timestamp for helping applications to synchronize delivery • Uses UDP (because ...
Actiontec PK5000 Wireless DSL Modem Router Product Datasheet
... The PK5000 has been designed from the ground up for compactness and usability. Since both its footprint and weight have been decreased compared to earlier models, the shipping costs for DSL carriers will be lowered considerably. Despite these size and weight reductions, we've managed to include two ...
... The PK5000 has been designed from the ground up for compactness and usability. Since both its footprint and weight have been decreased compared to earlier models, the shipping costs for DSL carriers will be lowered considerably. Despite these size and weight reductions, we've managed to include two ...
Ethernet Services
... The NFS protocol specifies a way of authorizing the user to access a specific server. These parameters are setup using the User ID and Group ID parameters. If these parameters are not used which usually is the case on a PC, set them to the default value 0. Note that these two parameters must be the ...
... The NFS protocol specifies a way of authorizing the user to access a specific server. These parameters are setup using the User ID and Group ID parameters. If these parameters are not used which usually is the case on a PC, set them to the default value 0. Note that these two parameters must be the ...
Технология на програмирането
... There is no practical limitation for VLANs count Most scalable and fastest solution Sometimes may not fulfill all the requirements (i.e. BGP routing with the ISP’s) ...
... There is no practical limitation for VLANs count Most scalable and fastest solution Sometimes may not fulfill all the requirements (i.e. BGP routing with the ISP’s) ...
Chapter 4 slides
... 4.4.3 Datagram format 4.4.4 IP fragmentation 4.4.5 ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol ...
... 4.4.3 Datagram format 4.4.4 IP fragmentation 4.4.5 ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol ...