IP Based VPNs
... of interest, and is constructed through some form of partitioning of a common underlying communications medium, where this underlying communications medium provides services to the network on a nonexclusive basis." “A VPN is a private network constructed within a public network infrastructure, such ...
... of interest, and is constructed through some form of partitioning of a common underlying communications medium, where this underlying communications medium provides services to the network on a nonexclusive basis." “A VPN is a private network constructed within a public network infrastructure, such ...
ppt - The Fengs
... – Forges the 3rd handshake (ack) from the client to the destination – This moves connection out of backlog queue, freeing resources – If this is attack, no “real” ack will happen • Destination will send RST packet terminating connection – If this is actual connection request the eventual ack will be ...
... – Forges the 3rd handshake (ack) from the client to the destination – This moves connection out of backlog queue, freeing resources – If this is attack, no “real” ack will happen • Destination will send RST packet terminating connection – If this is actual connection request the eventual ack will be ...
Slim Fly: A Cost Effective Low-Diameter Network
... Several metrics have to be taken into account while designing an efficient topology. First, high bandwidth is indispensable as many applications perform all-to-all communication [38]. Second, networks can account for as much as 33% of the total system cost [27] and 50% of the overall system energy c ...
... Several metrics have to be taken into account while designing an efficient topology. First, high bandwidth is indispensable as many applications perform all-to-all communication [38]. Second, networks can account for as much as 33% of the total system cost [27] and 50% of the overall system energy c ...
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4)
... • Packets entering your network • Ingress traffic depends on: – What information you send and to who – Based on your addressing and ASes – Based on others’ policy (what they accept from you and what they do with it) ...
... • Packets entering your network • Ingress traffic depends on: – What information you send and to who – Based on your addressing and ASes – Based on others’ policy (what they accept from you and what they do with it) ...
Routing/Routed Protocols
... • Can be used in large networks. • Uses a different metric than RIP – IGRP uses bandwidth and delay of line by default. This is called a “composite metric.” – Reliability, load, and MTU can also be used, although they are not by default. ...
... • Can be used in large networks. • Uses a different metric than RIP – IGRP uses bandwidth and delay of line by default. This is called a “composite metric.” – Reliability, load, and MTU can also be used, although they are not by default. ...
downloading
... b. What capacity do you have now? c. Remove one of the links in the bundle. What happens? 8. Suppose you wanted to load balance the traffic from the two VLANs across both aggregation switches. How can you achieve this? (Only done if MSTP is supported). a. Configure MSTP using Appendix G. b. Verify s ...
... b. What capacity do you have now? c. Remove one of the links in the bundle. What happens? 8. Suppose you wanted to load balance the traffic from the two VLANs across both aggregation switches. How can you achieve this? (Only done if MSTP is supported). a. Configure MSTP using Appendix G. b. Verify s ...
slides - The Fengs
... – Forges the 3rd handshake (ack) from the client to the destination – This moves connection out of backlog queue, freeing resources – If this is attack, no “real” ack will happen • Destination will send RST packet terminating connection – If this is actual connection request the eventual ack will be ...
... – Forges the 3rd handshake (ack) from the client to the destination – This moves connection out of backlog queue, freeing resources – If this is attack, no “real” ack will happen • Destination will send RST packet terminating connection – If this is actual connection request the eventual ack will be ...
3214W17Ch4
... traditional computers with switching under direct control of CPU packet copied to system’s memory speed limited by memory bandwidth (2 bus crossings per datagram) ...
... traditional computers with switching under direct control of CPU packet copied to system’s memory speed limited by memory bandwidth (2 bus crossings per datagram) ...
WAVE Interface Modules
... WAVE appliances can be installed physically between two network devices (such as the branch office router and branch office LAN switch) by connecting the WAVE inline network adapter ports to the network devices using the proper cables. If you are connecting a WAVE inline appliance between two device ...
... WAVE appliances can be installed physically between two network devices (such as the branch office router and branch office LAN switch) by connecting the WAVE inline network adapter ports to the network devices using the proper cables. If you are connecting a WAVE inline appliance between two device ...
the document - Support
... Traffic filtering based on the ACL carried in a BGP Flowspec route or the local policy that the route attribute matches ...
... Traffic filtering based on the ACL carried in a BGP Flowspec route or the local policy that the route attribute matches ...
Chapter 6 Dynamic Routing
... A distance vector protocol learns: The distance to a network, measured in hops or in some other way The direction of the network: which port should be used to reach it It puts the routes in the routing table It does not know any more details of the route or the other routers along the way ...
... A distance vector protocol learns: The distance to a network, measured in hops or in some other way The direction of the network: which port should be used to reach it It puts the routes in the routing table It does not know any more details of the route or the other routers along the way ...
In classful addressing, the network address
... Find the error, if any, in the following IP addresses: a. 111.56.045.78 ...
... Find the error, if any, in the following IP addresses: a. 111.56.045.78 ...
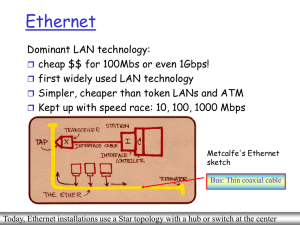
Ethernet Switches
... which interfaces by maintaining a filtering table when a frame received, the bridge ''learns'' the location of the sender: incoming LAN segment records sender location in filtering table filtering table entry: (Node LAN Address, Bridge Interface, Time Stamp) stale entries in the Filtering ...
... which interfaces by maintaining a filtering table when a frame received, the bridge ''learns'' the location of the sender: incoming LAN segment records sender location in filtering table filtering table entry: (Node LAN Address, Bridge Interface, Time Stamp) stale entries in the Filtering ...
A Comparative Study of Multicast Protocols: Top, Bottom, or In the
... shortest path trees rooted at the source, and a softstate approach is employed by periodically refreshing the multicast forwarding states. Application layer multicast: We evaluate NARADA, a protocol targeted at applications with small and sparse groups, and NICE, a scalable application layer multica ...
... shortest path trees rooted at the source, and a softstate approach is employed by periodically refreshing the multicast forwarding states. Application layer multicast: We evaluate NARADA, a protocol targeted at applications with small and sparse groups, and NICE, a scalable application layer multica ...
Address Resolution Protocol
... The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to associate known IP addresses to unknown physical hardware, MAC, addresses. A node uses ARP with another node when it determines that the destination address is on a directly attached network. The node can determine if the host is local by comparing th ...
... The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to associate known IP addresses to unknown physical hardware, MAC, addresses. A node uses ARP with another node when it determines that the destination address is on a directly attached network. The node can determine if the host is local by comparing th ...
PHD Proposal Draft
... Trunking, defined in IEEE 802.3ad [3]. It is a method of combining multiple physical network links between two devices into a single logical link for increased bandwidth. The upper layer applications or protocols, such as a MAC client, can treat the link aggregation group as if it were a single link ...
... Trunking, defined in IEEE 802.3ad [3]. It is a method of combining multiple physical network links between two devices into a single logical link for increased bandwidth. The upper layer applications or protocols, such as a MAC client, can treat the link aggregation group as if it were a single link ...
PYLON: An Architectural Framework for Ad-Hoc QoS
... Both SWAN and INSIGNIA are lacking the mechanism and the means to deal with extranet policy-driven QoS traffic. Both models use bandwidth only to handle QoS requirements. Ad-hoc domains that employ either model will have to map services to classical DiffServ with DSCP of known PHB (probably based on ...
... Both SWAN and INSIGNIA are lacking the mechanism and the means to deal with extranet policy-driven QoS traffic. Both models use bandwidth only to handle QoS requirements. Ad-hoc domains that employ either model will have to map services to classical DiffServ with DSCP of known PHB (probably based on ...
Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS)
... • The practice of using a modified loopback IP address as the system ID may now be considered outdated because of the dynamic host name feature. This feature uses a new Type Length Value (TLV 137) to map the router’s host name to the system ID. • Each device must have a unique system ID within the a ...
... • The practice of using a modified loopback IP address as the system ID may now be considered outdated because of the dynamic host name feature. This feature uses a new Type Length Value (TLV 137) to map the router’s host name to the system ID. • Each device must have a unique system ID within the a ...