pptx - Caltech
... Spanning tree protocol Three criteria 1. The root switch always forwards messages on all its ports 2. Each switch computes its shortest path (in #bridges) to root 3. All switches connected to a LAN elect a designated switch for the LAN to send packets towards root switch A switch that is not elec ...
... Spanning tree protocol Three criteria 1. The root switch always forwards messages on all its ports 2. Each switch computes its shortest path (in #bridges) to root 3. All switches connected to a LAN elect a designated switch for the LAN to send packets towards root switch A switch that is not elec ...
Chapter 17-20
... suffix occurs after the first 17 bits Each network can be as large or small as needed (power of two) ...
... suffix occurs after the first 17 bits Each network can be as large or small as needed (power of two) ...
network number
... connects regional networks in 1990, this backbone was NSFNET, funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) ...
... connects regional networks in 1990, this backbone was NSFNET, funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) ...
Chapter 17-20
... suffix occurs after the first 17 bits Each network can be as large or small as needed (power of two) ...
... suffix occurs after the first 17 bits Each network can be as large or small as needed (power of two) ...
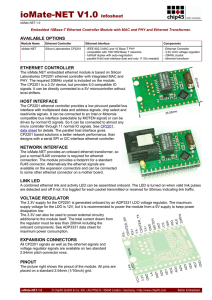
Integrated Packet Exchange Functionality for the SN 9000 Switching
... End-customers have come to expect a high level of reliability from the services they receive from the carrier. Operating the packet layer at Layer 2 (Ethernet and MPLS) rather than at the IP service layer (Layer 3) provides more flexibility for carriers to offer a range of service types, with varyin ...
... End-customers have come to expect a high level of reliability from the services they receive from the carrier. Operating the packet layer at Layer 2 (Ethernet and MPLS) rather than at the IP service layer (Layer 3) provides more flexibility for carriers to offer a range of service types, with varyin ...
WaveReady® System Controller with Built-in OSC
... craft port, and two fast Ethernet optical supervisory channel (OSC) ports. The USB craft port can be used to directly connect to the COM-300 module for initial configuration and to locally manage other modules. The two small form factor pluggable (SFP) interfaces can be used to directly connect to r ...
... craft port, and two fast Ethernet optical supervisory channel (OSC) ports. The USB craft port can be used to directly connect to the COM-300 module for initial configuration and to locally manage other modules. The two small form factor pluggable (SFP) interfaces can be used to directly connect to r ...
The Interplanetary Internet Implemented on a Terrestrial testbed
... widespread deployment can occur to make IPN feasible. Delay is an important factor in space communication and its nature is completely different from terrestrial delay environments. Moreover, space deployments and testing in space environments are very costly and time consuming. We propose a design ...
... widespread deployment can occur to make IPN feasible. Delay is an important factor in space communication and its nature is completely different from terrestrial delay environments. Moreover, space deployments and testing in space environments are very costly and time consuming. We propose a design ...
UNDERLAYS
and
MIDDLEBOXES
READING:
SECTION
8. COS
461:
Computer
Networks
Spring
2010
(MW
3:00‐4:20
in
COS
105)
... • Main idea: Virtual circuit – Packets forwarded based only on circuit idenNfier Source 1 Destination Source 2 ...
... • Main idea: Virtual circuit – Packets forwarded based only on circuit idenNfier Source 1 Destination Source 2 ...
Follow this link to Chapter 10
... One of the most important characteristics of a packet switching network is whether it uses datagrams or virtual circuits. There are 2 dimensions of this characteristic; one for the interface between station and it corresponding network node (external), and the other for the network itself (interna ...
... One of the most important characteristics of a packet switching network is whether it uses datagrams or virtual circuits. There are 2 dimensions of this characteristic; one for the interface between station and it corresponding network node (external), and the other for the network itself (interna ...
Chord
... Decentralization: chord is fully distributed, no node is more important than any other, improves robustness Scalability: logarithmic growth of lookup costs with the number of nodes in the network, even very large systems are feasible Availability: chord automatically adjusts its internal tables to e ...
... Decentralization: chord is fully distributed, no node is more important than any other, improves robustness Scalability: logarithmic growth of lookup costs with the number of nodes in the network, even very large systems are feasible Availability: chord automatically adjusts its internal tables to e ...
Monitoring, Alerting, DevOps, SLAs, and all that
... • The “API” is a simple text format slurm_node_state,host=node001 partition="hpc",state="allocated" ...
... • The “API” is a simple text format slurm_node_state,host=node001 partition="hpc",state="allocated" ...
What Is P2P…
... access direct (numeric) positions within the list of peers (as opposed to using the peerid as a hash key). These functions should not be used concurrently with the prior three. getpeerids(): Return a list of all known peer ids. numberofpeers(): maxpeersreached(): checklivepeers(): Attempt to ...
... access direct (numeric) positions within the list of peers (as opposed to using the peerid as a hash key). These functions should not be used concurrently with the prior three. getpeerids(): Return a list of all known peer ids. numberofpeers(): maxpeersreached(): checklivepeers(): Attempt to ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... Scale-free networks Scale-free networks are characterized by a power-law degree distribution; the probability that a node has k links follows P(k) ~ k- -, where is the degree exponent. The probability that a node is highly connected is statistically more significant than in a random graph, the n ...
... Scale-free networks Scale-free networks are characterized by a power-law degree distribution; the probability that a node has k links follows P(k) ~ k- -, where is the degree exponent. The probability that a node is highly connected is statistically more significant than in a random graph, the n ...
Fig. 12-1: Network topologies
... • Main technologies: SONET/SDH, ATM, WDM – Voice circuits vs. data packets – Non-optical technologies:T1(1.544 Mb/s)/E1(2.048 Mb/s), DS-3 (44.736 Mb/s ), Frame Relay – Standards bodies include ITU-T, IETF, ATM Forum, ...
... • Main technologies: SONET/SDH, ATM, WDM – Voice circuits vs. data packets – Non-optical technologies:T1(1.544 Mb/s)/E1(2.048 Mb/s), DS-3 (44.736 Mb/s ), Frame Relay – Standards bodies include ITU-T, IETF, ATM Forum, ...
15-744: Computer Networking
... • Compared properties of generated graphs with those of measured graphs to validate generator • What is wrong with these topologies? Li et al [SIGCOMM04] • Many graphs with similar distribution have different properties • Random graph generation models don’t have network-intrinsic meaning • Should l ...
... • Compared properties of generated graphs with those of measured graphs to validate generator • What is wrong with these topologies? Li et al [SIGCOMM04] • Many graphs with similar distribution have different properties • Random graph generation models don’t have network-intrinsic meaning • Should l ...
A Survey on Void Handling Techniques for Geographic
... planarization algorithm. The most well-known planar graph based void-handling technique is perimeter routing that used in Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR) protocol [13] and two other of these techniques are Request-Response algorithm (RR) in Beacon-Less Routing (BLR) [14] and 2-Hop Forwardi ...
... planarization algorithm. The most well-known planar graph based void-handling technique is perimeter routing that used in Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR) protocol [13] and two other of these techniques are Request-Response algorithm (RR) in Beacon-Less Routing (BLR) [14] and 2-Hop Forwardi ...
Segment Routing
... –Improve scale, simplify operations –Minimize introduction complexity/disruption ...
... –Improve scale, simplify operations –Minimize introduction complexity/disruption ...
PDF
... a node or path are not merely descriptive, but form a tuple that defines a unique node or path. In this way, the model allows superimposition of multiple topologies over the actual physical nodes and paths, allowing the behavior of the network under different types of traffic to be characterized sep ...
... a node or path are not merely descriptive, but form a tuple that defines a unique node or path. In this way, the model allows superimposition of multiple topologies over the actual physical nodes and paths, allowing the behavior of the network under different types of traffic to be characterized sep ...
Transport Issues in Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks
... ATP also allows for the priority levels for different applications to be determined dynamically, allowing for more flexibility in multiple application environments. ATP is based on a good idea that applications should be able todynamically set their priority. Example: parametic needs to look u ...
... ATP also allows for the priority levels for different applications to be determined dynamically, allowing for more flexibility in multiple application environments. ATP is based on a good idea that applications should be able todynamically set their priority. Example: parametic needs to look u ...