Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocol
... All routing protocols have the same purpose - to learn about remote networks and to quickly adapt whenever there is a change in the topology. The method that a routing protocol uses to accomplish this depends upon the algorithm it uses and the operational characteristics of that protocol. In g ...
... All routing protocols have the same purpose - to learn about remote networks and to quickly adapt whenever there is a change in the topology. The method that a routing protocol uses to accomplish this depends upon the algorithm it uses and the operational characteristics of that protocol. In g ...
Customizable virtual private network service with QoS
... In this paper, we propose and implement Virtual Network Service (VNS), a value-added network service for deploying virtual private networks (VPNs) in a managed wide-area IP network. The key feature of VNS is its capability of providing a customer with a VPN that is customizable with management capab ...
... In this paper, we propose and implement Virtual Network Service (VNS), a value-added network service for deploying virtual private networks (VPNs) in a managed wide-area IP network. The key feature of VNS is its capability of providing a customer with a VPN that is customizable with management capab ...
Chapter 6 - YSU Computer Science & Information Systems
... used to support reliable, sequenced delivery of packets • One field in each row of the table is populated with the last sequence number of the packet received from that neighbor • EIGRP uses this field for two purposes: – Sequence numbers are used to acknowledge specific packets that were delivered ...
... used to support reliable, sequenced delivery of packets • One field in each row of the table is populated with the last sequence number of the packet received from that neighbor • EIGRP uses this field for two purposes: – Sequence numbers are used to acknowledge specific packets that were delivered ...
PHysical laYer protocol
... • Logical link control (LLC): communicates with upper layers in the computer • Naming: provides a unique MAC address identifier • Framing: part of the encapsulation process, packaging the bits for transport ...
... • Logical link control (LLC): communicates with upper layers in the computer • Naming: provides a unique MAC address identifier • Framing: part of the encapsulation process, packaging the bits for transport ...
Deploying the Dell Force10 MXL into a Cisco Nexus Network
... To present the above configuration options as clearly as possible in this document, they have been integrated into a single example network. The full details of the example network, including overall topology and the complete configurations of the participating devices, are presented in Appendix A. ...
... To present the above configuration options as clearly as possible in this document, they have been integrated into a single example network. The full details of the example network, including overall topology and the complete configurations of the participating devices, are presented in Appendix A. ...
Adopting Ideas from Interplanetary Networking for Sensor
... • Bad things can still happen with Custody Transfer • Brings up the question of trust. When should a node trust another more than it itself? • Risk vs. Resource trade-off ...
... • Bad things can still happen with Custody Transfer • Brings up the question of trust. When should a node trust another more than it itself? • Risk vs. Resource trade-off ...
Ethernet POWERLINK (DRAFT)
... Asynchronous transmit requests may be prioritized by 3 PR bits in the PRes, the IdentResponse and StatusResponse frame.[2, page 45, chapter 4.2.] POWERLINK supports eight priority levels. Two of these levels are dedicated to POWERLINK purpose: I ...
... Asynchronous transmit requests may be prioritized by 3 PR bits in the PRes, the IdentResponse and StatusResponse frame.[2, page 45, chapter 4.2.] POWERLINK supports eight priority levels. Two of these levels are dedicated to POWERLINK purpose: I ...
Cisco Nexus 3048 Switch Product Overview
... The Cisco Nexus 3048 is supported in Cisco DCNM. Cisco DCNM is designed for hardware platforms enabled for Cisco NX-OS, which consist of the Cisco Nexus Family of products. Cisco DCNM is a Cisco management solution that increases overall data center infrastructure uptime and reliability, hence impro ...
... The Cisco Nexus 3048 is supported in Cisco DCNM. Cisco DCNM is designed for hardware platforms enabled for Cisco NX-OS, which consist of the Cisco Nexus Family of products. Cisco DCNM is a Cisco management solution that increases overall data center infrastructure uptime and reliability, hence impro ...
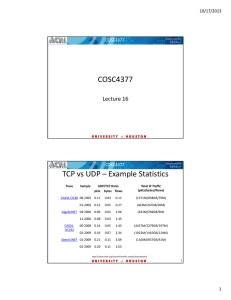
COSC4377 TCP vs UDP – Example Statistics
... – Stateless auto‐configuration requires no manual configuration of hosts, minimal (if any) configuration of routers, and no additional servers. The stateless mechanism allows a host to generate its own addresses using a combination of locally available information and information advertised by r ...
... – Stateless auto‐configuration requires no manual configuration of hosts, minimal (if any) configuration of routers, and no additional servers. The stateless mechanism allows a host to generate its own addresses using a combination of locally available information and information advertised by r ...
Packet Tracer Network Simulator
... brief description on other end devices such as tablets and televisions. End devices are the ones used by end users, with desktops and laptops being the most common ones. Chapter 4, Creating a Network Topology, explains different connectors, creating network topologies, and configuring them with Cisc ...
... brief description on other end devices such as tablets and televisions. End devices are the ones used by end users, with desktops and laptops being the most common ones. Chapter 4, Creating a Network Topology, explains different connectors, creating network topologies, and configuring them with Cisc ...
Underground Sensor Networks: Research Challenges
... End-to-end QOS guarantees are not easy to achieve! When sensed data from the field is sent via the Internet, a single routing metric is unsuitable for the entire path between source and end user. Decoupling of reliability and routing parameters at such network boundaries and a seamless integra ...
... End-to-end QOS guarantees are not easy to achieve! When sensed data from the field is sent via the Internet, a single routing metric is unsuitable for the entire path between source and end user. Decoupling of reliability and routing parameters at such network boundaries and a seamless integra ...
Chapter 9: Wavelength Routing Optical Networks
... • If all four fibers are cut between nodes 2 and 3, then the traffic will be diverted to the working fibers in the opposite direction. • In this case, the lightpath from A to B will be routed back to node 1, and then to node 3 through node 4. Connection-Oriented Networks ...
... • If all four fibers are cut between nodes 2 and 3, then the traffic will be diverted to the working fibers in the opposite direction. • In this case, the lightpath from A to B will be routed back to node 1, and then to node 3 through node 4. Connection-Oriented Networks ...
Assortativity and Mixing Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, 2009 Prof. Peter Dodds .
... Basic idea: I ...
... Basic idea: I ...
Network and Service Discovery in Distributed Environments
... • others are forwarded to greater than “minimum distance-routing” links • (optical buffer may still be used here) • source-destination pair routes are no longer fixed, i.e. different routes possible as in IP • parameters that affect performance of deflection routing • network diameter (max. # of hop ...
... • others are forwarded to greater than “minimum distance-routing” links • (optical buffer may still be used here) • source-destination pair routes are no longer fixed, i.e. different routes possible as in IP • parameters that affect performance of deflection routing • network diameter (max. # of hop ...
Generalized MPLS
... (today: centralized computation based on restricted scenarios implying restoration time > 5s) and Signalled Protection in < 50ms (as specified in ITU-T G.841) ...
... (today: centralized computation based on restricted scenarios implying restoration time > 5s) and Signalled Protection in < 50ms (as specified in ITU-T G.841) ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... When and why should this be used? Rarely done over twisted-pair or fiber optic links Usually done over lossy links for performance improvement (versus correctness) 5: DataLink Layer ...
... When and why should this be used? Rarely done over twisted-pair or fiber optic links Usually done over lossy links for performance improvement (versus correctness) 5: DataLink Layer ...
Introduction to VLANs
... Switches will flood unicast traffic out all ports if it does not have the destination MAC address in its source address table. This can be especially true for large flat networks where switches cannot contain all of the MAC addresses. – MAC address table can be 1,024 (or less) and more than 16,000 a ...
... Switches will flood unicast traffic out all ports if it does not have the destination MAC address in its source address table. This can be especially true for large flat networks where switches cannot contain all of the MAC addresses. – MAC address table can be 1,024 (or less) and more than 16,000 a ...
Study on a Fast OSPF Route Reconstruction Method Under Network
... ISPs and the government reexamined the plan for disaster estimation and protection against disasters. According to this protection plan, commercial ISPs must reconstruct robust networks against disasters. Networks require high reliability and fast recovery. One of the important problems for these re ...
... ISPs and the government reexamined the plan for disaster estimation and protection against disasters. According to this protection plan, commercial ISPs must reconstruct robust networks against disasters. Networks require high reliability and fast recovery. One of the important problems for these re ...
Chap10_Peer-to-Peer_Team4
... The participated Hosts are fully self organizing and obtaining the data need to construct a routing table and other required state from existing members in O(log N) messages, where N is the number of hosts participating in the overlay When a node fails, the remaining nodes can detect its absence and ...
... The participated Hosts are fully self organizing and obtaining the data need to construct a routing table and other required state from existing members in O(log N) messages, where N is the number of hosts participating in the overlay When a node fails, the remaining nodes can detect its absence and ...
HEW evaluation metrics
... – In the response LS [3], WFA suggests to consider the evaluation metrics • Cell edge (5%), average (50%) and area (aggregate) throughputs • Fairness (inverse standard deviation of per-user throughputs) • Outage rate (% of users with links unable to achieve 5Mbps throughput – a normal minimum satisf ...
... – In the response LS [3], WFA suggests to consider the evaluation metrics • Cell edge (5%), average (50%) and area (aggregate) throughputs • Fairness (inverse standard deviation of per-user throughputs) • Outage rate (% of users with links unable to achieve 5Mbps throughput – a normal minimum satisf ...