Book 1 Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal
... impermeable to most all plasma proteins and is highly permeable to essentially all small-sized dissolved substances. ...
... impermeable to most all plasma proteins and is highly permeable to essentially all small-sized dissolved substances. ...
The Hexose-Proton Cotransport System of Chlorella pH
... is working. In addition the unprotonated form of the carrier has the same affinity to the substrate at the inside as at the outside and also for that reason should not be an important factor contributing to accumulation. The accumulation capacity would, therefore, be expected to correlate with the a ...
... is working. In addition the unprotonated form of the carrier has the same affinity to the substrate at the inside as at the outside and also for that reason should not be an important factor contributing to accumulation. The accumulation capacity would, therefore, be expected to correlate with the a ...
On the basis of animal function
... 04 stimulus dependent force generation 05 the length - tension relationship 06 principles of summation and tetanus 07 EMG and twitch amplitude Resting potential 08 resting potential and external K 09 resting potential and external Na Action potentials 10 the compound action potential 11 conduction v ...
... 04 stimulus dependent force generation 05 the length - tension relationship 06 principles of summation and tetanus 07 EMG and twitch amplitude Resting potential 08 resting potential and external K 09 resting potential and external Na Action potentials 10 the compound action potential 11 conduction v ...
Contraction - Anatomy Freaks
... – Respond rapidly to nervous stimulation, contain myosin that can break down ATP more rapidly than that in Type I, less blood supply, fewer and smaller mitochondria than slow-twitch (adapted to perform anaerobic respiration) – Lower limbs in sprinter, upper limbs of most people. White meat in chicke ...
... – Respond rapidly to nervous stimulation, contain myosin that can break down ATP more rapidly than that in Type I, less blood supply, fewer and smaller mitochondria than slow-twitch (adapted to perform anaerobic respiration) – Lower limbs in sprinter, upper limbs of most people. White meat in chicke ...
tutorial 1 GUS
... • The is the plasma level at which the glucose first appears in the urine . • The actual renal threshold is about • 200 mg/dL of arterial plasma, • which corresponds to a venous level of about 180 mg/dL. ...
... • The is the plasma level at which the glucose first appears in the urine . • The actual renal threshold is about • 200 mg/dL of arterial plasma, • which corresponds to a venous level of about 180 mg/dL. ...
of the smooth muscles
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
Cardiovascular Physiology 2016
... pace is too slow (28 bpm) and is not really compatible with life Ectopic Foci • abnormal conducting or contractile cells that generate AP’s and override the impulse rhythm of the SA or AV node ...
... pace is too slow (28 bpm) and is not really compatible with life Ectopic Foci • abnormal conducting or contractile cells that generate AP’s and override the impulse rhythm of the SA or AV node ...
autorhythmic cell
... • E.C.G.interpretation is easy if you remember the directions from which the various leads look at the heart. • Standard ECG uses 9 electrodes which are used to form 12 ‘lead's recording axis. • Six of these recording axis are in the frontal plane,6 in the horizontal plane. ...
... • E.C.G.interpretation is easy if you remember the directions from which the various leads look at the heart. • Standard ECG uses 9 electrodes which are used to form 12 ‘lead's recording axis. • Six of these recording axis are in the frontal plane,6 in the horizontal plane. ...
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 134. What group of medicines are used when a person has too much glutamate released (such as after a stroke)? 135. Antagonists to which neurotransmitter helps stop neuronal death after a stroke? 136. Why are strokes or trauma to the brain so dangerous in relation to neurotransmitters? 137. What effe ...
... 134. What group of medicines are used when a person has too much glutamate released (such as after a stroke)? 135. Antagonists to which neurotransmitter helps stop neuronal death after a stroke? 136. Why are strokes or trauma to the brain so dangerous in relation to neurotransmitters? 137. What effe ...
of the smooth muscles
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
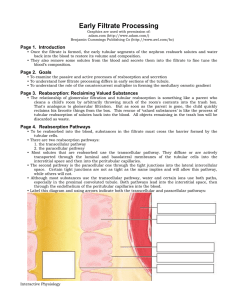
Early Filtrate Processing
... • The activity of all these channels and carrier molecules depends on sodium/potassium ATPase ion pump activity in the basolateral membrane. • Sodium Channels. The sodium ion concentration of the cytosol has been lowered by the activity o f the sodium/potassium pumps in the basolateral membrane. As ...
... • The activity of all these channels and carrier molecules depends on sodium/potassium ATPase ion pump activity in the basolateral membrane. • Sodium Channels. The sodium ion concentration of the cytosol has been lowered by the activity o f the sodium/potassium pumps in the basolateral membrane. As ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... • As the loop of Henle ascends toward the cortex, the thin squamous cells transition to simple cuboidal cells of the thick ascending limb and early distal convoluted tubule. • Water permeability of these cells is greatly restricted by tight junctions and by a glycoprotein layer that covers the lumi ...
... • As the loop of Henle ascends toward the cortex, the thin squamous cells transition to simple cuboidal cells of the thick ascending limb and early distal convoluted tubule. • Water permeability of these cells is greatly restricted by tight junctions and by a glycoprotein layer that covers the lumi ...
Cell Membranes - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Phosphatidyl inositol – 2nd messenger: inositol triphosphate & diacylglycerol Glycolipids – receptors, antigens – only on outer surface of membrane ...
... Phosphatidyl inositol – 2nd messenger: inositol triphosphate & diacylglycerol Glycolipids – receptors, antigens – only on outer surface of membrane ...
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... It is an inhibitory VGC. If K+ leaves the cell or if Clenters the cell, the inside becomes more negative, farther from an AP It is an excitatory VGC. If Na+ or Ca++ enters the cell, the inside becomes more positive, making it closer to an AP Dendrites only On the axon, from the hillock to synaptic k ...
... It is an inhibitory VGC. If K+ leaves the cell or if Clenters the cell, the inside becomes more negative, farther from an AP It is an excitatory VGC. If Na+ or Ca++ enters the cell, the inside becomes more positive, making it closer to an AP Dendrites only On the axon, from the hillock to synaptic k ...
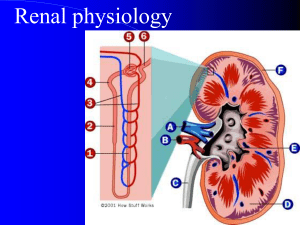
Renal Physiology - e-safe
... The glomerulus is the filter unit of the nephron. It passively lets water, amino acids, sodium and other free ions pass through its membranes and into the tubule system, but not charged proteins, large proteins or cells. The unique basement membrane, which is at the interface of the capillaries and ...
... The glomerulus is the filter unit of the nephron. It passively lets water, amino acids, sodium and other free ions pass through its membranes and into the tubule system, but not charged proteins, large proteins or cells. The unique basement membrane, which is at the interface of the capillaries and ...
Physiology 441 - West Virginia University
... • Chloride moves via electrical gradient that was established by Na+ • Sodium creates an osmotic gradient for the passive reabsorption of H2O via osmosis ...
... • Chloride moves via electrical gradient that was established by Na+ • Sodium creates an osmotic gradient for the passive reabsorption of H2O via osmosis ...
18 The Heart new
... – 80% of ventricular filling is passive – Atrial contraction occurs at the end of diastole • Atrial kick moves the remaining 20% of blood in atria into ventricles ...
... – 80% of ventricular filling is passive – Atrial contraction occurs at the end of diastole • Atrial kick moves the remaining 20% of blood in atria into ventricles ...
Role and deficiency symptoms of potassium in Mango
... Integrated nutrient management in grape Potassium plays an important role in large number of physiological process. High uptake of potassium in plants is mediated through an active uptake mechanism. K is extremely mobile element. It moves readily towards meristimatic tissues. For better crop growth ...
... Integrated nutrient management in grape Potassium plays an important role in large number of physiological process. High uptake of potassium in plants is mediated through an active uptake mechanism. K is extremely mobile element. It moves readily towards meristimatic tissues. For better crop growth ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
************G*** #********** #**************b
... proximal tubules, two NH4+ ions are secreted into the urine and two HCO3- ions are reabsorbed into the blood. The HCO3- generated by this process constitutes new bicarbonate. ...
... proximal tubules, two NH4+ ions are secreted into the urine and two HCO3- ions are reabsorbed into the blood. The HCO3- generated by this process constitutes new bicarbonate. ...
Cardiac Qs
... scenario. The nerves are distributed not only to the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes but also to the cardiac muscle of both ventricles and atria. The effects of sympathetic innervation can be broken down into increasing the heart’s rate of pumping and also increasing the heart’s strength of co ...
... scenario. The nerves are distributed not only to the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes but also to the cardiac muscle of both ventricles and atria. The effects of sympathetic innervation can be broken down into increasing the heart’s rate of pumping and also increasing the heart’s strength of co ...
Transport through plasma membranes
... Water molecules are polar, but are small enough to pass through cell membranes. Because O2 and CO2 are soluble in lipids, they can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Because the size and polarity of Glucose and sucrose, they cannot diffuse directly through ...
... Water molecules are polar, but are small enough to pass through cell membranes. Because O2 and CO2 are soluble in lipids, they can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Because the size and polarity of Glucose and sucrose, they cannot diffuse directly through ...
Fatigue
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
Threshold potential

The threshold potential is the critical level to which the membrane potential must be depolarized in order to initiate an action potential. Threshold potentials are necessary in order to regulate and propagate signaling in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).Most often the threshold potential is a membrane potential value between –40 and –55 mV, but it can vary based upon several factors. A neuron's resting membrane potential (–70 mV) can be altered to either increase or decrease likelihood of reaching threshold via sodium and potassium ions. An influx of sodium into the cell through open, voltage-gated sodium channels can depolarize the membrane past threshold and thus excite it while an efflux of potassium or influx of chloride can hyperpolarize the cell and thus inhibit threshold from being reached.